Abstract
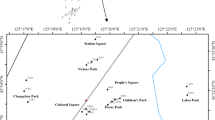
A study on heavy metal pollution was undertaken in the re-suspended road dusts from different functional areas in Xi’an City of China to investigate the impacts of human activities and land uses on urban environment. The concentrations of Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, V, and Zn were determined using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, and their accumulations were analyzed using enrichment factor. Correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis, combined with the concentration property and enrichment factor, were used to identify the possible sources of heavy metals investigated. The investigated re-suspended road dusts had Co, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn concentrations higher than background levels. Samples from different functional areas had diverse heavy metal concentration levels. Co, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn presented moderate/significant enrichment in the samples. The source analyses indicated that Mn, Ni, V, Pb, and Zn had the mixed sources of nature and traffic, Cr and Cu mainly originated from traffic source, while Co was primarily derived from construction source. Traffic and construction activities had a significant impact on urban environment. This preliminary research provides a valuable basis for urban environment protection and management.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter MS, Madany IM (1993) Heavy metals in street and house dust in Bahrain. Water Air Soil Pollut 66:111–119
Al-Khashman OA (2007) Determination of metal accumulation in deposited street dusts in Amman, Jordan. Environ Geochem Health 29:1–10
Banerjee ADK (2003) Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environ Pollut 123:95–105
Bergamaschi L, Rizzio E, Valcuvia MG, Verza G, Profumo A, Gallorini M (2002) Determination of trace elements and evaluation of their enrichment factors in Himalayan lichens. Environ Pollut 120:137–144
Buat-Menard P, Chesselet R (1979) Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet Sci Lett 42:398–411
Chen XD, Lu XW, Yang G (2012) Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. Catena 98:73–78
Chen H, Lu XW, Li LY, Gao TN, Chang YY (2014) Metal contamination in campus dust of Xi’an, China: a study based on multivariate statistics and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 484:27–35
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Centre) (1990) The background values of Chinese soils. Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
De Miguel E, Llamas JF, Chacón E, Berg T, Larssen S, Røyset O, Vadset M (1997) Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmos Environ 31:2733–2740
Ferreira-Baptista L, De Miguel E (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 38:4501–4512
Han YM, Du PX, Cao JJ, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Han YM, Cao JJ, Posmentier ES, Fung K, Tian H, An ZS (2008) Particulate-associated potentially harmful elements in urban road dusts in Xi’an, China. Appl Geochem 23:835–845
Hernandez L, Probst A, Probst JL, Ulrich E (2003) Heavy metal distribution in some French forest soils: evidence for atmospheric contamination. Sci Total Environ 312:195–219
Herngren L, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2006) Analysis of heavy metals in road-deposited sediments. Anal Chim Acta 571:270–278
Isakson J, Oblad M, Lindgren ES, Fridell MD, Pacyna JM, Mäkinen M (1997) Perturbation of background aerosol at rural sites in the Nordic countries. Atmos Environ 31:3077–3086
Langer S, Weschler CJ, Fischer A, Bekö G, Toftum J, Clausen G (2010) Phythalate and PAH concentrations in dust collected from Danish homes and daycare centers. Atmos Environ 44:2294–2301
Losha K, Wiechula D (2003) Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere 51:723–733
Lu XW, Wang LJ, Li LY, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173:744–749
Lu XW, Zhang XL, Li LY, Chen H (2014) Assessment of metals pollution and health risk in dust from nursery schools in Xi’an, China. Environ Res 128:27–34
Maas S, Scheifler R, Benslama M, Crini N, Lucot E, Brahmia Z, Bnyacoub S, Giraudoux P (2010) Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in urban, suburban and agricultural soils in a Mediterranean city of Algeria. Environ Pollut 158:2294–2301
Nolting RF, Ramkema A, Everaarts JM (1999) The geochemistry of Cu, Cd, Zn, Ni and Pb in sediment cores from the continental slope of the Banc d’Arguin (Mauritania). Cont Shelf Res 19:665–691
Quevauviller P, Lavigne R, Cortez L (1989) Impact of industrial and mine drainage wastes on the heavy metal distribution in the drainage basin and estuary of the Sado River (Portugal). Environ Pollut 59:267–286
Shi GT, Chen ZL, Bi CJ, Wang L, Teng JY, Li YS, Xu SY (2011) A comparative study of health risk of potential metals in urban and suburban road dust in the most populated city of China. Atmos Environ 45:764–771
Surtherland RA (2000) Bad sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39:611–627
Tang RL, Ma KM, Zhang YX, Mao QZ (2013) The spatial characteristics and pollution levels of metals in urban street dust of Beijing, China. Appl Geochem 35:88–98
Wei BG, Yang LS (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
Wei X, Gao B, Wang P, Zhou HD, Lu J (2015) Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:186–192
Xu X, Lu XW, Han XF, Zhao N (2015) Ecological and health risk assessment of metal in resuspended particles of urban street dust from an industrial city in China. Curr Sci 108:72–79
Zhao N, Lu XW, Chao SG (2016) Risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in smaller than 100-μm street dust particles from a valley-city in northwestern China. Environ Geochem Health 38:483–496
Zhao N, Lu XW, Chao SG (2014) Level and contamination assessment of environmentally sensitive elements in smaller than 100 μm street dust particles from Xining, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:2536–2549
Zhao N, Lu XW, Chao SG, Xu X (2015) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in less than 100 μm particles of street dust from Xining, China. Environ Earth Sci 73:2319–2327
Zhao HT, Li XY, Wang XM, Tian D (2010) Grain size distribution of road-deposited sediment and its contribution to heavy metal pollution in urban runoff in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 183:203–210
Zheng N, Liu JS, Wang QC, Liang ZZ (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, northeast of China. Sci Total Environ 408:726–733
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China through Grant 41271510 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities through Grant GK 201601009. All the experiments were conducted in the Environmental Science Lab of Shaanxi Normal University. We thank Na Yin, Yuxin Li, and Ying Liu for their help with the sample preparation and the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Lu, X. & Pan, H. Analysis of heavy metals in the re-suspended road dusts from different functional areas in Xi’an, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 19838–19846 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7200-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7200-5