Abstract
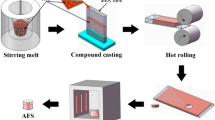
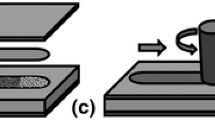
Aluminum foam sandwich was prepared by rolling-bonding/powder metallurgical foaming technology, and the effects of rolling on bond strength of face sheet/powders and powder density were studied. Moreover, the foaming agent, TiH2, was heat treated and a certain amount of Mg was added into powder in an attempt to understand how the stability and uniformity of foam was improved. The experimental results show that the foaming precursors with ideal quality were obtained by rolling-bonding process. When rolling reduction is 67%, the consistency of powders reach to 99.87%. Throughout consideration of the bonding of face sheet/core layer powders and deformation characteristic of powders, the optimum rolling reduction is 60%–70%. Cracks and drainage during foaming were inhibited by heat treatment of foaming agent TiH2 and the addition of a certain amount of Mg. The optimum heat treatment way of TiH2 is that heat preserving 1 hour at 450 °C; the amount of adding Mg is 1wt%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reyes V G, Cantwell W J. Low Belocity Impact Tesponse of Novel Fiber-reinforced Aluminum Foam Sandwich Structures[J].J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2003,22(6):417–422
Seeliger H W. Aluminium Foam Sandwich (AFS) Ready for Market Introduction[J]. Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004,6(6):448–451
Harte A M, Fleck N A, Ashby M F. Sandwich Panel Design Using Aluminum Alloy Foam[J]. Adv. Eng. Mater., 2000,2(4):219–222
Maurer M, Zhao L, Lugscheider E. Surface Refinement of Metal Foams[J]. Adv. Eng. Mater., 2002,4(10):791–797
Körner C, Singer R F. Processing of Metal Foams Challenges and Opportunities[J]. Adv. Eng. Mater., 2000,2(4):159–165
Höpler T, Schörghober M, Simancik F. Metal Foams and Porous Metal Structures[M]. Bremen: MIT-Verlag, 1999:79
Matijasevic L B, Banhart J, Fiechter S, et al. Modification of Titanium Hydride for Improved Aluminium Foam Manufacture[J]. Acta Mater., 2006,54(7):1 887–1 900
Banhart J, Bellmann D, Clemens H. Investigation of Metal Foam Formation by Microscopy and Ultra Small-angle Neutron Scattering[J]. Acta Mater., 2001,49(17):3 409–3 420
Zeppelin F, Hirscher M, Stanzick H, et al. Desorption of Hydrogen From Blowing Agents Used for Foaming Metals[J]. Comp. Sci. Tech., 2003,63(16):2 293–2 300
Duarte I, Banhart J. A Study of Aluminium Foam Formation-Kinetics and Microstructure[J]. Acta Mater., 2000, 48(9): 2 349–2 362
Stobener K, Lehmhus D, Avalle M, et al. Aluminum Goampolymer Hybrid Structures (APM aluminum foam) in Compression Testing[J]. Int. J. Solids Struct., 2008,45(21): 5 627–5 641
Zhang M, Zu GY, Yao GC. The Effect of Mg Addition on the Stability of Foams in Preparation of Foam Aluminum Sandwich [J]. Funct. Mater., 2007,38(4):576–579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fundeded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.50704012) and the Science and Technology Foundation of Shenyang (No. F10-205-1-59)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zu, G., Song, B., Guan, Z. et al. Preparation of aluminum foam sandwich by rolling-bonding/powder metallurgy foaming technology. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 26, 671–674 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0289-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0289-y