Abstract
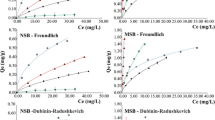
Rice and coffee husks (raw and chemically activated) are examined as potential biosorption materials regarding their capacity to remove U (total), 241Am, and 137Cs. The physical parameters evaluated were the morphological characteristics of the biomass, real and apparent density, and surface area. Contact times for the batch experiments were 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 h, and the concentrations tested ranged between 10% of the total concentration and the radioactive waste itself without any dilution. The results were evaluated by experimental sorption capacity, ternary isotherm, and kinetics models. The kinetics results showed that equilibrium was reached after 2 h for all biomass. Raw coffee husk showed the best adsorption results in terms of maximum capacity (qmax) for all three radionuclides, which were 1.96, 39.4 × 10−6, and 46.6 × 10−9 mg g−1 for U, Am, and Cs, respectively. The biosorption process for the raw and activated rice husks was best represented by the Langmuir ternary isotherm model with two sites. For the coffee husk, in the raw and activated states, the biosorption process was best described by the modified Jain and Snoeyink ternary model. These results suggest that biosorption with these biomaterials can be applied in the treatment of liquid organic radioactive waste containing mainly uranium and americium.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmal M, Ali Khan Rao R, Anwar S, Ahmad J, Ahmad R (2003) Adsorption studies on rice husk: removal and recovery of Cd(II) from wastewater. Bioresour Technol 86:147–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00159-1
Alhogbi BG (2017) Potential of coffee husk biomass waste for the adsorption of Pb(II) ion from aqueous solutions. Sustain Chem Pharm 6:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2017.06.004
Almeandros AI, Martín-Lara MA, Ronda A, Pérez A, Blásquez G, Calero M (2015) Physico-chemical characterization of pine cone shell and its use as biosorbent and fuel. Bioresour Technol 196:406–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.109
Bağda E, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2017) Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic investigations for biosorption of uranium with green algae (Cladophora hutchinsiae). J Environ Radioact 175–176:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.04.004
Bai J, Yao H, Fan F, Lin M, Zhang L, Ding H, Lei F, Wu X, Li X, Guo J, Qin Z (2010) Biosorption of uranium by chemically modified Rhodotorula glutinis. J Environ Radioact 101:969–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVRAD.2010.07.003
Cardoso SL, Costa CSD, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2018) Dealginated seaweed waste for Zn(II) continuous removal from aqueous solution on fixed-bed column. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:1183–1189. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5479
Chakraborty D, Maji S, Bandyopadhyay A, Basu S (2007) Biosorption of cesium-137 and strontium-90 by mucilaginous seeds of Ocimum basilicum. Bioresour Technol 98:2949–2952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.035
Dhami PS, Kannan R, Naik PW, et al (2002) Biosorption of americium using biomasses of various Rhizopus species. 885–889
Febrianto J, Kosasih AN, Sunarso J, Ju YH, Indraswati N, Ismadji S (2009) Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: a summary of recent studies. J Hazard Mater 162:616–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.042
Ferreira RVP, Dutra F, Bellini MH et al (2012) Treatment of radioactive liquid organic waste using bacteria community. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291:811–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1564-2
Ferreira RVP, Silva EA, Canevesi RLS, Ferreira EGA, Taddei MHT, Palmieri MC, Silva FRO, Marumo JT (2018) Application of the coconut fiber in radioactive liquid waste treatment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:1629–1640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1541-6
Katz J, Seaborg GT, Morss LR (1987) The chemistry of the actinide elements. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht
Korotkova TG, Ksandopulo SJ, Donenko AP, et al (2016) Physical properties and chemical composition of the rice husk and dust. Orient J Chem 32:3213–3219. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/320644
Krestou A, Xenidis A, Panias D (2003) Mechanism of aqueous uranium (VI) uptake by natural zeolitic tuff. Miner Eng 16:1363–1370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2003.08.012
Krishnani KK, Meng X, Boddu VM (2008) Fixation of heavy metals onto lignocellulosic sorbent prepared from paddy straw. Water Environ Res 80:2165–2174. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143008X304785
Kumar U, Bandyopadhyay M (2006) Sorption of cadmium from aqueous solution using pretreated rice husk. Bioresour Technol 97:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.027
Lee K-Y, Lee S-H, Lee JE, Lee S-Y (2019) Biosorption of radioactive cesium from contaminated water by microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis and Chlorella vulgaris. J Environ Manag 233:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.022
Li Y, Liu F, Xia B, du Q, Zhang P, Wang D, Wang Z, Xia Y (2010) Removal of copper from aqueous solution by carbon nanotube/calcium alginate composites. J Hazard Mater 177:876–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.114
Liao J, Yang Y, Luo S, Liu N, Jin J, Zhang T, Zhao P (2004) Biosorption of americium-241 by immobilized Rhizopus arrihizus. Appl Radiat Isot 60:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APRADISO.2003.10.001
Liu N, Luo S, Yang Y, Zhang T, Jin J, Liao J (2002) Biosorption of americium-241 by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 252:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015276813386
