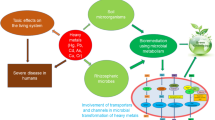
Abstract
Fluoride (F), anion of fluorine which is naturally present in soil and water, behaves as toxic inorganic pollutant even at lower concentration and needs immediate attention. Its interaction with flora, fauna and other forms of life, such as microbes, adversely affect various physiochemical parameters by interfering with several metabolic pathways. Conventional methods of F remediation are time-consuming, laborious and cost intensive, which renders them uneconomical for sustainable agriculture. The solution lies in cracking down this environmental contaminant by adopting economic, eco-friendly, cost-effective and modern technologies. Biological processes, viz. bioremediation involving the use of bacteria, fungi, algae and higher plants that holds promising alternative to manage F pollution, recover contaminated soil and improve vegetation. The efficiency of indigenous natural agents may be enhanced, improved and selected over the hazardous chemicals in sustainable agriculture. This review article emphasizes on various biological approaches for the remediation of F-contaminated environment, and exploring their potential applications in environmental clean-up. It further focuses on thorough systemic study of modern biotechnological approaches such as gene editing and gene manipulation techniques for enhancing the plant-microbe interactions for F degradation, drawing attention towards latest progresses in the field of microbial assisted treatment of F-contaminated ecosystems. Future research and understanding of the molecular mechanisms of F bioremediation would add on to the possibilities of the application of more competent strains showing striking results under diverse ecological conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah FB, Elloumi N, Mezghani I, Garrec JP, Boukhris M (2006) Industrial fluoride pollution of Jerbi grape leaves and the distribution of F, Ca, mg and P in them. Fluoride 39:43–48
Ali S, Thakur SK, Sarkar A, Shekhar S (2016) Worldwide contamination of water by fluoride. Environ Chem Lett 14:291–315
Amin F, Talpur FN, Baloucha A, Surhioa MA, Bhutto MA (2015) Biosorption of fluoride from aqueous solution by white-rot fungus Pleurotus eryngii ATCC 90888. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 3:30–37
Arlappa N, Qureshi A, Srinivas R (2013) Fluorosis in India: an overview. Int J Res Dev Health 1:97–102
Baker AJM, McGrath SP, Reeves RD, Smith JAC (2000) Metal hyper accumulator plants: a review of the ecology and physiology of a biological resource for phytoremediation of metal-polluted soils. Phytorem Contaminated Soil Water:85–107
Baker JL, Sudarsan N, Weinberg Z, Roth A, Stockbridge RB, Breaker RR (2012) Widespread genetic switches and toxicity resistance proteins for fluoride. Science 335:233–235
Banerjee G, Sengupta A, Roy T, Banerjee PP, Chattopadhyay A, Raya AK (2016) Isolation and characterization of fluoride resistant bacterial strains from fluoride endemic areas of West Bengal: assessment of their fluoride absorption efficiency. Fluoride 49:414–425
Barbier O, Arreola-Mendoza L, Del Razo LM (2010) Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chem Biodivers 188:319–333
Baunthiyal M, Ranghar S (2013) Accumulation of fluoride by plants: potential for phytoremediation. Clean Soil Air Water 43:127–132
Baunthiyal M, Sharma V (2012) Phytoremediation of fluoride contaminated water and soil: a search for fluoride hyperaccumulators. J Agri Tech 8:1965–1978
Bazrafshan E, Balarak D, Panahi AH, Kamani H, Mahvi AH (2016) Fluoride removal from aqueous solutions by cupricoxide nanoparticles. Fluoride 49:233–244
Bhatnagar M, Bhatnagar A (2000) Algal and cyanobacterial responses to fluoride. Fluoride 33:55–65
Biswas G, Thakurta SG, Chakrabarty J, Adhikari K, Dutta S (2018) Evaluation of fluoride bioremediation and production of biomolecules by living cyanobacteria under fluoride stress condition. Ecotox Environ Saf 148:26–36
Breaker RR (2012) New insight on the response of bacteria to fluoride. Caries Res 46:78–81
Cardoso PF, Priscila LG, Rui AG, Leonardo OM, Ricardo AA (2005) Response of Crotalaria juncea to nickel exposure. J Plant Physiol 17:267–272
