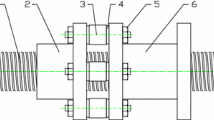
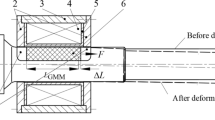
Abstract
In order to achieve automatic adjustment of the double-nut ball screw preload, a magnetostrictive ball screw preload system is proposed. A new cylindrical giant magnetostrictive actuator (CGMA), which is the core component of the preload system, is developed using giant magnetostrictive material (GMM) with a hole. The pretightening force of the CGMA is determined by testing. And the magnetic circuit analysis method is introduced to calculate magnetic field intensity of the actuator with a ball screw shaft. To suppress the thermal effects on the magnetostrictive outputs, an oil cooling method which can directly cool the heat source is adopted. A CGMA test platform is established and the static and dynamic output characteristics are respectively studied. The experimental results indicate that the CGMA has good linearity and no double-frequency effect under the bias magnetic field and the output accuracy of the CGMA is significantly improved with cooling measures. Although the output decreased with screw shaft through the actuator, the performance of CGMA meets the design requirements for ball screw preload with output displacement more than 26 μm and force up to 6200 N. The development of a CGMA will provide a new approach for automatic adjustment of double-nut ball screw preload.
摘要
为实现双螺母滚珠丝杠副预紧力的自动调整, 提出一种磁致伸缩滚珠丝杠副预紧系统。以中空 的超磁致伸缩材料(GMM)为核心, 完成了新型环状超磁致伸缩致动器(CGMA)的结构设计; 通 过测试数据确定了CGMA 的预压力; 利用磁路分析法对穿入丝杠后致动器内部磁场进行了分析计算; 为抑制发热对磁致伸缩输出的影响, 提出了直接冷却发热源的油冷散热方法。对自行研制的预紧用致 动器输出的位移和力进行了实验研究, 结果表明, 偏置磁场可以消除CGMA 的倍频效应, 改善线性 度; 油冷散热可有效减小热变形影响, 使CGMA 磁致伸缩输出特性稳定; 穿入滚珠丝杠后致动器的 输出减小, 但在工作区间内输出位移可达26 μm、输出力超过6200 N, 满足所选滚珠丝杠副预紧系统 设计要求。新型CGMA 的研制为双螺母滚珠丝杠副预紧力的自动调整提供一种新的方法。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FUKADA S, FANG B, SHIGENO A. Experimental analysis and simulation of nonlinear microscopic behavior of ball screw mechanism for ultra-precision positioning [J]. Precision Engineering, 2011, 35(4): 650–668. DOI: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2011.05.006.
ZHANG Jun, ZHANG Hui, DU Chao, ZHAO Wan. Research on the dynamics of ball screw feed system with high acceleration [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2016, 111: 9–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.09.001.
CHEN Yong, TANG Wen, WANG Jie. Influence factors on stiffness of a ball screw [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(11): 70–74. (in Chinese)
XU Xiang, SONG Xian, JIANG Hong, LI Yan. Influence factors comparison and analysis of axial contact stiffness between single-nut and double-nut ball screws [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 889–890: 555–558. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.889–890. 555.
HU Jian, WANG Min, GAO Xiang, ZAN Tao. Axial contact stiffness analysis of position preloaded ball screw mechanism [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(7): 60–69. (in Chinese)
VERL A, FREY S. Correlation between feed velocity and preloading in ball screw drives [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2010, 59(1): 429–32. DOI: 10. 1016/j.cirp.2010.03.136.
TSAI P C, CHENG C C, HWANG Y C. Ball screw preload loss detection using ball pass frequency [J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2014, 48(1, 2): 77–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.02.017.
BRAGHIN F, CINQUEMANI S, RESTA F. A model of magnetostrictive actuators for active vibration control [J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2011, 165(2): 342–350. DOI: 10.1016/j.sna.2010.10.019.
YANG Bin, YANG De, XU Peng, CAO Yu, FENG Zhi, MENG Guang. Large stroke and nanometer-resolution giant magnetostrictive assembled actuator for driving segmented mirrors in very large astronomical telescopes [J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2012, 179(3): 193–203. DOI: 10.1016/j.sna. 2012. 02.045.
