Abstract
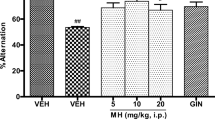
The present study was designed to investigate the role of curcumin in chronic stress and chronic unpredictable stress-induced memory deficits and alteration of functional homeostasis in mice. Chronic stress was induced by immobilizing the animal for 2 h daily for 10 days, whereas chronic unpredictable stress was induced by employing a battery of stressors of variable magnitude and time for 10 days. Curcumin was administered to drug-treated mice prior to induction of stress. Body weight, adrenal gland weight, ulcer index and biochemical levels of glucose, creatine kinase, cholesterol, corticosterone, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and reduced glutathione (GSH) were evaluated to assess stress-induced functional changes. Memory deficits were evaluated using the elevated plus maze (EPM) model. Chronic stress and chronic unpredictable stress significantly increased the levels of corticosterone, glucose and creatine kinase and decreased cholesterol levels. Moreover, chronic stress and chronic unpredictable stress resulted in severe memory deficits along with adrenal hypertrophy, weight loss and gastric ulceration. Chronic stress and chronic unpredictable stress also increased oxidative stress assessed in terms of increase in TBARS and decrease in GSH levels. Pretreatment with curcumin (25 and 50 mg/kg p.o.) attenuated chronic stress and chronic unpredictable stress-associated memory deficits, biochemical alterations, pathological outcomes and oxidative stress. It may be concluded that curcumin-mediated antioxidant actions and decrease in corticosterone secretion are responsible for its adaptogenic and memory restorative actions in chronic and chronic unpredictable stress.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kvetnansky R, Pacak K, Fukuhara K, Viskupic E, Hiremagalur B, Nankova B et al (1995) Sympathoadrenal system in stress. Interaction with the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical system. Ann NY Acad Sci 771:131–158
Venihaki M, Gravanis A, Margioris AN (1997) Comparative study between normal rat chromaffin and PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells: production and effects of Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH). Endocrinology 138:698–704
Roy MP, Kirschbaum C, Steptoe A (2001) Psychological cardiovascular and metabolic correlates of individual differences in cortisol stress recovery in young men. Psychoneuroendocrinology 26:375–391
Yadin E, Thomas E (1993) Stimulation of the lateral septum attenuates immobilization-induced stress ulcers. Physiol Behav 59:883–886
Fitzpatrick F, Christedd N, Durant S, Dardenne M, Nunez EA, HomoDelarche F (1992) Glucocorticoids in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse: basal serum levels, effect of endocrine manipulation and immobilization stress. Life Sci 50:1063–1069
Purret SB (2001) Quantitative aspects of stress-induced immunomodulation. Int Immunol Pharmacol 1:507–520
Rai D, Bhatia G, Sen T, Palit G (2001) Anti-stress effects of Ginkgo biloba and Panax ginseng: a comparative study. J Pharamcol Sci 93:458–464
Rai D, Bhatia G, Palit G, Pal R, Singh S, Singh HK (2003) Adaptogenic effects of Bacopa monniera (Brahmi). Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:823–830
Muruganandam AV, Bhattacharya SK (2003) Adaptogenic activity of Withania somnifera: an experimental study using a rat model of chronic stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:547–555
Ravindran R, Rathinaswamy SD, Samson J, Senthilvelan M (2005) Noise-stress-induced brain neurotransmitter changes and the effect of Ocimum sanctum (Linn) treatment in albino rats. J Pharm Sci 98:354–360
Siripurapu KB, Gupta P, Bhatia G, Maurya R, Nath C, Palit G (2005) Adaptogenic and anti-amnesic properties of Evolvulus alsinoides in rodents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:424–432
Ammon HP, Wahl MA (1991) Pharmacology of Curcuma longa. Planta Med 57:1–7
Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Mandal D, Saha B, Sen GS, Das T et al (2007) Curcumin prevents tumor-induced T-cell apoptosis through Stat-5a-mediated Bcl-2 induction. J Biol Chem 282:15954–15964
