Abstract
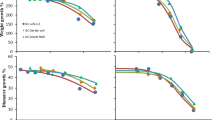
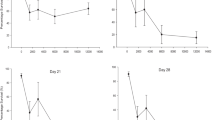
Major concerns exist regarding the environmental and human health risks caused by exposure to heavy metals. Spiders are often used as a model in ecotoxicological studies to assess soil pollution. Here, we measured the bioaccumulation of copper (Cu) and lead (Pb) in spiders, Lycosa terrestris and Pardosa birmanica, by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). We investigated whether Cu and Pb accumulation differs according to different spider species, single versus combined metal exposure, and routes of exposure. Spiders were exposed to 10 mM CuSO4 and 10 mM PbCl2 solutions separately or in combination (10 mM + 10 mM) through different exposure routes (spiked soil and food) for 6 weeks. The effect of metals on the survival and body mass of exposed and unexposed (control) spiders was determined. We found that in both spider species, accumulation of metals increased with exposure time. In single metal exposure, Cu accumulation from food was higher than soil exposure in both spider species, whereas the opposite was observed for Pb. The simultaneous uptake of Cu and Pb significantly decreased from food and soil, respectively. Soil exposure caused more accumulation of metals in L. terrestris than P. birmanica. Metal exposure via contaminated food caused higher mortality compared to soil exposure. Body mass of both spider species was significantly decreased and negatively correlated with metal’s concentration. Overall, our results show that bioaccumulation efficiency of Cu and Pb differs significantly in spiders exposed to metal’s mixture compared to single metal exposure and is dependent on the exposure route, the type of metal, and spider species. More understanding of the effects of exposure to metal mixture and exposure routes is essential for designing and supporting risk assessment and ecological monitoring programs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad K, Ashfaq A, Khan ZI, Bashir H, Sohail M, Mehmood N, Dogan Y (2018) Metal accumulation in Raphanus sativus and Brassica rapa: an assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:16676–16685
Amalin DM, Pena JE, Reiskind J, McSorley R (2001) Comparison of the survival of three species of sac spiders on natural and artificial diets. J Arachnol 29:253–262
Babczynska A, Wilczek G, Szulinska E, Franiel I (2011a) Quantitative immunodetection of metallothioneins in relation to metals concentration in spiders from variously polluted areas. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1498–1503
Babczynska A, Wilczek G, Wilczek P, Szulinska E, Witas I (2011b) Metallothioneins and energy budget indices in cadmium and copper exposed spiders Agelena labyrinthica in relation to their developmental stage, gender and origin. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 154:161–171
Bednarek A, Sawadro M, Babczynska A (2016) Modulation of the response to stress factors of Xerolycosa nemoralis (Lycosidae) spiders living in contaminated environments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 131:1–6
Bednarska AJ, Opyd M, Zurawicz E, Laskowski R (2015) Regulation of body metal concentrations: toxicokinetics of cadmium and zinc in crickets. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:9–14
Chen H, Mu L, Cao J, Mu J, Klerks PL, Luo Y, Guo Z, Xie L (2016) Accumulation and effects of Cr (VI) in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) during chronic dissolved and dietary exposures. Aquat Toxicol 176:208–216
Chen XQ, Zhang ZT, Liu R, Zhang XL, Chen J, Peng Y (2011) Effects of the metals lead and zinc on the growth, development, and reproduction of Pardosa astrigera (Araneae: Lycosidae). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:203–207
Chiroma TM, Abdulkarim BI, Kefas HM (2007) The impact of pesticide application on heavy metal (cd, Pb and cu) levels in spinach. Leonardo El J Pract Technol 11:117–122
Cooper NL, Bidwell JR, Kumar A (2009) Toxicity of copper, lead, and zinc mixtures to Ceriodaphnia dubia and Daphnia carinata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1523–1528
Dallinger R (1993) Strategies of metal detoxification in terrestrial invertebrates. In: Dallinger R, Rainbow PS (eds) Ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates. Lewis Publishers, London, pp 245–280
Dallinger R, Rainbow PS (1993) Ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates. Lewis Publishers
Eraly D, Hendrickx F, Backeljau T, Bervoets L, Lens L (2011) Direct and indirect effects of metal stress on physiology and life history variation in field populations of a lycosid spider. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1489–1497
Flouty R, Estephane G (2012) Bioaccumulation and biosorption of copper and lead by a unicellular algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in single and binary metal systems: a comparative study. J Environ Manag 111:106–114
Flouty R, Khalaf G (2015) Role of cu and Pb on Ni bioaccumulation by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: validation of the biotic ligand model in binary metal mixtures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:79–86
