Abstract
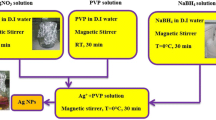
Mono-disperse silver nanoparticles with tunable morphologies have been fabricated by reducing AgNO3 in the presence of N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and larger molecular weight poly (vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP). By adjusting the reaction temperature, the conversion of the morphology can be easily and effectively controlled. The crystal structures and growth mechanism of mono-disperse silver nanoparticles were studied by using TEM, HR-TEM, FFT, XRD and UV-Vis spectra data. The results show that the morphologies of nanoparticles with spherical shape can be adjusted to a truncated triangle/hexagon along with the change of reaction temperature from 80 to 120 °C. It is found that the shape transformation from sphere to truncated triangle is caused by the difference in surface energy and the selective adsorption of PVP on silver atom.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D Li, L J Pan, S. Li, et al. Controlled Preparation of Uniform TiO2-Catalyzed Silver Nanoparticle Films for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(13): 6 861–6 871
S Tokonami, N Morita, K Takasaki, et al. Novel Synthesis, Structure, and Oxidation Catalysis of Ag/Au Bimetallic Nanoparticles[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(23): 10 336–10 341
K S Chen, X R Feng, R Hu, et al. Effect of Ag Nanoparticle Size on the Photoelectrochemical Properties of Ag Decorated TiO2 Nanotube Arrays[J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 554: 72–79
F Liu, J M Nunzi. Enhanced Organic Light Emitting Diode and Solar Cell Performances Using Silver Nano-clusters[J]. Org. Electronics, 2012, 13: 1 623–1 632
K L Kelly, E Coronado, L L Zhao, et al. The Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Size, Shape, and Dielectric Environment [J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107: 668–677
M Pelton, J Aizpurua, G Bryant. Metal-nanoparticle Plasmonics[J]. Laser & Photon Rev., 2008. 2(3): 136–159
J J Mock, M Barbic, D R Smith. et al. Shape Effects in Plasmon Resonance of Individual Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles[J]. J. Chem. Phys., 2002, 116(15): 6 755–6 759
Y Wang, D H Wan, S F Xie, et al. Synthesis of Silver Octahedra with Controlled Sizes and Optical Properties via Seed-Mediated Growth[J]. ACS Nano., 2013, 7(5): 4 586–4 594
S J Chang, K Chen, H Qing, et al. Evidence for the Growth Mechanisms of Silver Nanocubes and Nanowires[J]. J.phys.Chem.C, 2011, 115(16): 7 979–7 982
B Tang, S P Xu, J An, et al. Photoinduced Shape Conversion and Reconstruction of Silver Nanoprisms[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113: 7 025–7 030
H B Mao, J Y Feng, X Ma, et al. One-dimensional Silver Nanowires Synthesized by Self-seeding Polyol process [J]. J.Nanopart. Res., 2012, 14: 887–890
X He, X J Zhao. Solvothermal Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of Chain-like Triangular Silver Nanoplate Assemblies: Application to Metal-enhanced Fluorescence (MEF) [J]. Appl Surf. Sci., 2009, 255: 7 361–7 368
X He, X J Zhao, Y X Chen. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanowires with Zigzag Morphology in N, N-dimethylformamide [J]. J. Solid State Chem., 2007, 180: 2 262–2 267
P S Isabel, M L Luis, N. N-Dimethylformamide as a Reaction Medium for Metal Nanoparticle Synthesis[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2009, 19: 679–688
Y Gao, P Jiang, et al. Studies on Silver Nanodecahedrons Synthesized by PVP-assisted N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) Reduction[J]. J. Cryst Growth, 2006, 289: 376–380
P S Isabel, M L Luis. Synthesis of Silver Nanoprisms in DMF [J]. Nano Lett., 2002, 2(8): 903–905
P S Isabel, M L Luis. Formation and Stabilization of Silver Nanoparticles through Reduction by N, N-Dimethylformamide[J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15: 948–951
P Y Silvert, R H Urbinab, K T Elhsissena. Preparation of Colloidal Silver Dispersions by the Polyol Process, Part 2[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 1997, 7(2): 293–299
P S Isabel, M L Luis. Formation of PVP-Protected Metal Nanoparticles in DMF[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18: 2 888–2 894
M Tsuji, X L Tang, M Mika, et al. Shape Evolution of Flag Types of Silver Nanostructures from Nanorod Seeds in PVP-Assisted DMF Solution[J]. Cryst. Growth Des., 2010, 10(12): 5 238–524
Y J Bae, N H Kim, M J Kim, et al. Anisotropic Assembly of Ag Nanoprisms[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130: 5 432–5 433
X M Zhu, X J Zhao, Z Y Ning, et al. Effect of Polyvinylpyrrolidone Molecular Weight on the Silver Morphology Synthesized by N, N-dimethylformamide Reduction[J]. Key Eng. Mater., 2012, 509: 245–252
S H Chen, L C David. Synthesis and Characterization of Truncated Triangular Silver Nanoplates[J]. Nano Lett., 2002,2(9): 1 003–1 007
B J Wiley, S H Im, Z Y Li, et al. Maneuvering the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Silver Nanostructures through Shape-Controlled Synthesis[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(32): 15 666–15 675
C Noguez. Surface Plasmons on Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Shape and Physical Environment [J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111: 3 806–3 819
C Noguez. Optical Properties of Isolated and Supported Metal Nanoparticles[J]. Opt. Mater., 2005, 27: 1 204–1 211
S Gabriella, C Mirkin. Rapid Thermal Synthesis of Silver Nanoprisms with Chemical Tailorable Thickness[J]. Adv. Mater., 2005, 17(4):412–415
Tang B, Xu S P, Hou X L, et al. Shape Evolution of Silver Nanoplates Through Heating and Photoinduction[J]. Appl. Mater. Interface, 2013, 5: 646–653
Y G Sun, B Mayers, Y N Xia. Transformation of Silver Nanospheres into Nanobelts and Triangular Nanoplates through a Thermal Process [J]. Nano Lett., 2003, 3(5): 675–679
B Tang, J An, X L Zheng, et al. Silver Nanodisk with Tunable Size by Heat Aging[J]. J.Phys.Chem. C, 2008, 112: 18 361–18 367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China(NSFC) (Nos.51032005, 51372180), National Basic Research Program of China (No.2009CB939704) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Wuhan University of Technology)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Ma, X., Chang, H. et al. Morphology tuning of mono-disperse silver nanoparticles by reaction temperature adjustment. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 29, 40–43 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-014-0864-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-014-0864-0