Abstract
In order to recover salt and minimize waste volume, a sequential precipitation method was proposed to remove rare earth (RE = La, Sm, Nd, Dy), Cs, Sr, and Ba from spent electrolyte in the form of phosphate and carbonate precipitation, respectively. The thermodynamic calculation confirmed the feasibility of the process. The precipitation results indicated that RE3+ and Cs+ could be converted to insoluble phosphates using Na3PO4, whereas Sr2+ and Ba2+ to insoluble carbonates by adding K2CO3. Meanwhile, the phosphate precipitation process was monitored online by square wave voltammetry, and the results showed that with the addition of Na3PO4, the peak current densities corresponding to the reduction of RE3+ decreased gradually. The molten salt containing La3+, Sm3+, Nd3+, Dy3+, Cs+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ was used to simulate the waste electrolyte for sequential precipitation; the removal rates of RE, Sr, and Ba were found to be over 95.00%, except for Cs 79.17%.
Graphical abstract
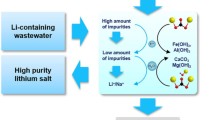
In order to recover the molten salt, the sequential precipitation method was proposed to remove rare earth (RE = La, Sm, Nd, Dy), Cs, Sr, and Ba from spent electrolyte. RE and Cs were separated using Na3PO4 and Sr and Ba using K2CO3. The removal rates estimated by ICP-OES were found to be over 95.00%, except for Cs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu K, Chai Z, Shi W (2018) Uranium dendritic morphology in the electrorefining: influences of temperature and current density. J Electrochem Soc 165:D98–D106. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0281803jes
Han W, Li W, Li M, Li Z, Sun Y, Yang X, Zhang M (2018) Electrochemical co-reduction of Y(III) and Zn(II) and extraction of yttrium on Zn electrode in LiCl-KCl eutectic melts. J Solid State Electrochem 22:2435–2444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-3956-5
Han W, Li Z, Li M, Hu X, Yang X, Zhang M, Sun Y (2017) Electrochemical behavior and extraction of holmium on Cu electrode in LiCl-KCl molten salt. J Electrochem Soc 164:D934–D943. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0101714jes
Wang J, Li M, Han W, Liu ZY, Zhang ML (2018) Electrochemical co-reduction of holmium and magnesium ions in eutectic LiCl-KCl salts. Rare Met. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1157-0
Han W, Li W, Li M, Yang Z, Chen L, Zhang Y, Meng Y (2020) Electrochemical extraction of metallic Y using solid and liquid double cathodes. Electrochim Acta 346:136233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136233
Li M, Wang J, Han W, Dong Y, Wang W, Zhang M, Yang X, Sun Y (2018) Recovery of terbium from LiCl-KCl-TbCl3 system by electrodeposition using different electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 165:D704–D710. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0551814jes
Li W, Han W, Li M, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yue M, Sun Y (2020) Electroreduction of Dy(III) assisted by Zn and its co-deposition with Zn(II) in LiCl-KCl molten salt. Appl Organomet Chem 34:e5817. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5817
Li M, Sun Z, Guo D, Han W, Sun Y, Yang X, Zhang M (2020) Electrode reaction of Pr(III) and coreduction of Pr(III) and Pb(II) on W electrode in eutectic LiCl-KCl. Ionics 26:3901–3909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03518-4
Han W, Wang W, Li M, Meng Y, Ji W, Sun Y (2020) Electrochemical coreduction of Gd(III) with Pb(II) and recovery of Gd from LiCl-KCl eutectic assisted by Pb metal. J Electrochem Soc 167:142505. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abc723
Krishna GM, Suneesh AS, Venkatesan KA, Antony MP (2018) Anodic Dissolution of uranium and zirconium metals and electrochemical behavior of U(IV) and Zr(IV) in ionic liquid medium for metallic fuel reprocessing. J Electrochem Soc 165:C206–C212. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0281805jes
Z. Li, Z. Liu, W. Li, W. Han, M. Li, M. Zhang, Electrochemical recovery of dysprosium from LiCl-KCl melt aided by liquid Pb metal, separation and purification technology, 250 (2020) 117124 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117124