Gaetke LM, Chow Johnson HS, Chow CK (2014) Copper: toxicological relevance and mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 88:1929–1938
Goulle JP, Mahieu L, Castermant J, Neveu N, Bonneau L, Laine G, Bouige D, Lacroix C (2005) Metal and metalloid multi-elementary ICP-MS validation in whole blood, plasma, urine and hair. Forensic Sci 153:39–44
Hendrickx F, Maelfait JP, Speelmans M, Van Straalen NM (2003) Adaptive reproductive variation along a pollution gradient in a wolf spider. Oecol 134:189–194
Holmstrup M, Petersen BF, Larsen MM (1998) Combined effects of copper, desiccation, and frost on the viability of earthworm cocoons. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:897–901
Hopkin SP (1989) Ecophysiology of metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Elsevier Applied Science, London
Huang D, Kong J, Seng Y (2012) Effects of the heavy metal Cu2+ on growth, development, and population dynamics of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Econ Entomol 105:288–294
Iqbal M, Khera RA (2015) Adsorption of copper and lead in single and binary metal system onto Fumaria indica biomass. Chem Int 1:157b–163b
ISO (2008) Soil quality—requirements and guidance for the selection and application of methods for the assessment of bioavailability of contaminants in soil and soil materials. ISO 17402:2008. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
Jamal Q, Durani P, Khan K, Munir S, Hussain S, Munir K, Anees M (2013) Heavy metals accumulation and their toxic effects: review. JBMS 1:27–36
Joy EJ, Broadley MR, Young SD, Black CR, Chilimba AD, Ander EL, Barlow TS, Watts MJ (2015) Soil type influences crop mineral composition in Malawi. Sci Total Environ 505:587–595
Jung CS, Lee SB, Jung MP, Lee JH, Lee S, Lee SH (2005) Accumulated heavy metal content in wolf spider, Pardosa astrigera (Araneae: Lycosidae), as a bioindicator of exposure. J Asia Pac Entomol 8:185–192
Jung M, Kim H, Kim ST, Lee JH (2007) Risk analysis of heavy metal contaminated habitats using a wolf spider, Pardosa astrigera (Araneae: Lycosidae). In: C A Brebbia (Ed) Environ Health Risk IV, WIT, Southampton pp 229–236
Kammenga J, Arts M, Doroszuk A (2000) Multi-generation effects at the population level: fitness maximisation and optimal allocation in a nematode. In: Kammenga J, Laskowski R (eds) Demography in ecotoxicology. John Wiley, New York, pp 164–177
Komjarova I, Blust R (2008) Multi-metal interactions between cd, cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in water flea Daphnia magna, a stable isotope experiment. Aquat Toxicol 90:138–144
Koster M, Reijnders L, van Oost NR, Peijnenburg WJ (2005) Comparison of the method of diffusive gels in thin films with conventional extraction techniques for evaluating zinc accumulation in plants and isopods. Environ Pollut 133:103–116
Kovats N, Abdel Hameid NA, Kovacs K, Paulovits G (2010) Sensitivity of three unionid glochidia to elevated levels of copper, zinc and lead. Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosyst 4:1–8
Kumar PN, Dushenkov V, Motto H, Raskin I (1995) Phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils. Environ Sci Technol 29:1232–1238
Li CC, Wang Y, Li GY, Yun YL, Dai YJ, Chen J, Peng Y (2016) Transcriptome profiling analysis of wolf spider Pardosa pseudoannulata (Araneae: Lycosidae) after cadmium exposure. Int J Mol Sci 17:2033
Liu J, Gao J, Yun Y, Hu Z, Peng Y (2013) Bioaccumulation of mercury and its effects on survival, development and web-weaving in the funnel-web spider Agelena labyrinthica (Araneae: Agelenidae). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90:558–562
Mleiki A, Irizar A, Zaldibar B, El Menif NT, Marigómez I (2016) Bioaccumulation and tissue distribution of Pb and cd and growth effects in the green garden snail, Cantareus apertus (born, 1778), after dietary exposure to the metals alone and in combination. Sci Total Environ 547:148–156
Pavlaki MD, Morgado RG, Soares AM, Calado R, Loureiro S (2018) Toxicokinetics of cadmium in Palaemon varians postlarvae under waterborne and/or dietary exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:1614–1622
Pedersen MB, van Gestel CA, Elmegaard N (2000) Effects of copper on reproduction of two collembolan species exposed through soil, food, and water. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2579–2588
Peterson EK, Wilson DT, Possidente B, McDaniel P, Morley EJ, Possidente D, Hollocher KT, Ruden DM, Hirsch HV (2017) Accumulation, elimination, sequestration, and genetic variation of lead (Pb2+) loads within and between generations of Drosophila melanogaster. Chemosphere 181:368–375
Ramirez MG, McCallum JE, Landry JM, Vallin VA, Fukui SA, Gergus HE, Torres JD, Sy CL (2011) Relationships between physiological characteristics and trace metal body burdens of banded garden spiders Argiope trifasciata (Araneae, Araneidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1081–1088
Rogers JT, Patel M, Gilmour KM, Wood CM (2005) Mechanisms behind Pb-induced disruption of Na+ and cl− balance in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289:463–472
