Abstract
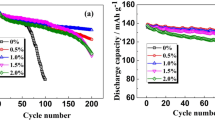
A thin-film lithium phosphorous oxynitride (LiPON) layer on the top of a graphite anode is synthesized via radio frequency magnetron sputtering, whereas the thickness of the film is about 0.3 ~ 1.3 μm. The field emission scanning electron microscopy on the samples confirms the even-coated layer on the anode, while the thickness of layer is reconfirmed by weighing the area density of sputtered anode. The storage experiment at elevated temperature of LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2/graphite cells with and without a LiPON layer on anode reveals that the LiPON layer on the anode would restrain the capacity loss when compared with bare anode. Moreover, it is found that a thicker LiPON layer on anode would provide better capacity retention during storage aging. Meanwhile, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy is recorded during aging and its equivalent circuit simulation is proposed. Also, the anode surface morphology with and without a LiPON layer is observed before and after aging. Based on these investigations and analysis, we conclude that the LiPON layer on the top of the anode would act as a protective layer and improve the capacity retention during storage aging at elevated temperature.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas EV, Bloom I, Christophersen JP, Battaglia VS (2012) Ratebased degradation modeling of lithium-ion cells. J Power Sources 206:378–382
Christophersen JP, Bloom I, Thomas E, Battaglia V (2012) Battery calendar life estimate manual modeling and simulation. INL/EXT-08015136
Agubra V, Fergus J (2013) Lithium ion battery anode aging mechanisms. Materials 6:1310–1325
Barré A, Deguilhem B, Grolleau S, Gérard M, Suard F, Riu D (2013) A review on lithium-ion battery ageing mechanisms and estimations for automotive applications. J Power Sources 241:680–689
Sarre G, Blanchard P, Broussely M (2004) Aging of lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 127:65–71
Schlasza C, Ostertag P, Chrenko D, Kriesten R (2014) Review on the aging mechanisms in Li-ion batteries for electric vehicles based on the FMEA method. Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo 1-6
Vetter J, Novák P, Wagner MR, Veit C, Möller KC, Besenhard JO, Winter M, Wohlfahrt-Mehrens M, Vogler C, Hammouche A (2005) Ageing mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 147:269–281
Waldmann T, Wilka M, Kasper M, Fleischhammer M, Wohlfahrt- Mehrens M (2014) Temperature dependent ageing mechanisms in Lithium-ion batteries – a post-mortem study. J Power Sources 262:129–135
Broussely M, Herreyre S, Biensan P, Kasztejna P, Nechev K, Staniewicz RJ (2001) Aging mechanism in Li ion cells and calendar life predictions. J Power Sources 97-98:13–21
Roberts M, Biendicho JJ, Hull S, Beran P, Gustafsson T, Svensson G, Edström K (2013) Design of a new lithium ion battery test cell for in-situ neutron diffraction measurements. J Power Sources 226:249–255
Prasad GK, Rahn CD (2013) Model based identification of aging parameters in lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 232:79–85
Yoshida T, Takahashi M, Morikawa S, Ihara C, Katsukawa H, Shiratsuchi T, Yamaki JI (2006) Degradation mechanism and life prediction of lithium-ion batteries. J Jpn Soc Nat Disaster Sci 153:A576–A582
Xu K (2014) Electrolytes and interphases in li-ion batteries and beyond. Chem Rev 114:11503
Verma P, Maire P, Novák P (2010) A review of the features and analyses of the solid electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 55:6332–6341
An SJ, Li J, Danie C, Mohanty D, Nagpure S, Wood DL (2016) The state of understanding of the lithium-ion-battery graphite solid electrolyte interphase(SEI) and its relationship to formation cycling. Carbon 105:52–76
Li NW, Yin YX, Yang CP, Guo YG (2016) An artificial solid electrolyte interphase layer for stable lithium metal anodes. Adv Mater 28:1853
Li J, Dudney NJ, Nanda J, Liang C (2014) Artificial solid electrolyte interphase to address the electrochemical degradation of silicon electrodes. Acs Appl Mater Int 6:10083–10088