Cecchi G, Vagge G, Cutroneo L, Greco G, Di Piazza S (2019) Fungi as potential tool for polluted port sediment remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:35602–35609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04844-5
Chaudhary K, Khan S (2016) Physiochemical characterization of fluoride contaminated soil and its microbe-assisted bioremediation by Prosopis juliflora. J Plant Biol Soil Health 3:8
Cho S, Luong TT, Lee D, Lee T (2011) Reuse of effluent water from a municipal wastewater treatment plant in microalgae cultivation for biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 102:8639–8645
Choubisa SL, Sompura K (1996) Dental fluorosis in tribal villages of Dungarpur district (Rajasthan). Pollut Res 15:45–47
Chouhan S, Lomash V, Flora SJS (2009) Fluoride-induced changes in haem biosynthesis pathway, neurological variables and tissue histopathology of rats. Appl Toxicol 30:63–73
Chouhan S, Tuteja U, Flora SJS (2012) Isolation, identification and characterization of fluoride resistant bacteria: possible role in bioremediation. J App Biochem Microbiol 48:43–50
Christina E, Viswanathan P (2015) Development of a novel nano-biosorbent for the removal of fluoride from water. J Chem Eng 23:924–933
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clément C, Barka EA (2005) Use of plant growth promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4951–4959
Cooke JA, Johnson MS, Davidson AW, Bradshaw AD (1976) Fluoride in plants colonising fluorspar mine waste in the peak district and Weardale. Environ Pollut 11:10–13
Davis RD (1980) Uptake of fluoride by rye-grass in soil treated with sewage sludge. Environ Pollut 1:277–284
Deshmukh R, Sonah H, Patil G, Chen W, Prince S, Mutava R, Vuong T, Valliyodan B, Nguyen HT (2014) Integrating omic approaches for abiotic stress tolerance in soybean. Front Plant Sci 5:244
Deverapalli P, Kumawath RN (2015) Metagenomics- a technological drift in bioremediation. In: Shiomi N (ed) advances in bioremediation of wastewater and polluted soil. InTech, Europe. https://doi.org/10.5772/60749
Dixit R, Wasiullah MD, Pandiyan K, Singh UB, Sahu A, Shukla R, Singh BP, Rai JP, Sharma PK, Lade H, Paul D (2015) Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environmental: an overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustain 7:2189–2212
Doble M, Kumar A (2005) Biotreatment of industrial effluents. Elsevier, Butterworth-Heinemann
Elloumi N, Abdallah FB, Mezghani I, Rhouma A, Boukhris M (2005) Effect of fluoride on almond seedlings in culture solution. Fluoride 38:193–198
Ericsson Y (1970) Fluorides and human health. Lancet 2:351–352
Gadd GM (2010) Metals: minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiol 156:609–643
Gamalero E, Glick BR (2011) Mechanisms used by plant growth-promoting Bacteria. In: Maheshwari D (ed) Bacteria in agrobiology: plant nutrient management. Springer, Berlin
Gentil FG, Fick J (2016) Algal cultivation in urban wastewater: an efficient way to reduce pharmaceutical pollutants. J Appl Phycol29:255–262
Ghormade V, Deshpande MV, Paknikar KM (2011) Perspectives for nano-biotechnology enabled protection and nutrition of plants. Biotechnol Adv 29:792–803
Ghosh A, Mukherjee K, Ghosh SK (2013) Sources and toxicity of fluoride in environment. Res Chem Intermed 39:2881–2915
Glick BR (2012) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica:1–15
Gouda S, Kerry RG, Das G, Paramithiotis S, Shin HS, Patra JK (2018) Revitalization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for sustainable development in agriculture. Microbiol Res 206:131–140
Halder GN, Sinha S, Dhawane S (2015) Defluoridation of wastewater using powdered activated carbon developed from Eichhornia crassipes stem: optimization by response surface methodology. Desal Water Treat 56:953–966
Hamilton IR (1990) Biochemical effects of fluoride on oral bacteria. J Dent Res 69:660–667
He LF, Chen JG (2006) DNA damage, apoptosis and cell cycle changes induced by fluoride in rat oral mucosal cells and hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 1:144–1148
Hussein H, Moawad H, Farag S (2004) Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas resistant to heavy metals contaminants. Arab Biotech 7:13–22
