Abstract
Objective
To observe the clinical efficacy of acupuncture plus navel acupuncture for patients with urinary retention after radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
Methods
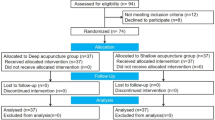
A total of 64 patients with urinary retention after radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer was divided into a navel acupuncture group (22 cases), an acupuncture group (18 cases) and an acupuncture plus navel acupuncture group (24 cases). All three groups received bladder function training and neuromuscular electrical stimulation. In addition, navel points were combined in the navel acupuncture group. Electroacupuncture was conducted to Qihai (CV 6), Zhongji (CV 3), Dahe (KI 12), Shuidao (ST 28), Ciliao (BL 32) and Huiyang (BL 35) in the acupuncture group. The acupuncture plus navel acupuncture group received both treatments. The catheter was removed after 3 d of treatment. Spontaneous urination, residual urine volume, urinary catheter dependence and recurrence after 3 d, 6 d and 9 d of treatment in each group were observed, respectively.
Results
In the acupuncture plus navel acupuncture group, the markedly effective rates after 3 d, 6 d and 9 d of treatment were significantly higher than those in the navel acupuncture group and the acupuncture group; the urinary catheter dependence was lower than that of the other two groups, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05, P<0.01); the spontaneous urination time was shorter than that of the navel acupuncture group and the acupuncture group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05, P<0.01); the residual urine volume was significantly less than that of the navel acupuncture group and the acupuncture group, and the differences were statistically significant (both P<0.01). After the catheter was removed, recurrence was observed from the next day after spontaneous urination was resumed. There were 2 cases of recurrence in the navel acupuncture group, 2 cases in the acupuncture group and 1 case in the acupuncture plus navel acupuncture group. The recurrence rate of the acupuncture plus navel acupuncture group was significantly lower than that of the navel acupuncture group and the acupuncture group (both P<0.01).
Conclusion
Acupuncture plus navel acupuncture has satisfactory efficacy for urinary retention after radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer. It can significantly shorten the urinary retention time, reduce the patient’s dependence on urinary catheter, and reduce the residual urine volume.
摘要
目的
观察针刺加脐针疗法治疗宫颈癌根治术后尿潴留的临床疗效。
方法
将64例宫颈癌根治术后尿潴留患者分为三组, 脐针组22例、 针刺组18例和针刺加脐针组24例。 三组患者均接受膀胱功能训练及神经肌肉电刺激治疗。 此外, 脐针组患者接受针刺脐穴治疗, 针刺组接受电针气海、 中极、 大赫、 水道、 次髎和会阳治疗, 针刺加脐针组同时接受电针和脐针治疗。 治疗3 d后拔除导尿管。 分别观察三组患者治疗3 d、 6 d 及9 d后的自主排尿情况、 残余尿量、 尿管依赖及复发情况。
结果
针刺加脐针组患者治疗3 d、6 d、9 d后的显效率明显高于脐针组和针刺组, 其尿管依赖情况低于脐针组和针刺组, 组间差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05, P<0.01), 其自主排尿时间短于脐针组和针刺组, 组间差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05, P<0.01); 其残余尿量明显少于脐针组及针刺组, 组间差异均具有统计学意义(均P<0.01)。 拔管后, 恢复自主排尿次日起观察复发情况, 其中脐针组2例、 针刺组2例、 针刺加脐针组1例, 针刺加脐针组复发率明显低于脐针组和针刺组(P<0.01)。
结论
针刺加脐针治疗对宫颈癌根治术后尿潴留具有良好的疗效, 能明显缩短患者尿潴留时间, 降低患者对尿管的依赖, 减少残余尿量。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim K, Zang R, Choi SC, Ryu SY, Kim JW. Current status of gynecological cancer in China. J Gynecol Oncol, 2009, 20(2): 72–76.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A, Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394–424.
Wang YL, Li GW, Han XW. Research progress of treating advanced cervical cancer. Zhongguo Weisheng Biaozhun Guanli, 2016, 7(1): 29–32.
Jiang QM. Analysis of screening results of cervical cancer. Jilin Yixue, 2014, 35(11): 2390–2391.
Bogani G, Cromi A, Uccella S, Serati M, Casarin J, Pinelli C, Ghezzi F. Laparoscopic versus open abdominal management of cervical cancer: long-term results from a propensity-matched analysis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol, 2014, 21(5): 857–862.
Johansen G, Lönnerfors C, Falconer H, Persson J. Reproductive and oncologic outcome following robotassisted laparoscopic radical trachelectomy for early stage cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol, 2016, 141(1): 160–165.
Uccella S, Laterza R, Ciravolo G, Volpi E, Franchi M, Zefiro F, Donadello N, Ghezzi F. A comparison of urinary complications following total laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and laparoscopic pelvic lymphadenectomy to open abdominal surgery. Gynecol Oncol, 2007, 107 (Suppl 1): S147–S149.
