Abstract
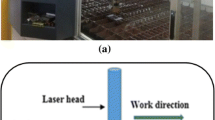
Laser surface alloying is one of the recent technologies used in the manufacturing sector for improving the surface properties of the metals. Light weight materials like aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, and magnesium alloys are used in the locomotive, aerospace, and structural applications. In the present work, an experimental study was conducted to improve the surface hardness of commercially pure aluminum plate. CO2 laser is used to melt pre-placed powders of pure copper, manganese, and magnesium. Microstructure of alloyed surface was analyzed using optical microscope. The best surface alloying was obtained at the optimum values of laser parameters, viz., laser power, scan speed, and laser beam diameter. In the alloyed region, microhardness increased from 30 HV0.5 to 430 HV0.5, while it was 60 HV0.5 in the heat-affected region. Tensile tests revealed some reduction in the strength and total elongation due to alloying. On the other hand, corrosion resistance improved.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.M. Zhang, M. Hida, A. Sakakibara, and Y. Takemoto, Influence of WC Addition on Microstructures of Laser-Melted Ni-Based Alloy Coating, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2002, 11(6), p 667–674
A. Wang, C. Fan, C. Xie, W. Huang, and K. Cui, Laser Cladding of Iron-Base Alloy on Al-Si Alloy and Its Relation to Cracking at the Interface, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1996, 5(6), p 775–783
J.S. Selvan, G. Soundararajan, and K. Subramanian, Laser Alloying of Aluminium with Electrodeposited Nickel: Optimisation of Plating Thickness and Processing Parameters, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2000, 124(2-3), p 117–127
S. Tomida, K. Nakata, S. Saji, and T. Kubo, Formation of Metal Matrix Composite Layer on Aluminum Alloy with Tic-Cu Powder by Laser Surface Alloying Process, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2001, 142-144, p 585–589
S. Tomida and K. Nakata, Fe-Al Composite Layers on Aluminum Alloy Formed by Laser Surface Alloying with Iron Powder, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 174-175, p 559–563
R.S. Rajamure, H.D. Vora, N. Gupta, S. Karewar, S.G. Srinivasan, and N.B. Dahotre, Laser Surface Alloying of Molybdenum on Aluminum for Enhanced Wear Resistance, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 258, p 337–342
A. Almeida, P. Petrov, I. Nogueira, and R. Vilar, Structure and Properties of Al-Nb Alloys Produced by Laser Surface Alloying, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2001, 303(1-2), p 273–280
S. Ignat, P. Sallamand, D. Grevey, and M. Lambertin, Magnesium Alloys Laser (Nd: YAG) Cladding and Alloying with Side Injection of Aluminium Powder, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2004, 225(1-4), p 124–134
M. Zhong and W. Liu, Laser Surface Cladding: The State of the Art and Challenges, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 2010, 224, p 1041–1060
W.U.H. Syed and L. Li, Effects of Wire Feeding Direction and Location in Multiple Layer Diode Laser Direct Metal Deposition, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2005, 248(1-4), p 518–524
J.-D. Kim and Y. Peng, Melt Pool Shape and Dilution of Laser Cladding with Wire Feeding, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 104(3), p 284–293
L. Dubourg, H. Pelletier, D. Vaissiere, F. Hlawka, and A. Cornet, Mechanical Characterisation of Laser Surface Alloyed Aluminium-Copper Systems, Wear, 2002, 253(9-10), p 1077–1085
L. Dubourg, F. Hlawka, and A. Cornet, Study of Aluminium-Copper-Iron Alloys: Application for Laser Cladding, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2002, 151-152, p 329–332
M.A. Pinto, N. Cheung, M.C.F. Ierardi, and A. Garcia, Microstructural and Hardness Investigation of an Aluminum-Copper Alloy Processed by Laser Surface Melting, Mater. Charact., 2003, 50(2-3), p 249–253
A.P.I. Popoola, S.L. Pityana, and O.M. Popoola, Laser Deposition of (Cu + Mo) Alloying Reinforcements on Al1200 Substrate for Corrosion Improvement, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2011, 6, p 5038–5051
S.W. Chen and C.C. Huang, Solidification Curves of AlCu, AlMg and AlCuMg Alloys, Acta Mater., 1996, 44(5), p 1955–1965
B.V. Zlatičanin, S. Đurić, B.M. Jordović, and B. Radonjić, Characterization of Microstructure and Properties of AlCuMg Alloys, J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall., 2003, 39(3-4), p 509–526
J.G. Kaufman, Aluminum Alloys, Mechanical Engineers Handbook, Materials Mechanical Design, 3rd ed., M. Kutz, Ed., Wiley, New York, 2006, p 59–116
S. Nam and D. Lee, The Effect of Mn on the Mechanical Behavior of Al Alloys, Met. Mater., 2000, 6(1), p 13–16
R. Modlinski, R. Puers, and I. De Wolf, AlCuMgMn Micro-Tensile Samples: Mechanical Characterization of MEMS Materials at Micro-Scale, Sens. Actuators, A, 2008, 143(1), p 120–128
L.A. Dobrzański, M. Piec, and A. Klimpel, Improvement of the Hot Work Tool Steel Surface Layers Properties Using a High Power Diode Laser, J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng., 2007, 21(1), p 13–22
L.A. Dobrzański, K. Labisz, E. Jonda, and A. Klimpel, Comparison of the Surface Alloying of the 32CrMoV12-28 Tool Steel Using TiC and WC Powder, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 191(1), p 321–325
K. Labisz, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High Power Diode Laser (HPDL) Treated Cast Aluminium Alloys, Materialwiss. Werkstofftech., 2014, 45(4), p 314–324
A.S.T.M. E8/E8 M Standard, Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2009. doi:10.1520/E0008-E0008M-09. www.astm.org.
ASTM-G31-72, Standard Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadephia, PA, USA, 2004
M.F. Schneider, “Laser Cladding with Powder: Effect of Some Machining Parameters on Clad Properties. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, Netherlands, 1998, p 181.
T.M. Yue and T. Li, Solidification Behaviour and the Evolution of Microstructure in the Laser Cladding of Aluminium on Magnesium Substrate, Mater. Trans., JIM, 2007, 48(5), p 1064–1069
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the facilities procured under Department of Science and Technology FIST Project Number: SR/FST/ETI-244/2008. The authors also acknowledge their access to XRD Xpert facility procured under Ministry of Steels sponsored Project Number ME/P/SKJ/04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiru, W.G., Sankar, M.R. & Dixit, U.S. Laser Surface Alloying of Copper, Manganese, and Magnesium with Pure Aluminum Substrate. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 1172–1181 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1922-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1922-x