Islam MS, Ueno Y, Sikder MT, Kurasaki M (2013) Phytofiltration of arsenic and cadmium from the water environment using Micranthemum umbrosum (GMEL) blake as a hyperaccumulator. Int J Phytoremed 15:1010–1021
Jayarathne A, Weerasooriya R, Chandrajith R (2014) A rapid method for the removal of fluoride in contaminated groundwater using natural crystalline apatite: a laboratory and field study. Environ Earth
Juwarkar A, Yadav S (2010) Bioaccumulation and biotransformation of heavy metals. Biorem Technol 9:266–284
Kamran MA, Amna MR, Mubariz N, Syed JH, Bano A, Javed MT, Munis MFH, Tan Z, Chaudhary HJ (2014) The potential of the flora from different regions of Pakistan in phytoremediation: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:801–812
Khan N, Bano A (2018) Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and Ag-nano particle in the bioremediation of heavy metals and maize growth under municipal wastewater irrigation. Int J Phytorem 18:211–221
Khan S, Hesham AEL, Qiao M, Rehman S, He JZ (2010) Effects of cd and Pb on soil microbial community structure and activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:288–296
Khandare AL, Rao GS (2006) Uptake of fluoride, aluminium and molybdenum by some vegetables from irrigation water. J Hum Ecol 19:283–288
Khandare RV, Desai SKB, Bhujbal SS, Watharkar AD, Biradar SP, Pawar PK, Govindwar SP (2017) Phytoremediation of fluoride with garden ornamentals Nerium oleander, Portulaca oleracea, and Pogonatherum crinitum. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6833–6839
Kotrba P, Najmanova J, Macek T, Ruml T, Mackova M (2009) Genetically modified plants in phytoremediation of heavy metal and metalloid soil and sediment pollution. Biotechnol Adv 27:799–810
Kumar V, Talreja N, Deva D, Sankararamakrishnan N, Sharma A, Verma N (2011) Development of bi-metal doped micro- and nano multi-functional polymeric adsorbents for the removal of fluoride and arsenic (V) from wastewater. Desalination 282:27–38
Levy LW, Strauss RL (1973) Sur L' insolubilisation de L' Ion fluor a L' etat- de fluorure de calcium chez Chara fragilis. Desvaux CR. Acad Sci 277:181–184
Liao Y, Brandt BW, Zhang M (2016) A single nucleotide change in the promoter mutp enhances fluoride resistance of Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:7509–7512
Liao Y, Brandt BW, Li J, Crielaard W, Loveren CV, Deng DM (2017) Fluoride resistance in Streptococcus mutans: a mini review. J Oral Microbiol 9:1344509
Lippmann B, Leinhos V, Bergmann H (1995) Influence of auxin producing rhizobacteria on root morphology and nutrient accumulation of crops, pt. 2: changes in root morphology and nutrient accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) caused by inoculation with indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) producing Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter strains or IAA applied exogenously. Angew Bot 69:31–36
Lorestani B, Cheraghi M, Yousefi N (2011) Phytoremediation potential of native plants growing on a heavy metals contaminated soil of copper mine in Iran. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 77:377–382
Luo S, Xu T, Chen L, Chen J, Rao C, Xiao X, Wan Y, Zeng G, Long F, Liu C, Liu Y (2012) Endophyte-assisted promotion of biomass production and metal-uptake of energy crop sweet sorghum by plant-growth-promoting endophyte Bacillus sp. SLS18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1745–1753
Ma X, Wang C (2010) Fullerene nanoparticle affect the fate and uptake of trichloroethylene in phytoremediation systems. Environ Eng Sci 27:989–992
Mahapatra DM, Chanakya HN, Ramachandra TV (2014) Bioremediation and lipid synthesis through mixotrophic algal consortia in municipal wastewater. Bioresour Technol 168:142–150
Martin BC, George SJ, Price CA, Ryan MH, Tibbett M (2014) The role of root exuded low molecular weight organic anions in facilitating petroleum hydrocarbon degradation: current knowledge and future directions. Sci Total Environ 472:642–653
Men X, Shibata Y, Takeshita T (2016) Identification of anion channels responsible for fluoride resistance in oral Streptococci. PLoS One 11:0165900
Messaitfa A (2008) Fluoride contents in ground waters and the main consumed foods (dates and tea) in southern Algeria region. Environ Geol 55:377–383