Lu X, Zhou X-j, Wang T-s (2013) Mechanism of uranium(VI) uptake by Saccharomyces cerevisiae under environmentally relevant conditions: batch, HRTEM, and FTIR studies. J Hazard Mater 262:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.051
Luo BS, Liu N, Yang Y, et al (2003) Biosorption of americium-241 by Candida sp . 318:315–318
Ma Y, Lin J, Zhang C, Ren Y, Lin J (2011) Cd(II) and As(III) bioaccumulation by recombinant Escherichia coli expressing oligomeric human metallothioneins. J Hazard Mater 185:1605–1608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.051
Mishra SP, Prasad SK, Dubey RS, Mishra M, Tiwari D, Lee SM (2007) Biosorptive behaviour of rice hulls for Cs-134 from aqueous solutions: a radiotracer study. Appl Radiat Isot 65:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2006.09.007
Mohan D, Singh KP (2002) Single- and multi-component adsorption of cadmium and zinc using activated carbon derived from bagasse-an agricultural waste. Water Res 36:2304–2318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00447-X
Oliveira LS, Franca AS, Alves TM, Rocha SDF (2008a) Evaluation of untreated coffee husks as potential biosorbents for treatment of dye contaminated waters. J Hazard Mater 155:507–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.093
Oliveira WE, Franca AS, Oliveira LS, Rocha SD (2008b) Untreated coffee husks as biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 152:1073–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.085
Pang C, Liu Y-H, Cao X-H, Li M, Huang GL, Hua R, Wang CX, Liu YT, An XF (2011) Biosorption of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution by dead fungal biomass of Penicillium citrinum. Chem Eng J 170:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2010.10.068
Raoul TTD, Gabche AS, Mbadcam KJ et al (2014) Kinetics and equilibrium studies of adsorption of phenol in aqueous solution onto activated carbon prepared from rice and coffee husks. Int J Eng Tech Res 2:166–173
Rocha CG, Zaia DAM, da Silva Alfaya RV, da Silva Alfaya AA (2009) Use of rice straw as biosorbent for removal of Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) ions in industrial effluents. J Hazard Mater 166:383–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.074
Saini AS, Melo JS (2015) Biosorption of uranium by human black hair. J Environ Radioact 142:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVRAD.2015.01.006
Shehee TC, Elvington MC, Rudisill TS, Hobbs DT (2012) Separation of actinides and fission products using titanium-based materials. Solvent Extr Ion Exch 30:669–682. https://doi.org/10.1080/07366299.2011.639262
Ting YP, Lawson F, Prince IG (1991) Uptake of cadmium and zinc by the alga Chlorella vulgaris: II. Multi-ion situation BiotechnolBioeng 37:445–455
Tripathi SC, Kannan R, Dhami PS, Naik PW, Munshi SK, Dey PK, Salvi NA, Chattopadhyay S (2011) Modified Rhizopus arrhizus biomass for sorption of 241Am and other radionuclides. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287:691–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0949-y
Vieira LC, de Araujo LG, Ferreira RVP et al (2019) Uranium biosorption by Lemna sp. and Pistia stratiotes. J Environ Radioact 203:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2019.03.019
Volesky B (2003) Biosorption process simulation tools. Hydrometallurgy 71:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(03)00155-5
Wan Ngah WS, Hanafiah MAKM (2008) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: a review. Bioresour Technol 99:3935–3948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.011
Wang J-s, Hu X-j, Wang J et al (2010) The tolerance of Rhizopus arrihizus to U(VI) and biosorption behavior of U(VI) onto R. arrihizus. Biochem Eng J 51:19–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2010.04.010
Wang F, Tan L, Liu Q, Li R, Li Z, Zhang H, Hu S, Liu L, Wang J (2015) Biosorption characteristics of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution by pollen pini. J Environ Radioact 150:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVRAD.2015.07.002
Wang Y, Nie X, Cheng W et al (2019) A synergistic biosorption and biomineralization strategy for Kocuria sp. to immobilizing U(VI) from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 275:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2018.11.079
Wei Y, Chen Z, Song H, et al (2019) The immobilization mechanism of U(VI) induced by Bacillus thuringiensis 016 and the effects of coexisting ions. Biochem Eng J 144:57–63. S1369703X19300130
Yi Z-j, Yao J, Chen H-l et al (2016a) Uranium biosorption from aqueous solution onto Eichhornia crassipes. J Environ Radioact 154:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.01.012
Yi Z, Yao J, Kuang Y, Chen HL, Wang F, Xu JS (2016b) Uptake of hexavalent uranium from aqueous solutions using coconut husk activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat 3994:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.977956
Zheng XY, Shen YH, Wang XY, Wang TS (2018) Effect of pH on uranium(VI) biosorption and biomineralization by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chemosphere 203:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2018.03.165
Acknowledgements
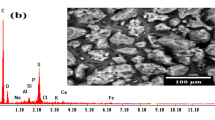
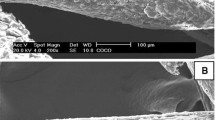
We are thankful to Dr. Flavia R.O. Silva and the Laboratório de Microscopia e Microanálise (LMM/IPEN) for the SEM/EDS analyses.
Funding
This research was supported by the Nuclear and Energy Research Institute, the Brazilian National Nuclear Energy Commission, and the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 728 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, R.V., de Araujo, L.G., Canevesi, R.L.S. et al. The use of rice and coffee husks for biosorption of U (total), 241Am, and 137Cs in radioactive liquid organic waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 36651–36663 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09727-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09727-8