Abstract
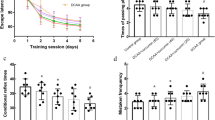
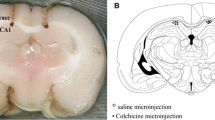
Curcumin is a molecule found in turmeric root that has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor properties and has been widely used as both an herbal drug and a food additive to treat or prevent neurodegenerative diseases. This study aimed to investigate the effect of curcumin on neurobehavioral and neuropathological alterations induced by acetamiprid on male rats. Three groups of ten male Wistar rats each were used for the study: the first was a control group (CTR) that did not consume acetamiprid (ACE); the second was an experimental group (ACE) that consumed 40 mg/kg body weight/day of acetamiprid; and the third group (CUR) received curcumin (100 mg/kg) and acetamiprid (40 mg/kg) in combination. Neurobehavioral evaluations including inclined plane performance and forepaw grip time were studied. Treatment with CUR significantly prevented ACE-treated rats from impairments in the performance of neurobehavioral tests, indicating the presence of deficits on sensorimotor and neuromuscular responses. In addition, Curcumin administration protects rats against acetamiprid-induced cerebellum toxicity such as increase in AChE and BChE activities, decrease on cells viability, oxidative stress, and an increase of intracellular calcium. Taken together, these results demonstrate for the first time that ACE treatment substantially impairs the survival of primary neuronal cells through the induction of necrosis concomitantly with the generation of an oxidative stress. Additionally, curcumin reduced histopathological changes caused by ACE.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Donia MB, Goldstein LB, Sarah B, Tu T, Khan WA, Dechkovskaia AM, Abdel-Rahman AA (2008) Imidacloprid induces neurobehavioral deficits and increases expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the motor cortex and hippocampus in offspring rats following in utero exposure. J Toxic Environ Health A 71:119–130
Aebi HE (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Andersen CS, Andersen AB, Finger S (1991) Neurological correlates of unilateral and bilateral “strokes” of the middle cerebral artery in the rat. Physiol Behav 50:263–269
Baltazar MT, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, de Lourdes Bastos M, Tsatsakis AM, Duarte JA, Carvalho F (2014) Pesticides exposure as etiological factors of Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases—a mechanistic approach. Toxicol.Lett 230(2):85–103
Bayomi SM, El-Kashef HA, El-Ashmawy MB, Nasr MNA, El-Sherbeny MA, Abdel-Aziz NI, El-Sayed MA-A, Suddek GM, El-Messery SM, Ghaly MA (2015) Synthesis and biological evaluation of new curcumin analogues as antioxidant and antitumor agents: molecular modeling study. Eur J Med Chem 101:584–594
Begue JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Casida JE (2010) Neonicotinoid metabolism: compounds, substituents, pathways, enzymes, organisms, and relevance. J Agric Food Chem 59:2923–2931
Chattopadhyay I, Biswas K, Bandyopdhyay U, Banerjee RK (2004) Turmeric and curcumin: biological actions and medicinal applications. Curr Sci 87:44–53
Cicchetti F, Drouin-Ouellet J, Gross RE (2009) Environmental toxins and Parkinson’s disease: what have we learned from pesticide-induced animal models? Trends PharmacolSci 30:475–483
Curtin JF, Donovan M, Cotter TG (2002) Regulation and measurement of oxidative stress in apoptosis. J Immunol Methods 265(1–2):49–72
Day T, Greenfield SA (2003) A peptide derived from acetylcholinesterase induces neuronal cell death: characterization of possible mechanisms. Exp Brain Res 153:334–342
Denizot F, Lang R (1986) Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods 89:271–277
Duzguner V, Erdogan S (2012) Chronic exposure to imidacloprid induces inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver and central nervous system of rats. Pestic Biochem Physiol 104:7
El-Gendy KS, Aly NM, Mahmoud FH, Kenawy A, El-Sebae AK (2010) The role of vitamin C as antioxidant in protection of oxidative stress induced by imidacloprid. Food ChemToxicol 48:215–221
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres VJ, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acethylcholinesterase activity. BiochemPhamacol 7:88–95
Fahn S, Cohen G (1992) The oxidant stress hypothesis in Parkinson’s disease: evidence supporting it. Ann Neurol 32:804–812
Goel A, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB (2008) Curcumin as “Curecumin”: from kitchen to clinic. BiochemPharmacol 75:787–809
Greig NH, Utsuki T, Ingram DK, Wang Y, Pepeu G, Scali C, Yu QS, Mamczarz J, Holloway HW, Giordano T, Chen D, Furukawa K, Sambamurti K, Brossi A, Lahiri DK (2005) Selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibition elevates brain acetylcholine, augments learning and lowers Alzheimer b-amyloid peptide in rodent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:17213–17218