Joe B, Lokesh BR (1997) Effect of curcumin and capsaicin on arachidonic acid metabolism and lysosomal enzyme secretion by rat peritoneal macrophages. Lipids 32:1173–1180
Taher MM, Lamering G, Hershey C, Valerie K (2003) Curcumin inhibits ultraviolet light induced human immunodeficiency virus gene expression. Mol Cell Biochem 254:289–297
Pal A, Pal AK (2000) Studies on the genotoxicity of turmeric extracts in bacterial system. Int J Antimicrob Agents 16:415–417
Jurgens TM, Frazier EG, Schaeffer JM, Jones TE, Zink DL, Boris RP et al (1994) Novel nematocidal agents from Curcuma comosa. J Nat Prod 57:230–235
Tirkey N, Kaur G, Vij G, Chopra K (2005) Curcumin, a diferuloylmethane, attenuates cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in rat kidneys. BMC Pharmacol 5:1–10
Kanitkar M, Galande S, Bhonde R (2007) Curcumin prevents streptozotocin-induced islet damage by scavenging free radicals: a prophylactic and protective role. Eur J Pharmacol 577:183–191
Salvioli S, Sikora E, Cooper EL, Franceschi C (2007) Curcumin in cell death processes: a challenge for CAM of age-related pathologies. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 4:181–190
Olalde Rangel JA (2005) The systemic theory of living systems and relevance to CAM. Part I: The theory. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2:13–18
Olalde Rangel JA, Magarici M, Amendola F, del Castillo O (2005) The systemic theory of living systems. Part IV: Systemic medicine—the Praxis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2:429–439
Olalde Rangel JA (2005) The systemic theory of living systems and relevance to CAM: The theory (Part II). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2:129–137
Olalde Rangel JA (2005) The systemic theory of living systems and relevance to CAM: the theory (Part III). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2:267–275
Zheng J, Dobner A, Babygirija R, Ludwig K, Takahashi T (2009) Effects of repeated restraint stress on gastric motility in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R1358–R1365
Xia X, Cheng G, Pan Y, Xia ZH, Kong LD (2007) Behavioral, neurochemical and neuroendocrine effects of the ethanolic extract from Curcuma longa L. in the mouse forced swimming test. J Ethnopharmacol 110:356–363
Kvetnansky R, Mikulai L (1970) Adrenal and urinary catecholamines in rats during adaptation to repeated immobilization stress. Endocrinology 81:738–743
Ortiz J, Fitizgerald LW, Lane S, Terwillinger R, Nestler EJ (1996) Biochemical adaptations in the mesolimbic dopamine system in response to repeated stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 14:443–452
Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T (1990) Utility of an elevated plus maze for the evaluation of memory in mice: effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive shock. Psychopharmacology 101:27–33
Parle M, Singh N (2004) Animal models for testing memory. Asia Pacific J Pharmacol 16:101–120
Trinder P (1969) Estimation of plasma glucose by glucose peroxidase method. Ann Clin Biochem 6:24
Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CSG, Richmond W, Paul CF (1974) Enzymatic determination of total plasma cholesterol. Clin Chem 20:470–474
Swanson JR, Wilkinson JH (1972) Measurements of creatine kinase in serum. Stan Methods Clin Chem 7:33
Katyare SS, Pandya JD (2005) A simplified fluorimetric method for corticosterone estimation in rat serum, tissue and mitochondria. Indian J Biochem Biophys 42:48–50
Satoh K (1978) Serum lipid peroxide in cerebrospinal disorder determined by a new colorimetric method. Clin Chem Acta 90:37–43
Tietze F (1969) Enzymatic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: application to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem 27:502–509
Main IHM, Whittle BJR (1975) Investigation of the vasodilator and antisecretory role of prostaglandins in the rat gastric mucosa by use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Pharmacol 53:217–224
Makara GB, Haller J (2001) Non-genomic effects of glucocorticoids in the neural system: evidence, mechanisms and implications. Prog Neurobiol 65:367–390
Walker C, Perrin M, Vale W, Rivier C (1986) Ontogeny of stress response in the rats: role of pituitary and the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 118:1445–1451