Lee JH, Kang YH, Hwang SC, Kim EH, Yoo JH, Park HS (2007) Separation characteristics of a spent fuel surrogate in the molten salt electrorefining process. J Mater Process Technol 189:268–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.01.034
Amamoto I, Kofuji H, Myochin M, Takasaki Y, Terai T (2009) Phosphates behaviours in conversion of FP chlorides. J Nucl Mater 389:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2009.01.019
Simpson MF, Yoo TS, Benedict RW, Phongikaroon S, Frank S, Sachdev P, Hartman K (2007) Strategic minimization of high level waste from pyroprocessing of spent nuclear fuel. Proc Ann Meet World Maric Soc 8:533–541. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.1977.tb00142.x
Hudry D, Bardez I, Rakhmatullin A, Bessada C, Bart F, Jobic S, Deniard P (2008) Synthesis of rare earth phosphates in molten LiCl-KCl eutectic: application to preliminary treatment of chlorinated waste streams containing fission products. J Nucl Mater 381:284–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.09.005
Leturcq G, Grandjean A, Rigaud D, Perouty P, Charlot M (2005) Immobilization of fission products arising from pyrometallurgical reprocessing in chloride media. J Nucl Mater 347:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2005.06.026
Volkovich VA, Griffiths TR, Thied RC (2003) Formation of lanthanide phosphates in molten salts and evaluation for nuclear waste treatment. Phys Chem Chem Phys 5:3053–3060. https://doi.org/10.1039/b302280n
Volkovich VA, Griffiths TR, Thied RC (2003) Treatment of molten salt wastes by phosphate precipitation: removal of fission product elements after pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels in chloride melts. J Nucl Mater 323:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2003.08.024
Cho YZ, Lee TK, Eun HC, Choi JH, Kim IT, Park GI (2013) Purification of used eutectic (LiCl-KCl) salt electrolyte from pyroprocessing. J Nucl Mater 437:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.01.344
Cho YZ, Yang HC, Park GH, Lee HS, Kim IT (2009) Treatment of a waste salt delivered from an electrorefining process by an oxidative precipitation of the rare earth elements. J Nucl Mater 384:256–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.11.020
Harrison MT, Simms HE, Jackson A, Lewin RG (2008) Salt waste treatment from a LiCl-KCl based pyrochemical spent fuel treatment process. Radiochim Acta 96:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1524/ract.2008.1490
Kim EH, Park GI, Cho YZ, Yang HC (2008) A new approach to minimize pyroprocessing waste salts through a series of fission product removal process. Nucl Technol 162:208–218. https://doi.org/10.13182/nt08-a3949
Eun HC, Choi JH, Kim NY, Lee TK, Han SY, Jang SA, Kim TJ, Park HS, Ahn DH (2017) A study of separation and solidification of group II nuclides in waste salt delivered from the pyrochemical process of used nuclear fuel. J Nucl Mater 491:149–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.04.060
Li M, Gu Q, Han W, Zhang X, Sun Y, Zhang M, Yan Y (2015) Electrochemical behavior of La(III) on liquid Bi electrode in LiCl-KCl melts Determination of thermodynamic properties of La-Bi and Li-Bi intermetallic compounds. RSC Advances 5:82471–82480. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra12723h
Barin I (1995) Thermochemical data of pure substances, 3rd edn. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, Germany
Sengupta P (2012) A review on immobilization of phosphate containing high level nuclear wastes within glass matrix-Present status and future challenges. J Hazard Mater 235:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.07.039
Eun HC, Choi JH, Kim NY, Lee TK, Han SY, Lee KR, Park HS, Ahn DH (2016) A reactive distillation process for the treatment of LiCl-KCl eutectic waste salt containing rare earth chlorides. J Nucl Mater 480:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2016.07.063
Funding
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science foundation of China (21790373, 11875116, 21876034, and 22076035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, W., Zhang, Y., Liu, R. et al. Purification of spent electrolyte by sequential precipitation method and its on-line monitoring. Ionics 27, 4829–4838 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04256-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04256-x