Abstract
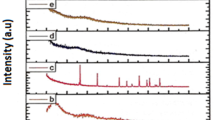
In this paper, we report the investigation on structural, electrical, dielectric properties, and ion dynamics of novel blend polymer electrolyte matrix (PEO-PEI) complexed with sodium hexafluorophosphate salt. All the solid polymer electrolyte films have been synthesized via solution cast method. The SPE films were characterized by the X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscope, impedance-dielectric spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. The morphology of the SPE alters with salt addition and confirms the blend polymer complex formation. The FTIR analysis evidenced the complex formation, and increase in the fraction of free ions is achieved. The ionic conductivity exhibits a maximum at the stoichiometric ratio O/Na = 10 and follows the Arrhenius behavior. The fraction of free ions is maximum for the SPE film with the highest ionic conductivity. The optimum electrolyte possesses a voltage stability window of about 4 V, excellent thermal stability up to 380 °C, and high ionic transference number (~ 1). The complex permittivity and conductivity have been simulated in whole frequency window to extract relaxation time and dielectric strength. The dielectric constant and relaxation time exhibited sequentially a maximum and minimum for the SPE film with the highest ionic conductivity. The loss tangent peak shifts toward high frequency with addition of salt, and it infers the faster ion dynamics in the polymer matrix. Then the ion transport parameters number density of charge carriers (n), ion mobility (μ), and diffusion coefficient (D) have been obtained by three methods (FTIR, impedance spectroscopy, and loss tangent method) and are in absolute correlation with the impedance results. An ion transport mechanism has been proposed based on experimental findings.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya A, Sharma AL (2017) Polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries: a critical study. Ionics. 23:497–540
Zhang H, Li C, Piszcz M, Coya E, Rojo T, Rodriguez-Martinez LM, Armand M, Zhou Z (2017) Single lithium-ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes: advances and perspectives. Chem Soc Rev 46:797–815
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2008) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature. 451:652
Saykar NG, Phatangare AB, Banerjee I, Bhoraskar VN, Ray AK, Mahapatra S (2019) Electron beam induced synthesis of Ru-rGO and its super capacitive behavior. 2D Mater 6:045030
Yue L, Ma J, Zhang J, Zhao J, Dong S, Liu Z, Cui G, Chen L (2016) All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Materials 5:139–164
Hasa I, Hassoun J, Passerini S (2017) Nanostructured Na-ion and Li-ion anodes for battery application: a comparative overview. Nano Res 10:3942–3969
Yang Q, Zhang Z, Sun XG, Hu YS, Xing H, Dai S (2018) Ionic liquids and derived materials for lithium and sodium batteries. Chem Soc Rev 47:2020–2064
Saykar NG, Pilania RK, Banerjee I, Mahapatra SK (2018) Synthesis of NiO-Co3O4 nanosheet and its temperature-dependent supercapacitive behavior. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:475501
Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Electrolyte for energy storage/conversion (Li+, Na+, Mg 2+) devices based on PVC and their associated polymer: a comprehensive review. J Solid State Electrochem 23:997–1059
Anilkumar KM, Jinisha B, Manoj M, Jayalekshmi S (2017) Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) – poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) blend polymer based solid electrolyte membranes for developing solid state magnesium ion cells. Eur Polym J 89:249–262
Arya A, Saykar NG, Sharma AL (2019) Impact of shape (nanofiller vs. nanorod) of TiO2 nanoparticle on free-standing solid polymeric separator for energy storage/conversion devices. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47361
Arya A, Sharma AL (2017) Insights into the use of polyethylene oxide in energy storage/conversion devices: a critical review. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:443002
Arya A, Sadiq M, Sharma AL (2019) Structural, electrical and ion transport properties of free-standing blended solid polymeric thin films. Polym Bull 76:5149–5172
Arya A, Sharma S, Sharma AL, Kumar D, Sadiq M (2016) Structural and dielectric behavior of blend polymer electrolyte based on PEO–PAN? LiPF 6. Asian J Eng Appl Technol 5:4–7
Bhat C, Swaroop R, Arya A, Sharma AL (2015) Effect of nano-filler on the properties of polymer nanocomposite films of PEO/PAN complexed with NaPF6. J Mater Sci Eng B 5:418–434
Arya A, Sharma AL (2016) Conductivity and stability properties of solid polymer electrolyte based on PEO-PAN+ LiPF6 for energy storage. Appl Sci Lett 2:72–75