Rouchon AM, Phillips NE (2017) Acute toxicity of copper, lead, zinc and their mixtures on the sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus. New Zeal J Mar Fresh 51:333–355
Saxe JK, Impellitteri CA, Peijnenburg WJ, Allen HE (2001) Novel model describing trace metal concentrations in the earthworm, Eisenia andrei. Environ Sci Technol 35:4522–4529
Shulman MV, Pakhomov OY, Brygadyrenko VV (2017) Effect of lead and cadmium ions upon the pupariation and morphological changes in Calliphora vicina (Diptera, Calliphoridae). Folia Oecol 44:28–37
Simon E, Harangi S, Feherne Baranyai E, Braun M, Fabian I, Mizser S, Nagy L, Tothmeresz B (2016) Distribution of toxic elements between biotic and abiotic components of terrestrial ecosystem along an urbanization gradient: soil, leaf litter and ground beetles. Ecol Indic 60:258–264
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18(2):321–336
Tahir HM, Butt A (2008) Activities of spiders in rice fields of Central Punjab, Pakistan. Acta Zool Sin 54:701–711
Van Ginneken M, De Jonge M, Bervoets L, Blust R (2015) Uptake and toxicity of cd, cu and Pb mixtures in the isopod Asellus aquaticus from waterborne exposure. Sci Total Environ 537:170–179
Van Ranst E, Verloo M, Demeyer A, Pauwels JM (1999) Manual for the soil chemistry and fertility laboratory. Ghent, Belgium: University of Ghent, pp 243
Vasak M (1991) Metal removal and substitution in vertebrate and invertebrate metallothioneins, Methods in enzymology. Elsevier, pp 452–458
Vijver MG, Vink JP, Jager T, Van Straalen NM, Wolterbeek HT, Van Gestel CA (2006) Kinetics of Zn and cd accumulation in the isopod Porcellio scaber exposed to contaminated soil and/or food. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1554–1563
Vijver MG, Vink JP, Miermans CJ, van Gestel CA (2003) Oral sealing using glue: a new method to distinguish between intestinal and dermal uptake of metals in earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 35:125–132
Walters DM, Mills MA, Fritz KM, Raikow DF (2009) Spider-mediated flux of PCBs from contaminated sediments to terrestrial ecosystems and potential risks to arachnivorous birds. Environ Sci Technol 44:2849–2856
Wijayawardena MA, Megharaj M, Naidu R, Stojanovski E (2018) Chronic and reproductive toxicity of cadmium, zinc, and lead in binary and tertiary mixtures to the earthworm (Eisenia fetida). J Soils Sediments 18:1602–1609
Wilczek G (2017) The use of spiders in the assessment of cellular effects of environmental stressors. In: Ecotoxicology and genotoxicology: non-traditional terrestrial models. Issues in Toxicology, Royal Society of Chemistry, pp. 96–124
Wilczek G, Babczynska A, Augustyniak M, Migula P (2004) Relations between metals (Zn, Pb, cd and cu) and glutathione-dependent detoxifying enzymes in spiders from a heavy metal pollution gradient. Environ Pollut 132:453–461
Wilczek G, Babczynska A, Wilczek P, Dolezych B, Migula P, Mlynska H (2008) Cellular stress reactions assessed by gender and species in spiders from areas variously polluted with heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70:127–137
Wilczek G, Rost Roszkowska M, Wilczek P, Babczyńska A, Szulinska E, Sonakowska L, Marek Swedziol M (2014) Apoptotic and necrotic changes in the midgut glands of the wolf spider Xerolycosa nemoralis (Lycosidae) in response to starvation and dimethoate exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 101:157–167
Wilczek G, Wisniewska K, Kozina B, Wilczek P, Rost-Roszkowska M, Stalmach M, Skowronek M, Kaszuba F (2018) Effects of food contaminated with cadmium and copper on hemocytes of Steatoda grossa (Araneae: Theridiidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:267–274
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36:169–182
Xu X, Li Y, Wang Y, Wang Y (2011) Assessment of toxic interactions of heavy metals in multi-component mixtures using sea urchin embryo-larval bioassay. Toxicol in Vitro 25:294–300
Yang H, Peng Y, Tian J, Wang J, Hu J, Wang Z (2016) Spiders as excellent experimental models for investigation of heavy metal impacts on the environment: a review. Environ Earth Sci 75:1059
Zeeshan M, Murugadas A, Ghaskadbi S, Rajendran RB, Akbarsha MA (2016) ROS dependent copper toxicity in Hydra-biochemical and molecular study. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 185:1–12
Zhang L, Van Gestel CA (2017) Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of lead in the soil invertebrate Enchytraeus crypticus. Environ Pollut 225:534–541
Zidar P, Van Gestel CA, Strus J (2009) Single and joint effects of Zn and cd on Porcellio scaber (Crustacea, Isopoda) exposed to artificially contaminated food. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:2075–2082
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aziz, N., Butt, A. & Elsheikha, H.M. Assessment of bioaccumulation of cu and Pb in experimentally exposed spiders, Lycosa terrestris and Pardosa birmanica, using different exposure routes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 3309–3319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07055-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07055-0