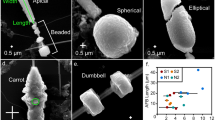
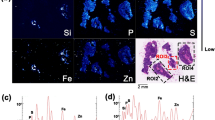
Abstract
Mesothelioma is a malignant tumor mainly correlated to occupational asbestos exposure. Rare reports describe its occurrence also in animals, mainly linked to asbestos in the environment. Asbestos exposure is demonstrated by the appearance of characteristic histological hallmarks: asbestos containing ferruginous bodies that are iron-based structures forming around fibers and also other dust particles. Here we present a clinical case of a suspect of mesothelioma in the peritoneum of a dog with parallel histological observation of ferruginous bodies. To possibly correlate the dog tumor to environmental exposure, we performed X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyses at two different synchrotrons to resolve the ferruginous bodies’ composition. While the histological examination diagnoses a tubulo-papillary mesothelioma, the XRF analyses show that ferruginous bodies contain Si particles, resembling formations of exogenous origin; however, the morphology is unlikely that of asbestos fibers. We speculate that the peritoneal mesothelioma of this dog could be related to environmental exposure to non-asbestos material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulanger G, Andujar P, Pairon J-C, Billon-Galland MA, Dion C, Dumortier P, Brochard P, Sobaszek A, Bartsch P, Paris C, Jaurand MC (2014) Quantification of short and long asbestos fibers to assess asbestos exposure: a review of fiber size toxicity. Environ Health Glob Access Sci Source 13:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-13-59
Cunningham AA, Dhillon AP (1998) Pleural malignant mesothelioma in a captive clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa nebulosa). Vet Rec 143:22–24
D’Angelo AR, Di Francesco G (2014) Sclerosing peritoneal mesothelioma in a dog: histopathological, histochemical and immunohistochemical investigations. Vet Ital 50:301–305. https://doi.org/10.12834/VetIt.20.1309.130
De Nardo (1996) Il mesotelioma pleurico del cane come indicatore di esposizione ambientale ad amianto. Rapporti ISTISAN 96:1–27
de Vuyst P, Jedwab J, Robience Y, Yernault JC (1982a) “Oxalate bodies”, another reaction of the human lung to asbestos inhalation? Eur J Respir Dis 63:543–549
de Vuyst P, Jedwab J, Robience Y, Yernault JC (1982b) “Oxalate bodies”, another reaction of the human lung to asbestos inhalation? Eur J Respir Dis 63:543–549
Dodson RF, O’Sullivan MF, Huang J et al (2000) Asbestos in extrapulmonary sites: Omentum and Mesentery. Chest 117:486–493
Donner E, de Jonge MD, Kopittke PM, Lombi E (2013) Mapping element distributions in plant tissues using synchrotron X-ray fluorescence techniques. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ 953:143–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-152-3_9
Gaensler EA, Addington WW (1969) Asbestos or ferruginous bodies. N Engl J Med 280:488–492
Geninet C, Bernex F, Rakotovao F, Crespeau FL, Parodi AL, Fontaine JJ (2003) Sclerosing peritoneal mesothelioma in a dog - a case report. J Vet Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med 50:402–405
Ghio AJ, Churg A, Roggli VL (2004) Ferruginous bodies: implications in the mechanism of fiber and particle toxicity. Toxicol Pathol 32:643–649. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230490885733
Gianoncelli A, Morrison GR, Kaulich B, Bacescu D, Kovac J (2006) Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy with a configurable detector. Appl Phys Lett 89:251117. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2422908
Gianoncelli A, Kaulich B, Alberti R, Klatka T, Longoni A, de Marco A, Marcello A, Kiskinova M (2009) Simultaneous soft X-ray transmission and emission microscopy. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 608:195–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2009.06.035
Gianoncelli A, Kourousias G, Stolfa A, Kaulich B (2013) Recent developments at the TwinMic beamline at ELETTRA: an 8 SDD detector setup for low energy X-ray fluorescence. J Phys Conf Ser 425:182001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/425/18/182001
Gianoncelli A, Kourousias G, Altissimo M et al (2016a) Combining multiple imaging techniques at the TwinMic X-ray microscopy beamline. AIP Conf Proc 1764:030002
Gianoncelli A, Kourousias G, Merolle L, Altissimo M, Bianco A (2016b) Current status of the TwinMic beamline at Elettra: a soft X-ray transmission and emission microscopy station. J Synchrotron Radiat 23:1526–1537. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600577516014405
Gianoncelli A, Rizzardi C, Salomon D, Canzonieri V, Pascolo L (2018) Nano-imaging of environmental dust in human lung tissue by soft and hard X-ray fluorescence microscopy. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 147:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2018.05.019
Glickman LT, Domanski LM, Maguire TG, Dubielzig RR, Churg A (1983) Mesothelioma in pet dogs associated with exposure of their owners to asbestos. Environ Res 32:305–313
Gross P, de Treville RT, Cralley LJ, Davis JM (1968) Pulmonary ferruginous bodies. Development in response to filamentous dusts and a method of isolation and concentration. Arch Pathol 85:539–546
Gualtieri AF, Bursi Gandolfi N, Pollastri S, Burghammer M, Tibaldi E, Belpoggi F, Pollok K, Langenhorst F, Vigliaturo R, Dražić G (2017) New insights into the toxicity of mineral fibres: a combined in situ synchrotron μ-XRD and HR-TEM study of chrysotile, crocidolite, and erionite fibres found in the tissues of Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Lett 274:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.04.004
