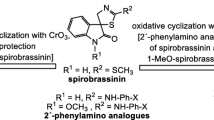
Abstract
The enantioselective synthesis of (S)-(−)-spirobrassinin, which features a unique sulfur-containing spirooxindole skeleton, was achieved by focusing on the phytoalexin generation in Brassicaceae plants. Specifically, (S)-(−)-spirobrassinin was obtained in a one-pot fashion from l-tryptophan through a reaction involving S-spirocyclization with various turnip enzymes and constituents, i.e., using the turnip as a reaction reagent, catalyst, and reaction vessel. Surprisingly, this strategy also enabled the one-pot enantioselective synthesis of the novel non-natural spirooxindole (S)-(−)-5-methylspirobrassinin from 5-methyl-dl-tryptophan.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takasugi M, Monde K, Katsui N, Shirata A (1987) Spirobrassinin, A Novel Sulfur-containing Phytoalexin from the Daikon Raphanus sativus L. var. hortensis (Cruciferae). Chem Lett:1631–1632
Monde K, Osawa S, Harada N, Takasugi M, Suchy M, Kutschy P, Dzurilla M, Balentova E (2000) Synthesis and absolute stereochemistry of cruciferous phytoalexine, (–)-spirobrassinin. Chem Lett:886–887
Suchy M, Kutschy P, Monde K, Goto H, Harada N, Takasugi M, Dzurilla M, Balentová E (2001) Synthesis, absolute configuration, and enantiomeric enrichment of a cruciferous oxindole phytoalexin, (S)-(–)-spirobrassinin, and its oxazoline analog. J Org Chem 66:3940–3947
Ye N, Chen H, Wold EA, Shi PY, Zhou J (2016) Therapeutic potential of spirooxindoles as antiviral agents. ACS Infect Dis 2:382–392
Pilátová M, Šarišský M, Kutschy P, Miroššay A, Mezencev R, Čurillová Z, Suchý M, Monde K, Mirossay L, Mojžiš J (2005) Cruciferous phytoalexins: antiproliferative effects in T-Jurkat leukemic cells. Leuk Res 29:415–421
Mezencev R, Galizzi M, Kutschy P, Docampo R (2009) Trypanosoma cruzi: antiproliferative effect of indole phytoalexins on intracellular amastigotes in vitro. Exp Parasitol 122:66–69
Kristofikova Z, Gazova Z, Siposova K, Bartos A, Ricny J, Kotoucova J, Sirova J, Ripova D (2014) Effects of ferrofluid and phytoalexin spirobrassinin on thioflavin-t-based fluorescence in cerebrospinal fluid of the elderly and multiple sclerosis patients. Neurochem Res 39:1502–1510
Kutschy P, Suchý M, Monde K, Harada N, Marušková R, Čurillová Z, Dzurilla M, Miklošová M, Mezencev R, Mojžiš J (2002) Spirocyclization strategy toward indole phytoalexins. The first synthesis of (±)-1-methoxyspirobrassinin, (±)-1-methoxyspirobrassinol, and (±)-1-methoxyspirobrassinol methyl ether. Tetrahedron Lett 43:9489–9492
Pedras MSC, Suchy M, Ahiahonu PWK (2006) Unprecedented chemical structure and biomimetic synthesis of erucalexin, a phytoalexin from the wild crucifer Erucastrum gallicum. Org Biomol Chem 4:691–701
Zhang Y, Li ZJ, Xu HS, Zhang Y, Wang W (2011) Organic asymmetric henry reaction of isatins: highly enantioselective synthesis of 3-hydroxy-2-oxindoles. RSC Adv 1:389–392
Liu L, Zhang S, Xue F, Lou G, Zhang H, Ma S, Duan W, Wang W (2011) Catalytic enantioselective henry reactions of isatins: application in the concise synthesis of (s)-(–)-spirobrassinin. Chem Eur J 17:7791–7795
Budovská M (2014) A novel palladium-catalyzed catalyzed cyclization of indole phytoalexin brassinin and its 1-substituted derivatives. RSC Adv 4:5575–5582
Zhu G, Bao G, Li Y, Sun W, Li J, Hong L, Wang R (2017) Efficient catalytic kinetic of spiro-epoxyoxindoles with concomitant asymmetric friedel-crafts alkylation of indoles. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:5332–5335
Budovská M, Tischlerová V, Mojžiš J, Harvanová M, Kozlov O, Gondová T, Tomášková N (2017) 2′-Aminoanalogues of the cruciferous phytoalexins spirobrassinin, 1-methoxyspirobrassinin and 1-methoxyspirobrassinol methyl ether: synthesis and anticancer properties. Tetrahedron 73:6356–6371
Monde K, Takasugi M (1991) Biosynthesis of cruciferous phytoalexins: the involvement of a molecular rearrangement in the biosynthesis of brassinin. J Chem Soc Chem Commun:1582–1583
Monde K, Takasugi M, Ohnishi T (1994) Biosynthesis of cruciferous phytoalexins. J Am Chem Soc 116:6650–6657
Pedras MSC, Montaut S (2004) The biosynthesis of crucifer phytoalexins: unprecedented incorporation of a 1-methoxyindolyl precursor. Chem Commun:452–453
Pedras MSC, Okinyo-Owiti DP, Thoms K, Adio AM (2009) The Biosynthetic pathway of crucifer phytoalexins and phytoanticipins: de novo incorporation of deuterated tryptophans and quasi-natural compounds. Phytochemistry 70:1129–1138
Klein AP, Sattely ES (2015) Two cytochromes P450 catalyze S-heterocyclizations in cabbage phytoalexin biosynthesis. Nat Chem Biol 11:837–839
Klein AP, Sattely ES (2017) Biosynthesis of cabbage phytoalexins from indole glucosinolate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:1910–1915
Monde K, Harada N, Takasugi M, Kutschy P, Suchy M, Dzurilla M (2000) Enantiomic excess of a cruciferous phytoalexin, spirobrassinin, and its enantiomeric enrichment in an achiral HPLC system. J Nat Prod 63:1312–1314
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grants 18J22755 (to K. R.), 20K07109 (to S. Nakamura), and 20H03397 (to S. Nakamura).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11418_2020_1468_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Experimental details including the analytical data (1H NMR, 13C NMR) for the new compounds are available free of charge via the internet (pdf 2136 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, K., Nakamura, S., Nakashima, S. et al. One-pot enantioselective synthesis of (S)-spirobrassinin and non-natural (S)-methylspirobrassinin from amino acids using a turnip enzyme. J Nat Med 75, 308–318 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-020-01468-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-020-01468-9