Abstract
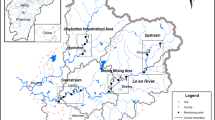
Samples were collected from two core sediments (C1 and C2) of Xiangjiang River, Chang-Zhu-Tan region, Hunan Province, China. The heavy metal contents are relatively higher, especially for the surface or near the surface layers. The calculated anthropogenic factor values indicate that all the heavy metals except for Cr in the core samples are enriched, especially for Cd, with the maximum enriching coefficients of 119.44, and 84.67 in C1 and C2, respectively. The correlation of heavy metals with sulphur indicates that they are precipitated as metal sulphides. Correlation matrix shows significant association between heavy metals and mud. Factor analysis identifies that signified anthropogenic activities affect the region of Xiangjiang River.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AYYAMPERUMAL T, JONATHAN M P, SRINIVASALU S, ARMSTRONG-ALTRIN J S, RAM-MOHAN V. Assessment of acid leachable trace metals in sediment cores from river up Panar, Cuddalore southeast coast of India [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 143: 34–45.
KUMAR S P, EDWARD J K P. Assessment of metal concentration in the sediment cores of Manakudy estuary south west coast of India [J]. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 2009, 38(2): 235–248.
JAYAPRAKASH M S, SRINIVASALU M P, JONATHAN R V. A baseline study of physico-chemical parameters and trace metals in waters of Ennore Creek, Chennai, India [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2005, 50(5): 583–589.
ALEMDAROGLU T, ONUR E, ERKAKAN F. Trace metal levels in surface sediments of lake Manyas, Turkey and tributary rivers [J]. Int J Environ Stud, 2003, 60(3): 287–298.
IP C C M, LI X D, ZHANG G, WAI O W H, LI Y S. Trace metal distribution in sediments of the pearl river estuary and the surrounding coastal area, south China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147: 311–323.
CHATTERJEE M, SILVA FILHO E V, SARKAR S K, SELLA S M, BHATTACHARYA A, SATPATHY K K, PRASAD M V R, CHAKRABORTY S, BHATTACHARYA B D. Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance[J]. Environment International, 2007, 33(3): 346–356.
RAVICHANDRAN M, BASKARAN M, SANTSCHI P H, BIANCHI T S. History of trace-metal pollution in Sabine-Neches estuary, Beaumount, Texas [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2009, 29(6): 1495–1503.
HARIKUMAR P S, NASIR U P, RAHMAN M. Distribution of heavy metals in the core sediments of a tropical wetland system [J]. Int J Environ Sci Tech, 2009, 6(2): 225–232.
XIA P, MENG X W, YIN P, CAO Z M, WANG X Q. Eighty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal inputs in the intertidal sediments from the Nanliu river estuary, Beibu gulf of south China sea [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159: 92–99.
PAN Bi-ling. Suggest the ecological environment of Xiangjiang drainage basin be one of key pollution control areas in China [R]. Association Central Committee Propaganda Department, 2010. (in Chinese).
CHEN Yong-shu, WU Fu-cheng, LU Huan-zhe, YAO Cheng-sheng. Analysis on the water quality changes in the Xiangjiang River from 1981 to 2000 [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangze Basin, 2004, 13(5): 508–512. (in Chinese).
HE Guang-hua. The heavy metal pollution in the Xiangjiang River seriously threatens the safety usage of water resources for 4000 million people in Hunan province [N]. The People’s Daily, 2009-04-27. (in Chinese)
TAO Diu-diu. Heavy metal pollution, heavy burden on Xiangjiang river [EN/OL]. China Economic Times, 2011-03-04. http://www.er-china.com/PowerLeader/html/2011/03/20110302092404.shtml. (in Chinese)
ZHOU Mian, TAN Jian, JIN Wei. Soil pollution: Heavy metals are greatly heavier than pesticides [N]. International Herald Leander. Beijing, China, 2011. (in Chinese)
DENG Li, LI Dang. The Chinese central government will investment more than billions to control the heavy metal pollution in 14 serious provinces [N]. 21 Century Economic Reportage, 2011-02-25. (in Chinese)
CLARK M W, MCCONCHIE D, LEWIS D W, SAENGER P. Redox stratification and heavy metal partitioning in Avicennia-dominated mangrove sediments: a geochemical model [J]. Chem Geol, 1998, 149: 147–171.
INGRAM R L. Procedures in sedimentary petrology [M]. Wiley, New York, 1970: 49–67.
PIERZYNSKI G M. Methods for phosphorus analysis for soils, sediments, residuals, and waters [J]. Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin, 2000, 396: 60–64.
USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). SW-846 test methods for evaluating solid waste physical/chemical methods [R]. Springfield, Virginia: Us Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and the National Technical Information Service, 1996.
MOSES C O, NORDSTROM D K, HERMAN J S, MILLS A L. Aqueous pyrite oxidation by dissolved by oxygen and by ferric iron [J]. Geochim Cosmochim, 1987, 51: 1561–1571.
LONG Y Z, DAI T G, ZOU H Y. The status QUO and evaluation of heavy metal pollution of soils in the Changsha, Zhuzhou and Xiangtan areas [J]. Earth and Environment, 2008, 36(3): 231–236.
ZHAO Lun-shan, ZHANG Ben-ren. Geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing Press, 1988: 60–70. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(1212010) supported by the China Geological Survey for Ecosystem Geochemistry Assessment in City of Changsha, Zhuzhou and Xiangtan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Yz., Dai, Tg., Chi, Gx. et al. Assessment of heavy metals in sediment cores from Xiangjiang River, Chang-Zhu-Tan region, Hunan Province, China. J. Cent. South Univ. 19, 2634–2642 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1321-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1321-x