Abstract
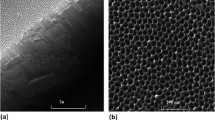
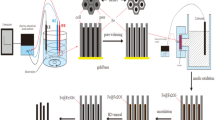
Fe96−x Zr x B4 (1<x<12) nanowires were prepared by electrodepositing into anodic aluminum oxide templates. The diameter of nanowires used is 100 nm and the aspect ratio is 75. The structure of the nanowire arrays was studied by selected area electron diffraction, X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer spectrometer. The phase structure of Fe96−x Zr x B4 nanowires is changed from a crystalline phase to a homogenous amorphous phase with the increasing of Zr content. The Fe96−x Zr x B4 nanowires are composed of α-Fe-like and Zr-rich FeZrB phases. With the increasing of Zr composition, the atoms of Fe site in both phases are more disorderly, and the α-Fe-like phase decreasing with the FeZrB phase increasing. The anisotropy of Fe96−x Zr x B4 nanowires becomes more obvious with the increasing of Zr content, and the easy magnetizing axis is parallel to the nanowire arrays.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen M H, Kim Y N, Lee H M, et al. Multifunctional magnetic silver nanoshells with sandwichlike nanostructures. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112: 8870–8874
Zavaliche F, Zhao T, Zheng H, et al. Electrically assisted magnetic recording in multiferroic nanostructures. Nano Lett, 2007, 7: 1586–1590
Bartlett S D, Brennen G K, Miyake A, et al. Quantum computational renormalization in the haldane Phase. Phys Rev Lett, 2010, 105: 110502–110505
Liang S, Fang X, Xia T L, et al. Self-assembled magnetic nanohead-FeSi nanowire epitaxial heterojunctions by chemical vapor deposition. J Phys Chem C, 2010, 114: 16187–16190
Goto K, Tanaka H, Kawai T. Controlled fabrication of epitaxial (Fe,Mn)3O4 artificial nanowire structures and their electric and magnetic properties. Nano Lett, 2009, 9: 1962–1669
Tsai C I, Wang C Y, Tang J, et al. Electrical properties and magnetic response of cobalt germanosilicide nanowires. ACS Nano, 2011, 5: 9552–9558
Wang J, Zhang L Y, Wei L M, et al. Novel nanotress of crystalline nickel formed via electrolytic approach. Nano-Micro Lett, 2011, 3: 264–269
Venkatesh R, Amrit J, Chalopin Y, et al. Thermal resistance of metal nanowire junctions in the ballistic regime. Phys Rev B, 2011, 83: 115425–115429
Li G R, Tong Y X, Kay L G, et al. Electrodeposition of Bi(x)Fe(1−x) intermetallic compound nanowire arrays and their magnetic properties. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 110: 8965–8970
Zhang L Y, Xue D S, Xu X F, et al. The fabrication and magnetic properties of nanowire-like iron oxide. J Phys-Condens Matter, 2004, 16: 4541–4548
She H, Chen Y Z, Wen R, et al. A nonaqueous approach to the preparation of iron phosphide nanowires. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2010, 5: 786–790
Shi H G, Xue D S. Fabrication and magnetic properties of amorphous Co1−x Px alloy nanowire arrays. Open Nanosci J, 2008, 2: 29–33
Xue D S, Fu J L, Shi H G. Preparation and magnetic properties of Fe0.88−x CoxP0.12 amorphous nanowire arrays. J Magn Magn Mater, 2007, 308: 1–4
Masuda H, Fukuda K. Fabrication of highly ordered structures using anodic porous alumina. Science, 1995, 268: 1466–1468
Chen Z Y, Zhan Q f, Xue D S, et al. Mossbauer study of Fe-Co nanowires. J Phys-Condens Matter, 2002, 14: 613–620
Barandiarán J M, Gorria P, Orúe I, et al. Magnetic and transport properties of Fe-Zr-B-(Cu) amorphous alloys. J Phys-Condens Matter, 1997, 9: 5671–5685
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, J., Zhu, M., Wang, W. et al. Structure and magnetic properties of Fe96−x Zr x B4 nanowire arrays. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56, 1840–1843 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5212-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5212-4