Zakashansky K, Chuang L, Gretz H, Nagarsheth NP, Rahaman J, Nezhat FR. A case-controlled study of total laparoscopic radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy versus radical abdominal hysterectomy in a fellowship training program. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2007, 17(5): 1075–1082.
Chen Y. Clinical analysis of acupuncture combined with traditional Chinese medicine on urinary retention after cesarean section. Neimenggu Zhongyiyao, 2017, 36(2): 127.
An CP, Chang CF, Zhao WJ, Zhu ZL. Studies on causes of gynecology postoperative urinary retention and its acupuncture treatment. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2013, 33(11): 1052–1056.
Moscicki AB, Flowers L, Huchko MJ, Long ME, MacLaughlin KL, Murphy J, Spiryda LB, Gold MA. Guidelines for cervical cancer screening in immunosuppressed women without HIV infection. J Low Genit Tract Dis, 2019, 23(2): 87–101.
China Anti-Cancer Association Gynecological Oncology Professional Committee. Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Cancer (4th Edition). Chin J Prac Gynecol Obstetr, 2018, 34(6): 613–622.
Wu JP. Wu Jie-ping’s Urology. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 2008: 1244–1245.
Xie L. Causes of urinary retention after radical resection of cervical cancer and research progress of clinical nursing. Zhongguo Shequ Yishi, 2017, 33(19): 9–11.
Lin L. Research progress on causes and nursing intervention of postoperative urinary retention in cervical cancer. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan, 2012, 10(29): 436–437.
Huang HQ, Zheng SL, Chen Q. Efficacy of acupuncture on urinary retention after radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hulixue Zazhi, 2016, 31(16): 90–94.
Xu QQ, Li F. Effect evaluation of retention enema of glycerin suppository treatment in patients with spinal postoperative urinary retention. Xinjiang Yike Daxue Xuebao, 2014, 37(9): 1191–1192, 1195.
Wen YM, Ouyang P, Yang HF, Yang SW, Song Y. Efficacy of pelvic floor muscle training and micturition interruption training on prevention of urinary retention after radical operation of gynecological tumor: a meta analysis. Zhonghua Xiandai Huili Zazhi, 2017, 23(33): 4244–4249.
Wang Y, Yang L, Kong DB, Jiang BT, Rao ZG. Clinical observation on short-term high-dose epristeride combined with tamsulosin for treating prostatic hyperplasia and urinary retention in 54 cases. Zhongguo Yaoye, 2018, 27(8): 77–79.
Liu DY, Hu S, Chu CL, Zhou YF, He HC, Wang J, Zhou WL. Minimally invasive transurethral plasmakinetic resection of prostate combined with endocrine therapy for advanced prostate cancer with urinary retention in elderly patients. Zhongguo Weichuang Waike Zazhi, 2017, 17(10): 919–921.
Zheng FW, Pan XX, Chen WL. Observation on clinical effects of Zhu Lian’s type ? excitation needling technique for postpartum urinary retention. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(4): 300–304.
Liu YL, Wang XD, Huang SF. Observation on the therapeutic effect of electroacupuncture on urinary retention due to prostatic hyperplasia. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2017, 36(11): 1318–1320.
Yang ZJ, Xiao XW. Effect of acupuncture plus mediumfrequency electric stimulation on bladder function after radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(5): 371–376.
Wang JH. Effect and Mechanism Research of Electroacupuncture at Guayuan (CV 4) Acupoint on Detrusor Urinae of Rats of Urinary Retention with Spinal Cord Injury. Wuhan: Doctor Thesis of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, 2009.
Gao YQ, Shi JH, Li XJ, Dong XC, Jia Q, Xie S, Yue H, Guan X. Clinical observation on electroacupuncture in treating urinary retention after spinal anesthesia. Shijie Zhongyiyao, 2017, 12(10): 2280–2283, 2287.
Yang Y, Zhang N, Duan Q. Clinical application and research progress of navel needling. Yunnan Zhongyi Zhongyao Zazhi, 2018, 39(1): 88–90.
Liu CC. Exciting the External Sensory and Motor Nervous Manipulation Mechanism of Detrusor Muscle by Electroacupuncture Ciliao (BL 32) and Zhongliao (BL 33) Acupoints. Beijing: Doctor Thesis of China Academy of Chinese Medical Siences, 2014.
Cheng J, Guo JB, Chen BL, Zhu Y. Acupuncture treatment for urinary retention following spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu, 2018, 22(12): 1962–1968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the recruited patients in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, J., Li, Xh., Zhou, Yh. et al. Therapeutic observation of acupuncture plus navel acupuncture for urinary retention after radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 245–252 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1123-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1123-x
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Umbilicus
- Uterine Cervical Neoplasms
- Postoperative Complications
- Urinary Retention
- Female