Rajendran S, Sivakumar M, Subadevi R (2004) Investigations on the effect of various plasticizers in PVA-PMMA solid polymer blend electrolytes. Mater Lett 58:641–649
Qiao J, Fu J, Lin R, Ma J, Liu J (2010) Alkaline solid polymer electrolyte membranes based on structurally modified PVA/PVP with improved alkali stability. Polymer. 5:4850–4859
Janakiraman S, Padmaraj O, Ghosh S, Venimadhav A (2018) A porous poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) based separator-cum-gel polymer electrolyte for sodium-ion battery. J Electroanal Chem 826:142–149
Arya A, Sadiq M, Sharma AL (2018) Effect of variation of different nanofillers on structural, electrical, dielectric, and transport properties of blend polymer nanocomposites. Ionics. 24:2295–2319
Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Investigation on enhancement of electrical, dielectric and ion transport properties of nanoclay‑based blend polymer nanocomposites. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02893-x
Harris CS, Shriver DF, Ratner MA (1986) Complex formation of poly(ethylenimine) with sodium triflate and conductivity behavior of the complexes. Macromolecules. 19:987–989
Paul JL, Jegat C, Lassegues JC (1992) Branched poly (ethyleneimine)-CF3SO3Li complexes. Electrochim Acta 37:1623–1625
Kaatze U, Göttmann O, Podbielski R, Pottel R (1988) Dielectric spectroscopy on aqueous solutions of some nitrogen-containing linear hydrocarbon polymers. J Mol Liq 37:127–141
Pehlivan IB, Granqvist CG, Marsal R, Georén P, Niklasson GA (2012) [PEI–SiO2]:[LiTFSI] nanocomposite polymer electrolytes: ion conduction and optical properties. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 98:465–471
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Effect of salt concentration on dielectric properties of Li-ion conducting blend polymer electrolytes. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:17903–17920
Sumisha A, Arthanareeswaran G, Ismail AF, Kumar DP, Shankar MV (2015) Functionalized titanate nanotube-polyetherimide nanocomposite membrane for improved salt rejection under low pressure nanofiltration. RSC Adv 5:39464–39473
Hashmi SA, Upadhyaya HM, Thakur AK, Verma AL (2000) Experimental investigations on poly(ethylene oxide) based sodium ion conducting composite polymer electrolytes dispersed with SnO2. Ionics. 6:248–259
Das A, Thakur AK, Kumar K (2013) Exploring low temperature Li + ion conducting plastic battery electrolyte. Ionics 19:1811–1823
Sharma AL, Shukla N, Thakur AK (2008) Studies on structure property relationship in a polymer-clay nanocomposite film based on (PAN)8LiClO4. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 46:2577–2592
Girard GM, Wang X, Yunis R, MacFarlane DR, Bhattacharyya AJ, Forsyth M, Howlett PC (2019) Sustainable, dendrite free lithium-metal electrode cycling achieved with polymer composite electrolytes based on a poly (ionic liquid) host. Batteries & Supercaps 2:229–239
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Structural, microstructural and electrochemical properties of dispersed-type polymer nanocomposite films. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:045504
Blonsky PM, Shriver DF, Austin P, Allcock PHR (1986) Complex formation and ionic conductivity of polyphosphazene solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 18:258–264
Pila CRM, Cappe EP, Mohallem NDS, Alves OL, Frutis MAA, Sánchez-Ramírez N et al (2019) Effect of the LLTO nanoparticles on the conducting properties of PEO-based solid electrolyte. Solid State Sci 88:41–47
Abdollahi S, Ehsani M, Morshedian J, Khonakdar HA, Reuter U (2018) Structural and electrochemical properties of PEO/PAN nanofibrous blends: prediction of graphene localization. Polym Compos 39:3626–3635
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Optimization of salt concentration and explanation of two peak percolation in blend solid polymer nanocomposite films. J Solid State Electrochem 22:2725–2745
Chen BK, Su CT, Tseng MC, Tsay SY (2006) Preparation of polyetherimide nanocomposites with improved thermal, mechanical and dielectric properties. Polym Bull 57:671–681
Burba CM, Frech R (2005) Spectroscopic measurements of ionic association in solutions of LiPF6. J Phys Chem B 109:15161–15164
Karmakar A, Ghosh A (2014) Structure and ionic conductivity of ionic liquid embedded PEO-LiCF3SO3 polymer electrolyte. AIP Adv 4:087112
Tang R, Jiang C, Qian W, Jian J, Zhang X, Wang H, Yang H (2015) Dielectric relaxation, resonance and scaling behaviors in Sr3Co2Fe24O41 hexaferrite. Sci Rep 5:13645
Jonscher AK (1983) Dielectric relaxation in solids. Chelsea Dielectric, London