Harbison ML, Godleski JJ (1983) Malignant mesothelioma in urban dogs. Vet Pathol 20:531–540
Kaulich B, Bacescu D, Susini J et al (2006) A European twin X-ray Microscopy Station commissioned at ELETTRA. ConfProcSeries IPAP 7(7):22–25
R. Kirkham, Dunn PA (2010) The Maia Spectroscopy Detector System: Engineering for Integrated Pulse Capture, Low-Latency Scanning and Real-Time Processing. Am Inst Phys Conf Proc 1234:. doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3463181
Koerten HK, Hazekamp J, Kroon M, Daems WT (1990) Asbestos body formation and iron accumulation in mouse peritoneal granulomas after the introduction of crocidolite asbestos fibers. Am J Pathol 136:141–157
Marruchella G, Di Guardo G, Albano M, Della Salda L (2002) Animali domestici come indicatori di rischio oncogeno per l’uomo. O&DV 12:55–62
Morrison GR, Gianoncelli A, Kaulich B, et al (2006)A Fast-readout CCD System for Configured-Detector Imaging in STXM. Proc 8th Int Conf X-ray Microscopy IPAP Conf Series 377–379
Nashiruddullah N, Chakraborty A (2003) Spontaneous neoplasms in captive wild carnivores of the Assam state zoo. Indian Journal of Veterinary Pathology 27:39–41
Pascolo L, Gianoncelli A, Kaulich B, Rizzardi C, Schneider M, Bottin C, Polentarutti M, Kiskinova M, Longoni A, Melato M (2011) Synchrotron soft X-ray imaging and fluorescence microscopy reveal novel features of asbestos body morphology and composition in human lung tissues. Part Fibre Toxicol 8:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-8-7
Pascolo L, Gianoncelli A, Schneider G, Salomé M, Schneider M, Calligaro C, Kiskinova M, Melato M, Rizzardi C (2013) The interaction of asbestos and iron in lung tissue revealed by synchrotron-based scanning X-ray microscopy Sci Report 3:. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01123
Pascolo L, Borelli V, Canzonieri V, Gianoncelli A, Birarda G, Bedolla DE, Salomé M, Vaccari L, Calligaro C, Cotte M, Hesse B, Luisi F, Zabucchi G, Melato M, Rizzardi C (2015) Differential protein folding and chemical changes in lung tissues exposed to asbestos or particulates. Sci Rep 5:12129. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12129
Pascolo L, Gianoncelli A, Rizzardi C, de Jonge M, Howard D, Paterson D, Cammisuli F, Salomé M, de Paoli P, Melato M, Canzonieri V (2016a) Focused X-ray histological analyses to reveal asbestos fibers and bodies in lungs and pleura of asbestos-exposed subjects. Microsc Microanal 22:1062–1071. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927616011685
Pascolo L, Zabucchi G, Gianoncelli A, Kourousias G, Trevisan E, Pascotto E, Casarsa C, Ryan C, Lucattelli M, Lungarella G, Cavarra E, Bartalesi B, Zweyer M, Cammisuli F, Melato M, Borelli V (2016b) Synchrotron X-ray microscopy reveals early calcium and iron interaction with crocidolite fibers in the lung of exposed mice. Toxicol Lett 241:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.11.016
Paterson D, de Jonge MD, Howard DL, et al (2011) The X-ray fluorescence microscopy Beamline at the Australian Synchrotron. Pp 219–222
Rao AT, Acharjyo LN (1994) Pleural mesothelioma in a tigress. Indian Journal of Veterinary Pathology 18:174–175
Ryan CG, Kirkham R, Hough RM, Moorhead G, Siddons DP, de Jonge MD, Paterson DJ, de Geronimo G, Howard DL, Cleverley JS (2010) Elemental X-ray imaging using the Maia detector array: the benefits and challenges of large solid-angle. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 619:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2009.11.035
Shin NS, Kwon SW, Kim DY et al (1998) Metastatic malignant mesothelioma in a tiger (Panthera tigris). J Zoo Wildl Med Off Publ Am Assoc Zoo Vet 29:81–83
Sole A, Papillon E, Cotte M et al (2007) A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 62:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2006.12.002
Stewart HL (1966) Pulmonary cancer and adenomatosis in captive wild mammals and birds from the Philadelphia zoo. J Natl Cancer Inst 36:117–138
Vascellari M, Carminato A, Camali G, Melchiotti E, Mutinelli F (2011) Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis in a dog: histological and immunohistochemical characterization. J Vet Diagn Investig Off Publ Am Assoc Vet Lab Diagn Inc 23:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063871102300125
Wiedner EB, Isaza R, Lindsay WA, Case AL, Decker J, Roberts J (2008) Pericardial mesothelioma in a Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris). J Zoo Wildl Med 39:121–123. https://doi.org/10.1638/2007-0080.1
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge a grant from Friuli Venezia Giulia Region, Commissione Amianto FVG, 2015. They are grateful to Elettra and the Australian Synchrotron for granting beamtimes. Part of this research was undertaken on the XFM beamline at the Australian Synchrotron, Victoria, Australia. The authors are grateful to the Australian Synchrotron for providing the beamtime and to D. Paterson, D. Howard, M. de Jonge, and K. Spiers for technical support at the XFM beamline.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Figure S1
(PDF 695 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pascotto, E., Gianoncelli, A., Calligaro, C. et al. Ferruginous bodies resolved by synchrotron XRF in a dog with peritoneal malignant mesothelioma. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 35707–35714 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3521-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3521-x