Mohan SV, Ramanaiah SV, Rajkumar B, Sarma PN (2007) Removal of fluoride from aqueous phase by biosorption onto algal biosorbent Spirogyra sp.-IO2: sorption mechanism elucidation. J Hazard Mater 141:465–474
Mosa KA, Saadoun I, Kumar K, Helmy M, Dhankher OP (2016) Potential biotechnological strategies for the cleanup of heavy metals and metalloids. Front Plant Sci 7:303
Mukherjee S, Halder G (2016) Assessment of fluoride uptake performance of raw biomass and activated biochar of Colocasia esculenta stem: optimization through response surface methodology. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 35:1305–1316
Mukherjee S, Yadav V, Mondal M, Banerjee S, Halder G (2015) Characterization of fluoride-resistant bacterium Acinetobacter sp. RH5 towards assessment of its water defluoridation capability. Appl Water Sci 7:1923–1930
Mukherjee S, Sahu P, Halder G (2017) Microbial remediation of fluoride-contaminated water via a novel bacterium Providencia vermicola (KX926492). J Env Manage 204:413–423
Mukherjee S, Sahu P, Halder G (2018) Comparative assessment of the fluoride removal capability of immobilized and dead cells of Staphylococcus lentus (KX941098) isolated from contaminated groundwater. Env Progress Sustainable Energy 37:5
Murata T, Hanada N (2016) Contribution of chloride channel permease to fluoride resistance in Streptococcus mutans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 363:101
Ojuederie OB, Babalola OO (2017) Microbial and plant-assisted bioremediation of heavy metal polluted environments: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:1504
Ouzounidou G, Moustakas M, Symeonidis L, Karataglis S (2006) Response of wheat seedlings to Ni stress: effects of supplemental calcium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:346–352
Pal KC, Mondal NK, Chatterjee S, Ghosh TS, Datta JK (2014) Characterization of fluoride-tolerant halophilic Bacillus flexus NM25 (HQ875778) isolated from fluoride-affected soil in Birbhum District, West Bengal, India. Environ Monit Assess 186:699–709
Patil SB, Jagdale AD, Patil DB, Kulkarni AS, Govindwar SP (2014) Evaluation of fluoride uptake and accumulation by Portulaca grandiflora hook. And Brassica oleracea Linn.From water. Int J Science Eng Tech Res 3:3474–3477
Paul E (2007) Soil microbiology, ecology, and biochemistry (3rd E). Vadose Zone J 8:1087–1088
Petzold CJ, Chan LJ, Nhan M, Adams PD (2015) Analytics for metabolic engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 3:135
Pollard AJ, Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2014) Facultative hyperaccumulation of heavy metals and metalloids. Plant Sci 218:8–17
Poulsen R (2011) The effect of fluoride pollution on soil microorganisms. Bachelor thesis Faculty of Physical Sciences University of Iceland 42
Prajapat R, Bhatnagar A, Gaur KR, Bajpai V (2010) Fluoride removal from water by sorbing on plant and fungal biomass. Int J Biotechnol 1:43–46
Rabara RC, Tripathi P, Rushton PJ (2017) Comparative metabolome profile between tobacco and soybean grown under water-stressed conditions. Biomed Res Int 3065251:18
Rajkumar M, Sandhya S, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2012) Perspectives of plant associated microbes in heavy metal phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 30:1562–1574
Ramachandra TV, Mahapatra DM, Samantray S, Joshi NV (2013) Biofuel from urban wastewater: scope and challenges. Renew Sust Energ Rev 21:767–777
Ramanaiah SV, Mohan SV, Sarma PN (2007) Adsorptive removal of fluoride from aqueous phase using waste fungus (Pleurotus ostreatus 1804) biosorbent: kinetics evaluation. Ecol Eng 31:47–56
Rangel NC, Velázquez ANR, Díaz MSS (2015) Fluoride bioaccumulation by hydroponic cultures of camellia (Camellia japonica spp.) and sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum spp.) chemosphere. 136:56–62
Rose D, Marier JR (1977) National Research Council of Canada, Associate Committee on Scientific Criteria for Environmental Quality NRCC No. J Environ Fluoride:16081
Saini P, Khan S, Baunthiyal M, Sharma V (2012) Organ-wise accumulation of fluoride in Prosopis juliflora and its potential for phytoremediation of fluoride contaminated soil. Chemosphere 89:633–635
Sajid M, Nadeem A, Zahir M, Naveed M, Arshad M, Shahzad SM (2006) Variation in growth and ion uptake of maize due to inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria under salt stress. Soil & Environ 25:78–84