Wan Z, Lei D, Yang W, Liu C, Shi K, Hao X, ... Kang F (2019) Low resistance–integrated all-solid-state battery achieved by Li7La3Zr2O12 nanowire upgrading polyethylene oxide (PEO) composite electrolyte and PEO cathode binder. Adv Funct Mater 29:1805301
Zhu Y, Cao J, Chen H, Yu Q, Li B (2019) High electrochemical stability of a 3D cross-linked network PEO@ nano-SiO2 composite polymer electrolyte for lithium metal batteries. J Mater Chem A 7:6832–6839
Jinisha B, Anilkumar KM, Manoj M, Pradeep VS, Jayalekshmi S (2017) Development of a novel type of solid polymer electrolyte for solid state lithium battery applications based on lithium enriched poly (ethylene oxide)(PEO)/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)(PVP) blend polymer. Electrochim Acta 235:210–222
Sharma AL, Thakur AK (2011) Polymer matrix-clay interaction mediated mechanism of electrical transport in exfoliated and intercalated polymer nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 46:1916–1931
Naveen Kumar P, Sasikala U, Sharma AK (2013) Investigations on conductivity and discharge profiles of novel (PEO+PEMA) polymer blend electrolyte. Int J Inno Res Sci Eng Tech 2:3575–3582
Ramamohan K, Umadevi C, Achari VBS, Sharma AK (2013) Conductivity studies on (PVC/PEMA) solid polymer blend electrolyte films complexed with NaIO4. Int J Plast Technol 17:139–148
Kesavan K, Mathew CM, Rajendran S, Ulaganathan M (2014) Preparation and characterization of novel solid polymer blend electrolytes based on poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) with various concentrations of lithium perchlorate. Materials Science and Engineering B: Solid-State Materials for Advanced Technology 184:26–33
Kumar KK, Ravi M, Pavani Y, Bhavani S, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVR (2014) Investigations on PEO/PVP/NaBr complexed polymer blend electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. J Membr Sci 454:200–211
Saikia D, Kumar A (2004) Ionic conduction in P(VDF-HFP)/PVDF-(PC + DEC)-LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 60:119–123
Chiang CK, Davis GT, Harding CA, Takahashi T (1985) Polyethylenimine-sodium iodide complexes. Macromolecules 18:825–827
Takahashi T, Davis GT, Chiang CK, Harding CA (1986) Chemical modification of poly (ethylene imine) for polymeric electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 18:321–325
Koduru HK, Marino L, Scarpelli F, Petrov AG, Marinov YG, Hadjichristov GB et al (2017) Structural and dielectric properties of NaIO4–complexed PEO/PVP blended solid polymer electrolytes. Curr Appl Phys 17:1518–1531
Kumar KK, Ravi M, Pavani Y, Bhavani S, Sharma AK, Rao VN (2011) Investigations on the effect of complexation of NaF salt with polymer blend (PEO/PVP) electrolytes on ionic conductivity and optical energy band gaps. Phys B Condens Matter 406:1706–1712
Harris CS, Ratner MA, Shriver DF (1987) Ionic conductivity in branched polyethylenimine-sodium trifluoromethanesulfonate complexes. Comparisons to analogous complexes made with linear polyethylenimine. Macromolecules 20:1778–1781
Latif F, Aziz M, Katun N, Yahya MZ (2006) The role and impact of rubber in poly (methyl methacrylate)/lithium triflate electrolyte. J Power Sources 159:1401–1404
Bloom H, Heymann E (1947) The electric conductivity and the activation energy of ionic migration of molten salts and their mixtures. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A Mathematical and Physical Sciences 188:392–414
Singh VK, Shalu SK, Chaurasia RK (2016) Singh, development of ionic liquid mediated novel polymer electrolyte membranes for application in Na-ion batteries. RSC Adv 6:40199–40210
Liu W, Lee SW, Lin D, Shi F, Wang S, Sendek AD, Cui Y (2017) Enhancing ionic conductivity in composite polymer electrolytes with well-aligned ceramic nanowires. Nat Energy 2:17035
Chen D, Cheng J, Wen Y, Cao G, Yang Y, Liu H (2012) Impedance study of electrochemical stability limits for electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:12383–12390
Sharma AL, Thakur AK (2013) Plastic separators with improved properties for portable power device applications. Ionics. 19:795–809
Koduru HK, Marinov YG, Hadjichristov GB, Petrov AG, Godbert N, Scaramuzza N (2018) Polyethylene oxide (PEO)–liquid crystal (E8) composite electrolyte membranes: microstructural, electrical conductivity and dielectric studies. J Non-Cryst Solids 499:107–116
Chaurasia SK, Chandra A (2017) Organic-inorganic hybrid electrolytes by in-situ dispersion of silica nanospheres in polymer matrix. Solid State Ionics 307:35–43
Halim SIA, Chan CH, Sim LH (2016) Thermal properties and intermolecular interaction of blends of poly (ethylene oxide) and poly (methyl acrylate). In Macromolecular Symposia 365:95–103
Elashmawi IS, Gaabour LH (2015) Raman, morphology and electrical behavior of nanocomposites based on PEO/PVDF with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Results in Physics 5:105–110
