Abstract
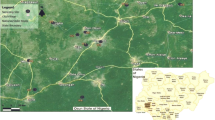
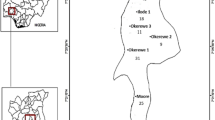
In most developing countries, especially in Southern Africa, little is known about the presence of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) pathotypes in riverbed sediments. The present study sought to investigate the presence of DEC virulence genes in riverbed sediments of the Apies River, a river used by many communities in Gauteng, South Africa. Water and sediment samples were collected from the river between July and August 2013 (dry season) and also between January and February 2014 (wet season) following standard procedures. Isolation of E. coli was done using the Colilert®-18 Quanti-Tray® 2000 system. DNA was extracted from E. coli isolates using the InstaGene™ matrix from Bio-Rad and used as template DNA for real-time PCR. Water pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, electrical conductivity and turbidity were measured in situ. Over 59 % of 180 samples analysed were positive for at least one of the seven DEC virulence genes investigated. The eaeA gene was the most isolated gene (29.44 %) while the ipaH gene the least isolated (8.33 %). The ipaH gene (p = 0.012) and the ST gene (stIa, p = 0.0001, and stIb, p = 0.019) were positively correlated with temperature. The detection of diarrhoeagenic E. coli virulence genes in the sediments of the Apies River shows that the sediments of this river might not only be a reservoir of faecal indicator bacteria like E. coli but also pathogenic strains of this bacterium. These organisms could represent a public health risk for poor communities relying on this water source for various purposes such as drinking and recreational use. There is therefore an urgent need to monitor these DEC pathotypes especially in areas without adequate water supplies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi P, Kargar M, Doosti A et al (2014) Multiplex real-time PCR assay for the detection of LT, STIa and STIb genes in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Int J Enteric Pathog 2:e16431
Abia ALK, Ubomba-Jaswa E, du Preez M, Momba MNB (2015a) Riverbed sediments in the Apies River, South Africa: recommending the use of both Clostridium perfringens and Escherichia coli as indicators of faecal pollution. J Soils Sediments 15:2412–2424. doi:10.1007/s11368-015-1209-0
Abia ALK, Ubomba-Jaswa E, Momba MNB (2015b) Impact of seasonal variation on Escherichia coli concentrations in the riverbed sediments in the Apies River, South Africa. Sci Total Environ 537:462–469. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.132
Abia LKA, Ubomba-Jaswa E, Ssemakalu CC, Momba MNB (2015c) Development of a rapid approach for the enumeration of Escherichia coli in riverbed sediment: case study, the Apies River, South Africa. J Soils Sediments 15:2425–2432. doi:10.1007/s11368-015-1081-y
An Y-J, Kampbell DH, Peter Breidenbach G (2002) Escherichia coli and total coliforms in water and sediments at lake marinas. Environ Pollut 120:771–778. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00173-2
APHA/AWWA/WEF (American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation) (2001) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. APHA/AWWA/WEF, Washington
Aslani MM, Alikhani MY, Zavari A, Yousefi R, Zamani Ali R (2011) Characterization of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC) clinical isolates and their antibiotic resistance pattern. Int J Infect Dis 15:e136–e139. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2010.10.002
Ateba CN, Mbewe M (2011) Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 virulence genes in isolates from beef, pork, water, human and animal species in the Northwest Province, South Africa : public health implications. Res Microbiol 162:240–248. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2010.11.008
Badgley BD, Thomas FIM, Harwood VJ (2010) The effects of submerged aquatic vegetation on the persistence of environmental populations of Enterococcus spp. Environ Microbiol 12:1271–1281. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02169.x
Badgley BD, Thomas FIM, Harwood VJ (2011) Quantifying environmental reservoirs of fecal indicator bacteria associated with sediment and submerged aquatic vegetation. Environ Microbiol 13:932–942. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02397.x
Balière C, Rincé A, Thevenot D, Gourmelon M (2015) Successful detection of pathogenic Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in shellfish, environmental waters and sediment using the ISO/TS-13136 method. Lett Appl Microbiol 60:315–320. doi:10.1111/lam.12386
Bisi-Johnson MA, Obi CL, Vasaikar SD, Baba KA, Hattori T (2011) Molecular basis of virulence in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli and Salmonella species from a tertiary hospital in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Gut Pathog 3:9. doi:10.1186/1757-4749-3-9