Santos-Díaz MS, Zamora-Pedrazaa C (2010) Fluoride removal from water by plant species that are tolerant and highly tolerant to hydrogen fluoride. Fluoride 43:150–156
Sarkar M, Banerjee A, Pramanick PP, Sarkar AR (2006) Use of laterite for the removal of fluoride from contaminated drinking water. J Colloid Interface Sci 302:432–441
Sehn P (2008) Fluoride removal with extra low energy reverse osmosis membranes: three years of large scale field experience in Finland. Desalination 223:73–84
Sheng X, Jiang C, He L (2008) Characterization of plant growth–promoting Bacillus edaphicus NBT and its effect on lead uptake by Indian mustard in a lead–amended soil. J Microbiol 54:417–422
Shivarajashankara YM, Shivashankara AR, Bhat PG, Rao SH (2002) Brain lipid peroxidation and antioxidant systems of young rats in chronic fluoride intoxication. Fluoride 35:197–203
Singh M, Verma KK (2013) Influence of fluoride-contaminated irrigation water on physiological responses of poplar seedlings (Populus deltoides L. clone-S7C15). Fluoride 46:83–89
Singh S, Singh J, Singh N (2013) Studies on the impact of fluoride toxicity on growth parameters of Raphanus sativus L. Indian J Sci Res 4:61–63
Stanic MH, Ravancic ME, Flanagan A (2014) A review on adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. Materials 7:6317–6366
Stevens DP (1996) Uptake of fluoride by plant roots. Thesis PhD. Dept of soil science. Uni Adelaide Australia
Stevens DP, McLaughlin MJ, Randall PJ, Keerthisinghe G (2000) Effects of fluoride supply on fluoride concentrations in five pasture species: levels required to reach phytotoxic or potentially zootoxic concentrations in plant tissue. Plant Soil 227:223–233
Tang SCN, Lo IMC (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles: essential factors for sustainable environmental applications. Water Res 47:2613–2632
Thijs S, Sillen W, Rineau F, Weyens N, Vangronsveld J (2016) Towards an enhanced understanding of plant–microbiome interactions to improve phytoremediation: engineering the metaorganism. Front Microbiol:7
Timmusk S, Seisenbaeva G, Behers L (2018) Titania (TiO2) nanoparticles enhance the performance of growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Sci Rep:8
Tscherko D, Kandeler E (1997) Ecotoxicological effects of fluorine deposits on microbial biomass and enzyme activities in grasslands. Eur J Soil Sci 48:329–335
Ullah A, Mushtaq H, Ali H, Munis MFH, Javed MT, Chaudhary HJ (2015) Diazotrophs-assisted phytoremediation of heavy metals: a novel approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2505–2514
van Loveren C, Hoogenkamp MA, Deng DM (2008) Effects of different kinds of fluorides on enolase and ATPase activity of a fluoride-sensitive and fluoride resistant Streptococcus mutans strain. Caries Res 42:429–434
Wang J, Zhao FJ, Meharg AA, Raab A, Feldmann J, McGrath SP (2002) Mechanisms of arsenic hyperaccumulation in Pteris vittata: uptake kinetics, interactions with phosphate, and arsenic speciation. Plant Physiol 130:1552–1561
World Health Organisation (2008) Chemical fact sheets: fluoride, guidelines for drinking water quality (electronic resource), 3rd ed. Incorporation first addendum, vol 1. WHO, Geneva, pp 375–377
Zhang WX (2003) Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J Nanopart Res 5:323–332
Zhang M, Wang A, Xia T, He P (2008) Effects of fluoride on DNA damage, S-phase cell-cycle arrest and the expression of NF-kappaB in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Toxicol Lett 179:1–5
Funding
The authors would like to thank University Grants Commission, New Delhi, and Scientific and Engineering Research Board, New Delhi, for awarding fellowships to Priya Katiyar and Neha Pandey, respectively. Authors are also grateful to Department of Science & Technology, New Delhi, for financial support through DST-FIST scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katiyar, P., Pandey, N. & Sahu, K.K. Biological approaches of fluoride remediation: potential for environmental clean-up. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 13044–13055 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08224-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08224-2