Lin YX, Liu Z, Leung K, Chen LQ, Lu P, Qi Y (2016) Connecting the irreversible capacity loss in Li-ion batteries with the electronic insulating properties of solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) components. J Power Sources 309:221–230
Wu NL, Weng YT, Li FS, Yang NH, Kuo CL, Li DS (2015) Polymeric artificial solid/electrolyte interphases for Li-ion batteries. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 25:563–571
Van-Jodin LL, Ducroquet F, Sabary F, Chevalier I (2013) Dielectric properties, conductivity and Li+ ion motion in LiPON thin films. Solid State Ionics 253:151–156
Senevirathne K, Day CS, Gross MD, Lachgar A, Holzwarth NW (2013) A new crystalline LiPON electrolyte: synthesis, properties, and electronic structure. Solid State Ionics 233:95–101
Dudney NJ (2000) Addition of a thin-film inorganic solid electrolyte (Lipon) as a protective film in lithium batteries with a liquid electrolyte. J Power Sources 89:176–179
Jouybari YH, Berkemeier F (2016) Enhancing silicon performance via LiPON coating: a prospective anode for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 217:171–180
Kim Y, Veith GM, Nanda J, Unocic R, Chi M, Dudney NJ (2011) High voltage stability of LiCoO2 particles with a nano-scale Lipon coating. Electrochim Acta 56:6573–6580
Nimisha CS, Rao KY, Venkatesh G, Rao GM, Munichandraiah N (2011) Sputter deposited LiPON thin films from powder target as electrolyte for thin film battery applications. Thin Solid Films 519:3401–3406
Bridges CA, Sun XG, Zhao J, Paranthaman MP, Dai S (2012) In situ observation of solid electrolyte interphase formation in ordered mesoporous hard carbon by small-angle neutron scattering. J Phys Chem C 116:7701–7711
Liu L, Park J, Lin X, Sastry AM, Lu W (2014) A thermalelectrochemical model that gives spatial-dependent growth of solid electrolyte interphase in a Li-ion battery. J Power Sources 268:482–490
Reichert MDA, Rösmann A, Janssen P, Bremes HG, Sauer DU, Passerini S, Winter M (2013) Influence of relaxation time on the lifetime of commercail lithium-ion cells. J Power Sources 239:45–53
Zhang SS, Xu K, Jow TR (2004) Electrochemical impedance study on the low temperature of Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 49:1057–1061
Prada E, Domenico DD, Creff Y, Bernard J, Sauvant-Moynot V, Huet F (2013) A simplified electrochemical and thermal aging model of LiFePO4-graphite Li-ion batteries: power and capacity fade simulations. J Electrochem Soc 160:A616–A628
Zhang D, Haran BS, Durairajan A, White RE, Podrazhansky Y, Popov BN (2000) Studies on capacity fade of lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 91:122–129
Bodenes L, Naturel R, Martinez H, Dedryvère R, Menetrier M, Croguennec L, Pérès JP, Tessier C, Fischer F (2013) Lithium secondary batteries working at very high temperature: capacity fade and understanding of aging mechanisms. J Power Sources 236:265–275
Röder P, Stiaszny B, Ziegler JC, Baba N, Lagaly P, Wiemhöfer HD (2014) The impact of calendar aging on the thermal stability of a LiMn2O4– Li(Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3)O2/graphite lithium-ion cell. J Power Sources 268:315–325
Agubra VA, Fergus JW (2014) The formation and stability of the solid electrolyte interface on the graphite anode. J Power Sources 268:153–162
Xu K, Lee U, Zhang SS, Jow TR (2004) Graphite/electrolyte interface formed in LiBOB-based electrolytes, II potential dependence of surface chemistry on graphitic anodes. J Electrochem Soc 151:A2106–A2112
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Project of National University of Defense Technology (ZDYYJCYJ 20140701). Meanwhile, we would gratefully like to thank the Zhong Fang Gai De Vacuum Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China, for providing us the rf magnetron sputtering equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Xie, K., Pan, Y. et al. LiPON as a protective layer on graphite anode to extend the storage life of Li-ion battery at elevated temperature. Ionics 24, 723–734 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2250-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2250-3