Bokranz W, Wang X, Tschäpe H, Römling U (2005) Expression of cellulose and curli fimbriae by Escherichia coli isolated from the gastrointestinal tract. J Med Microbiol 54:1171–1182. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.46064-0
Bray J (1945) Isolation of antigenically homogeneous strains of Bact. coli neapolitanum from summer diarrhoea of infants. J Pathol Bacteriol 57:239–247. doi:10.1002/path.1700570210
Caine L, Nwodo U, Okoh A, Ndip R, Green E (2014) Occurrence of virulence genes associated with diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from raw cow’s milk from two commercial dairy farms in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:11950–11963. doi:10.3390/ijerph111111950
Chandran A, Mazumder A (2013) Prevalence of diarrhea-associated virulence genes and genetic diversity in Escherichia coli isolates from fecal material of various animal hosts. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:7371–7380. doi:10.1128/AEM.02653-13
Chandran A, Mazumder A (2014) Occurrence of diarrheagenic virulence genes and genetic diversity in Escherichia coli isolates from fecal material of various avian hosts in British Columbia, Canada. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:1933–1940. doi:10.1128/AEM.03949-13
Chekabab SM, Daigle F, Charette SJ, Dozois CM, Harel J (2012) Survival of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in the presence of Acanthamoeba castellanii and its dependence on Pho regulon. Microbiologyopen 1:427–37. doi:10.1002/mbo3.40
Chen DH, Frankel G (2005) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: unravelling pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:83–98. doi:10.1016/j.femsre.2004.07.002
Cooper IR, Taylor HD, Hanlon GW (2007) Virulence traits associated with verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli O157 recovered from freshwater biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 102:1293–1299. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03178.x
Craig DL, Fallowfield HJ, Cromar NJ (2004) Use of microcosms to determine persistence of Escherichia coli in recreational coastal water and sediment and validation with in situ measurements. J Appl Microbiol 96:922–930. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02243.x
Dobrowsky PH, van Deventer A, De Kwaadsteniet M, Ndlovu T, Khan S, Cloete TE, Khan W (2014) Prevalence of virulence genes associated with pathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from domestically harvested rainwater during low- and high-rainfall periods. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:1633–1638. doi:10.1128/AEM.03061-13
Edberg SC, Rice EW, Karlin RJ, Allen MJ (2000) Escherichia coli: the best biological drinking water indicator for public health protection. J Appl Microbiol 88:106S–116S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2000.tb05338.x
Fagan PK, Hornitzky MA, Bettelheim KA, Djordjevic SP (1999) Detection of Shiga-like toxin (stx1 and stx2), intimin (eaeA), and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) hemolysin (EHEC hlyA) genes in animal feces by multiplex PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:868–872
Gonzales-Siles L, Sjöling Å (2015) The different ecological niches of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Environ Microbiol. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13106
Guion CE, Ochoa TJ, Walker CM, Barletta F, Cleary TG (2008) Detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli by use of melting-curve analysis and real-time multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol 46:1752–7. doi:10.1128/JCM.02341-07
Haller L, Poté J, Loizeau J, Wildi W (2009) Distribution and survival of faecal indicator bacteria in the sediments of the Bay of Vidy, Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Ecol Indic 9:540–547. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2008.08.001
Halliday E, Gast R (2010) Bacteria in beach sands: an emerging challenge in protecting coastal water quality and bather health. Environ Sci Technol 45:370–379. doi:10.1021/es102747s
Holzel A (1974) Bray’s discovery of pathogenic Esch. coli as a cause of infantile gastroenteritis. Arch Dis Child 49:668–668. doi:10.1136/adc.49.8.668-a
Hsu B-M, Wu S-F, Huang S-W, Tseng Y-J, Ji D-D, Chen J-S, Shih F-C (2010) Differentiation and identification of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli in environmental waters by a molecular method and biochemical test. Water Res 44:949–955. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.10.004
Huang DB, Dupont HL (2004) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli: an emerging pathogen in children. Semin Pediatr Infect Dis 15:266–271. doi:10.1053/j.spid.2004.07.008
Huang DB, Mohanty A, DuPont HL, Okhuysen PC, Chiang T (2006) A review of an emerging enteric pathogen: enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol 55:1303–1311. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.46674-0
