Abstract
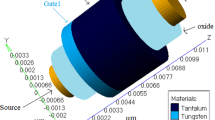
This paper presents an analytical threshold voltage model for back-gated fully depleted (FD), recessed-source drain silicon-on-insulator metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). Analytical surface potential models have been developed at front and back surfaces of the channel by solving the two-dimensional (2-D) Poisson’s equation in the channel region with appropriate boundary conditions assuming a parabolic potential profile in the transverse direction of the channel. The strong inversion criterion is applied to the front surface potential as well as on the back one in order to find two separate threshold voltages for front and back channels of the device, respectively. The device threshold voltage has been assumed to be associated with the surface that offers a lower threshold voltage. The developed model was analyzed extensively for a variety of device geometry parameters like the oxide and silicon channel thicknesses, the thickness of the source/drain extension in the buried oxide, and the applied bias voltages with back-gate control. The proposed model has been validated by comparing the analytical results with numerical simulation data obtained from ATLAS™, a 2-D device simulator from SILVACO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.P. Colinge, Rom. J. Inf. Sci. Technol. 11, 3 (2008).
K.K. Young, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36, 399 (1989).
V.P. Trivedi and J.G. Fossum, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 50, 2095 (2003).
A. Chaudhry and M.J. Kumar, IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 4, 99 (2004).
C.F. Beranger, S. Denorme, P. Perreau, C. Buj, O. Faynot, F. Andrieu, L. Tosti, S. Barnola, T. Salvetat, X. Garros, M. Cassé, F. Allain, N. Loubet, L. Pham-Nguyen, E. Deloffre, M. Gros-Jean, R. Beneyton, C. Laviron, M. Marin, C. Leyris, S. Haendler, F. Leverd, P. Gouraud, P. Scheiblin, L. Clement, R. Pantel, S. Deleonibus, and T. Skotnicki, Solid State Electron 53, 730 (2009).
M. Noguchi, T. Numata, Y. Mitani, T. Shino, S. Kawanaka, Y. Oowaki, and A. Toriumi, IEEE Electron Device Lett 22, 32 (2001).
M. Chan, F. Assaderaghi, S.A. Parke, and C. Hu, IEEE Electron Device Lett 15, 22 (1994).
C. Ahn, W. Cho, K. Im, J. Yang, I. BaekI, S. Lee, and S. Baek, (U.S. Patent) US20060131648 A1 [2006-06-22].
H. I. Hanafi, D. C. Boyd, K. K. Chan, W. Natzle, and L. Shi, (U.S. Patent) 6841831 B2 [2005-01-11].
B. Svilicic, V. Jovanovic’, and T. Suligoj, Solid State Electron 53, 540 (2009).
G.K. Saramekala, A. Santra, S. Dubey, S. Jit, and P.K. Tiwari, Superlattices Microstruct. 60, 580 (2013).
A. Kumar and P.K. Tiwari, Solid State Electron 95, 52 (2014).
G.K. Saramekala, S. Dubey, and P.K. Tiwari, Chin. Phys. B 24, 108505-1 (2015).
K.R. Han, B.K. Choi, H.I. Kwoni, and J.H. Lee, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 4385 (2008).
Y. Yang, S. Markov, and B. Cheng, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 60, 739 (2013).
I. Yang, C. Vieri, A. Chandraksan, and D. Antoniadis, Proceedings of IEDM (1995), p. 877. doi:10.1109/IEDM.1995. 499356.
T. Numata, M. Noguchi, and S. Takagia, Solid State Electron 48, 979 (2004).
A. Majumdar, Z. Ren, S.J. Koester, and W. Haensch, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56, 2270 (2009).
A. Biswas and S. Bhattacherjee, Microelectron. Reliab. 53, 363 (2013).
N. Fasarakis, T. Karatsori, D.H. Tassis, C.G. Theodorou, F. Andrieu, O. Faynot, G. Ghibaudo, and C.A. Dimitriadis, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61, 969 (2014).
S. Khandelwal, Y.S. Chauhan, D.D. Lu, S. Venugopalan, M.A.U. Karim, A.B. Sachid, B.-Y. Nguyen, O. Rozeau, O. Faynot, A.M. Niknejad, and C.C. Hu, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 2026 (2012).
Silvaco International, ATLAS User’s Manual (Santa Clara: Silvaco International, 2012).
A. Ortiz-Conde, F.J. Garcia Sanchez, J.J. Liou, A. Cerdeira, M. Estrada, and Y. Yue, Microelectron. Reliab. 42, 583 (2002).
Acknowledgements
One of the authors, Dr. Pramod Kumar Tiwari, acknowledges financial support received from the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Human Resource and Development, Government of India, under a young scientist research grant. The Grant No. is SB/FTP/ETA-415/2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saramekala, G.K., Tiwari, P.K. An Analytical Threshold Voltage Model of Fully Depleted (FD) Recessed-Source/Drain (Re-S/D) SOI MOSFETs with Back-Gate Control. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 5367–5374 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4752-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4752-6