Gultekin F, Delibas N, Yasar S, Kilinc I (2001) In vivo changes in antioxidant systems and protective role of melatonin and a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E on oxidative damage in erythrocytes induced by chlorpyrifos-ethyl in rats. Arch of Toxicol 75:88–96
Hu ML, Dillard CJ (1994) Plasma SH and GSH measurement. MethodsEnzymol 233:385–387
Jaques JAS, Ruchel JB, Schlemmer KB, Pimentel VC, Bagatini M, SouzaVdo C et al (2011) Effects of curcumin on the activities of the enzymes that hydrolyse adenine nucleotides in platelets from cigarette smoke-exposed rats. Cell Biochem Funct 29:630–635
Jeschke P, Nauen R, Schindler M, Elbert A (2011) Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J Agric Food Chem 59:2897–2908
Khan RN, Matharoo-Ball B, Shaw RW (2010) Antioxidant enzyme expression, lipid peroxidation, and protein oxidation in human myometrium with parturition. Reprod Sci 17:78–84
Kumi-Diaka J, Nguyen V, Butler A (1999) Cytotoxic potential of the phytochemical genisteinisoflavone (4′, 5′, 7-trihydroxyisoflavone) and certain environmental chemical compounds on testicular cells. Biol Cell 91:515–523
Lane RM, Kivipelto M, Greig NH (2004) Acetylcholinesterase and its inhibition in Alzheimer disease. ClinNeuropharmacol 27:141–149
Lonare M, Kumar M, Raut S, Badgujar P, Doltade S, Telang A (2014) Evaluation of imidacloprid-induced neurotoxicity in male rats: a protective effect of curcumin. NeurochemInt 78:122–129
Mani VM, Sadiq AMM (2014) Naringin modulates the impairment of memory, anxiety, locomotor, and emotionality behaviors in rats exposed to deltamethrin; a possible mechanism association with oxidative stress, acetylcholinesterase and ATPase. Biomed Prev Nutr 4(4):527
Marzouki S, Bini Dhouib I, Benabdessalem C, Rekik R, Doghri R, Maroueni A, Bellasfar Z, Fazaa S, Bettaieb J, Barbouche MR, Ben Ahmed M (2017) Specific immune responses in mice following subchronic exposure to acetamiprid. Life Sci 188:10–16
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J BiolChem 247:3170–3175
Oliveira SA, Chuffa LGA, Fioruci-Fontanelli BA, Neto FSL, Novais PC, Tirapelli LF, Oishi JC, Takase LF, Stefanini MA, Martinez M, Martinez FE (2014) Apoptosis of Purkinje and granular cells of the cerebellum following chronic ethanol intake. Cerebellum 13:728–738
Sahu PK (2016) Design, structure activity relationship, cytotoxicity and evaluation of antioxidant activity of curcumin derivatives/analogues. Eur J Med Chem 121:510–516
Singh TB, Mukhopadhayay SK, Sar TK, Ganguly S (2012) Acetamiprid induces toxicity in mice under experimental conditions with prominent effect on the hematobiochemical parameters. J Drug MetabToxicol 3:6
Singh V, Hussein M, Singh AK, Hassan MA, Gupta P (2015) Histological and immunohistochemical changes in cerebellum of chick embryos after exposure to neonicotinoid insecticide imidacloprid. J Anat Soc India 64(2):122–127
Stern J, Lewis WHP (1957) The colorimetric estimation of calcium in serum with O-cresolphtaleincomplexone. Clin Chim Acta 2:576–580
Thomas JD, Goodlett CR, West JR (1998) Alcohol-induced Purkinje cell loss depends on developmental timing of alcohol exposure and correlates with motor performance. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 105(2):159–166
Tomizawa M, Lee DL, Casida JE (2000) Neonicotinoid insecticides: molecular features conferring selectivity for insect versus mammalian nicotinic receptors. J Agric Food Chem 48:6016–6024
Tomizawa M, Lee DL, Casida JE (2005) Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: mechanisms of selective action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:247–268
Tran TD, Jackson HD, Horn KH, Goodlett CR (2005) Vitamin E does not protect against neonatal ethanolinduced cerebellar damage or deficits in eyeblink classical conditioning in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:117–129
Tsakiris S, Angelogianni P, Schulpis KH, Stavridis JC (2000) Protective effect of phenylalanine on rat brain acetylcholinesterase inhibiton induced by free radicals, Clin. Biochemist 33:103–106
Yang L, Heng-Yi H, Zhang XJ (2002) Increased expression of intranuclearAChE involved in apoptosis of SK-N-SH cells. Neurosci Res 42:261–268
Yang L, Calingasan NY, Chen J, Ley JJ, Becker DA, Beal MF (2005) A novel azulenyl nitrone antioxidant protects against MPTP and 3-nitropropionic acid neurotoxicities. Exp Neurol 191:86–93
Zhang J, Wang Y, Xiang H, Li M, Li W, Ma K, Wang X, Zhang J (2011) Oxidative stress: role in acetamiprid-induced impairment of the male mice reproductive System. Agric Sci China 10(5):786–796
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhouib, I.B., Annabi, A., Doghri, R. et al. Neuroprotective effects of curcumin against acetamiprid-induced neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in the developing male rat cerebellum: biochemical, histological, and behavioral changes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 27515–27524 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0331-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0331-5