Rivier C, Plotsky PM (1986) Mediation by corticotropin releasing factor of adrenohypophysial hormone secretion. Annu Rev Physiol 48:475–489
Zhang J, Zheng F (1997) The role of paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in stress-ulcer formation in rats. Brain Res 61:203–209
Kim JJ, Diamond DM (2002) The stressed hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:453–462
Eichenbaum H (2000) A cortical-hippocampal system for declarative memory. Nat Rev 1:41–50
Magarinos AM, Verdugo JMG, Mc Evans BS (1997) Chronic stress alters synaptic terminal structures in hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14002–14008
Biondi E (2006) The role of cholesterol in Alzheimer’s neuro-pathogenesis. Riv Biol 99:210–215
Padala KP, Padala PR, Potter JF (2006) Simvastatin-induced decline in cognition. Ann Pharmacother 40:1880–1883
Liu J, Wang X, Mori A (1994) Immobilization stress-induced antioxidant defense changes in rat plasma: effect of treatment with reduced glutathione. Int J Biochem 26:511–517
Liu J, Wang X, Shigenaga MK, Yeo HC, Mori A, Ames BN (1996) Immobilization stress causes oxidative damage to lipid, protein, and DNA in the brain of rats. FASEB J 10:1532–1538
Sapolsky RM, Krey LC, McEwen BS (1986) The neuroendocrinology of stress and aging: the glucocorticoid cascade hypothesis. Endocr Rev 7:284–301
Olivenza R, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, Lorenzo P, Fernandez AP, Rodrigo J et al (2000) Chronic stress induces the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat brain cortex. J Neurochem 74:785–791
Liu J, Mori A (1999) Stress, aging and brain oxidative damage. Neurochem Res 24:1479–1497
Biswas SK, McClure D, Jimenez LA, Megson IL, Rehman I (2005) Curcumin induces glutathione biosynthesis and inhibits NF-kappa B activation and interleukin-8 release in alveolar epithelial cells: mechanism of free radical scavenging activity. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:32–41
Kelly GS (1999) Nutritional and botanical interventions to assist with the adaptation to stress. Altern Med Rev 4:249–265
Akpinar D, Yargicoglu P, Derin N, Aliciguzel Y, Agar A (2007) The effect of lipoic acid on antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in rats exposed to chronic restraint stress. Physiol Res 56:163–171
Al-Ayadhi LY, Korish AA, Al-Tuwaijri AS (2006) The effect of vitamin E, l-arginine, N-nitro l-arginine methyl ester and forskolin on endocrine and metabolic changes of rats exposed to acute cold stress. Saudi Med J 27:17–22
Dhanalakshmi S, Devi RS, Srikumar R, Manikandan S, Thangaraj R (2007) Protective effect of Triphala on cold stress-induced behavioral and biochemical abnormalities in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi 127:1863–1867
Ataie A, Sabetkasaei M, Haghparast A, Moghaddam AH, Kazeminejad B (2010) Neuroprotective effects of the polyphenolic antioxidant agent, Curcumin, against homocysteine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:378–385
Ahmed T, Enam SA, Gilani AH (2010) Curcuminoids enhance memory in an amyloid-infused rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 169:1296–1306
Xu Y, Lin D, Li S, Li G, Shyamala SG, Barish PA, Vernon MM, Pan J, Ogle WO (2009) Curcumin reverses impaired cognition and neuronal plasticity induced by chronic stress. Neuropharmacology 57:463–471
Li YC, Wang FM, Pan Y, Qiang LQ, Cheng G, Zhang WY, Kong LD (2009) Antidepressant-like effects of curcumin on serotonergic receptor-coupled AC-cAMP pathway in chronic unpredictable mild stress of rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:435–449
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research, Punjabi University, Patiala, India, for supporting this study and providing technical facilities for the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, N., Jaggi, A.S., Singh, N. et al. Adaptogenic potential of curcumin in experimental chronic stress and chronic unpredictable stress-induced memory deficits and alterations in functional homeostasis. J Nat Med 65, 532–543 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0535-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0535-9