Sharma AL, Thakur AK (2011) AC conductivity and relaxation behavior in ion conducting polymer nanocomposite. Ionics. 17:135–143
Pawlicka A, Tavares FC, Dörr DS, Cholant CM, Ely F, Santos MJL, Avellaneda CO (2019) Dielectric behavior and FTIR studies of xanthan gum-based solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 305:232–239
Ravi M, Pavani Y, Kiran Kumar K, Bhavani S, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVR (2011) Studies on electrical and dielectric properties of PVP:KBrO4 complexed polymer electrolyte films. Mater Chem Phys 130:442–448
Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Tailoring the structural, morphological, electrochemical, and dielectric properties of solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 25:1617–1632
Duan H, Fan M, Chen WP, Li JY, Wang PF, Wang WP et al (2019) Extended electrochemical window of solid electrolytes via heterogeneous multilayered structure for high-voltage lithium metal batteries. Adv Materials 31:1807789
Cole KS, Cole RH (1941) Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics I. Alternating current characteristics. J Chem Phys 9:341–351
Fragiadakis D, Dou S, Colby RH, Runt J (2009) Molecular mobility and Li+ conduction in polyester copolymer ionomers based on poly(ethylene oxide). J Chem Phys 130:064907
Teeters D The concentration behavior of lithium triflate at the surface of polymer electrolyte materials. Solid State Ionics 85(2003):239–245
Pritam, Arya A, Sharma AL (2019) Dielectric relaxations and transport properties parameter analysis of novel blended solid polymer electrolyte for sodiumion rechargeable batteries. J Mater Sci 54:7131–7155
Ngai KS, Ramesh S, Ramesh K, Juan JC (2018) Electrical, dielectric and electrochemical characterization of novel poly (acrylic acid)-based polymer electrolytes complexed with lithium tetrafluoroborate. Chem Phys Lett 692:19–27
Chopra S, Sharma S, Goel TC, Mendiratta RG (2003) Structural, dielectric and pyroelectric studies of Pb1-XCaXTiO3 thin films. Solid State Commun 127:299–304
Sharma AL, Thakur AK (2015) Relaxation behavior in clay-reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Ionics 21:1561–1575
Arof AK, Amirudin S, Yusof SZ, Noor IM (2014) A method based on impedance spectroscopy to determine transport properties of polymer electrolytes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:1856–1867
Nakamura K, Saiwaki T, Fukao K (2010) Dielectric relaxation behavior of polymerized ionic liquid. Macromolecules. 43:6092–6098
Kisliuk A, Bocharova V, Popov I, Gainaru C, Sokolov AP (2019) Fundamental parameters governing ion conductivity in polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 299:191–196
Arya A, Sharma AL (2018) Structural, electrical properties and dielectric relaxations in Na+-ion-conducting solid polymer electrolyte. J Phys Condens Matter 30:165402
Kumar D, Kanchan DK (2019) Dielectric and electrochemical studies on carbonate free Na-ion conducting electrolytes for sodium-sulfur batteries. Journal of Energy Storage 22:44–49
Wei YZ, Sridhar S (1993) A new graphical representation for dielectric data. J Chem Phys 99:3119–3124
Shukla N, Thakur AK, Shukla A, Marx DT (2014) Ion conduction mechanism in solid polymer electrolyte: an applicability of almond-west formalism. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:7644–7659
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2015) Structural and dielectric studies of amorphous and semicrystalline polymers blend-based nanocomposite electrolytes. J Appl Polym Sci 132
Temperature and salt-dependent dielectric properties of blend solid polymer electrolyte complexed with LiBOB. Macromol Res27:334–345
Khamzin AA, Popov II, Nigmatullin RR (2014) Correction of the power law of ac conductivity in ion-conducting materials due to the electrode polarization effect. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys 89:032303
Roy A, Dutta B, Bhattacharya S (2016) Correlation of the average hopping length to the ion conductivity and ion diffusivity obtained from the space charge polarization in solid polymer electrolytes. RSC Adv 6:65434–65442
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (Pritam) is thankful to CSIR, New Delhi, for the award of JRF fellowship. AA is thankful to the Central University of Punjab, Bathinda, for providing fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pritam, Arya, A. & Sharma, A.L. Selection of best composition of Na+ ion conducting PEO-PEI blend solid polymer electrolyte based on structural, electrical, and dielectric spectroscopic analysis. Ionics 26, 745–766 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03245-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03245-5