GUO J, CHEE S K. An experimental study on characteristics of a magnetostrictive vibrator [J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2014, 222: 237–244. DOI: 10. 1016/j.sna.2014.12. 020.
XUE Guang, ZHANG Pei, HE Zhong, LI Dong, HUANG Ying, XIE Wen. Design and experimental study of a novel giant magnetostrictive actuator [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2016, 420: 185–191. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.07.037.
OHMATA K, ZAIKE M, KOH T. A three-link arm type vibration control device using magnetostrictive actuators [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1997, 258(1, 2): 74–78. DOI: 10.1016/S0925-8388(97)00071-6.
RAKHOVSKY V I. Power actuators for nanotechnology [C]//Nanostructure Science, Metrology, and Technology. Gaithersburg, 2002: 204–215. DOI: 10.1117/12.465224.
MOON S J, LIM C W, KIM B H, PARK Y. Structural vibration control using linear magnetostrictive actuators [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 302(4, 5): 875–891. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsv.2006.12.023.
ZHAI Peng, XIAO Bo, HE Kai, ZHANG Kun. Composite backward control for GMA and its application in high precision machining of variable ellipse pinhole [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(6): 1389–1398. (in Chinese)
LIN Ming, WANG Qing, JU Xiao, FAN Wen. The research of double-nut ball screw preload based on GMA [C]//International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence. Xi’an, 2016: 566–569. DOI: 10.1109/URAI.2016.7625780.
WANG Qing, LIN Ming. Electromechanical coupling measurement of a new giant magnetostrictive structure for double-nut ball screw pre-tightening [J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2016, 27(12): 125906. DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/27/12/125906.
CLARK A E. Magnetostrictive rare earth-Fe2 compounds [M]//WOHLFARTH E P, ed. Ferromagnetic Material. North-Holland Amsterdam, 1980.
JENNER A G, SMITH R J E, WILKINSON A J, GREENOUGH R D. Actuation and transduction by giant magnetostrictive alloys [J]. Mechatronics, 2000, 10(4, 5): 457–466. DOI: 10.1016/S0957-4158(99)00065-3.
ZHOU Shuo, YUAN Hui, MENG Guang. Analysis of disc spring in micro-displacement giant magnetostrictive actuator [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2004, 38(6): 923–926. (in Chinese)
KARUNANIDHI S, SINGAPERUMAL M. Design, analysis and simulation of magnetostrictive actuator and its application to high dynamic servo valve [J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2010, 157(2): 185–197. DOI: 10.1016/j.sna.2009.11.014.
NOH M D, PARK Y W. Topology selection and design optimization for magnetostrictive inertial actuators [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111(7): 07E715(1–3). DOI: 10.1063/1.3673431.
YANG Zhao, HE Zhong, LI Dong, RONG Ce. Bias magnetic field of stack giant magnetostrictive actuator: design, analysis, and optimization [J]. Advances in Material Science and Engineering, 2016: 1704594(1–13). DOI: 10. 1155/2016/1704594.
CLARK A E, CROWDER D. High temperature magnetostriction of TbFe2 and Tb.27Dy.73Fe2 [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1985, 21(5): 1945–1947.
ZHU Yu, JI Liang. Theoretical and experimental investigations of the temperature and thermal deformation of a giant magnetostrictive actuator [J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2014, 218: 167–178. DOI: 10.1016/j.sna. 2014.07.017.
CHEN J S, DWANG I C. A ballscrew drive mechanism with piezo-electric nut for preload and motion control [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2000, 40(4): 513–526. DOI: 10.1016/S0890-6955(99)00078-4.
HWANG Y K, LEE C M. Development of a newly structured variable preload control device for a spindle rolling bearing by using an electromagnet [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2010, 50(3): 253–259. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.12.002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(51475267) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, Xj., Lin, Mx., Fan, Wt. et al. Structure design and characteristics analysis of a cylindrical giant magnetostrictive actuator for ball screw preload. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 1799–1812 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3870-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3870-0
Key words
- ball screw preload
- cylindrical giant magnetostrictive actuator (CGMA)
- structure design
- output characteristics