Huang S, Hsu B, Su Y, Ji D-D, Lin W-C, Chen J-L, Shih F-C, Kao P-M, Chiu Y-C (2012) Occurrence of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli genes in raw water of water treatment plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2776–2783. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0777-4
Jafari A, Aslani MM, Bouzari S (2012) Escherichia coli: a brief review of diarrheagenic pathotypes and their role in diarrheal diseases in Iran. Iran J Microbiol 4:102–117
Jain S, Tyagi J, Singh V (2010) Simulation of runoff and sediment yield for a Himalayan watershed using SWAT model. J Water Resour Prot 2010:267–281. doi:10.4236/jwarp.2010.23031
Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Mobley HLT (2004) Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:123–140. doi:10.1038/nrmicro818
Kemper N (2008) Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol Indic 8:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2007.06.002
Kiliç A, Ertaş HB, Muz A, Özbey G, Kalender H (2007) Detection of the eaeA gene in Escherichia coli from chickens by polymerase chain reaction. Turkish J Vet Anim Sci 31:215–218
Kuhnert P, Boerlin P, Frey J (2000) Target genes for virulence assessment of Escherichia coli isolates from water, food and the environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:107–117
Kumar A, Taneja N, Sharma M (2014) An epidemiological and environmental study of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in India. Foodborne Pathog Dis 11:439–446. doi:10.1089/fpd.2013.1613
López-Saucedo C, Cerna JF, Villegas-Sepulveda N, et al (2003) Polymerase chain reaction to detect diverse loci associated with Escherichia coli. Emerg Infect Dis 9:127–131
Luna GM, Vignaroli C, Rinaldi C, Pusceddu A, Nicoletti L, Gabellini M, Danovaro R, Biavasco F (2010) Extraintestinal Escherichia coli carrying virulence genes in coastal marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5659–5668. doi:10.1128/AEM.03138-09
Mohammadi P, Abiri R (2012) Isolation of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) from raw milk in Kermanshah by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Jundishapur J Microbiol 6:e5439. doi:10.5812/jjm.5439
Moresco V, Viancelli A, Nascimento MA, Souza DSM, Ramos APD, Garcia LAT, Simões CMO, Barardi CRM (2012) Microbiological and physicochemical analysis of the coastal waters of southern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 64:40–48. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.10.026
Mudrak B, Kuehn MJ (2010) Heat-labile enterotoxin: beyond GM1 binding. Toxins (Basel) 2:1445–1470. doi:10.3390/toxins2061445
Mukhopadhyay C, Vishwanath S, Eshwara VK, Shankaranarayana SA, Sagir A (2012) Microbial quality of well water from rural and urban households in Karnataka, India: a cross-sectional study. J Infect Public Health 5:257–262. doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2012.03.004
Müller EE, Ehlers MM, Grabow WO (2001) The occurrence of E. coli O157:H7 in South African water sources intended for direct and indirect human consumption. Water Res 35:3085–8
Munshi SK, Rahman MM, Noor R (2012) Escherichia coli isolated from surface water of rivers surrounding Dhaka City. J Bangladesh Acad Sci 36:109–121
Nguyen TV, Le Van P, Le Huy C, Gia KN, Weintraub A (2005) Detection and characterization of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli from young children in Hanoi, Vietnam. J Clin Microbiol 43:755–760. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.2.755
Nguyen Y, Sperandio V (2012) Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) pathogenesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:1–7. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2012.00090
Obi CL, Green E, Bessong PO, de Villiers B, Hoosen AA, Igumbor EO, Potgieter N (2004) Gene encoding virulence markers among Escherichia coli isolates from diarrhoeic stool samples and river sources in rural Venda communities of South Africa. Water SA 30:37–42
Odonkor ST, Ampofo JK (2013) Escherichia coli as an indicator of bacteriological quality of water: an overview. Microbiol Res (Pavia) 4:5–11. doi:10.4081/mr.2013.e2
Okeke IN, Nataro JP (2001) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Lancet Infect Dis 1:304–313. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(01)00144-X
Omar KB, Barnard TG (2014) Detection of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli in clinical and environmental water sources in South Africa using single-step 11-gene m-PCR. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:2663–2671. doi:10.1007/s11274-014-1690-4
Omar KB, Potgieter N, Barnard TG (2010) Development of a rapid screening method for the detection of pathogenic Escherichia coli using a combination of Colilert ® Quanti-Trays/2000 and PCR. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 10:7–13. doi:10.2166/ws.2010.862
Pereira ACM, Britto-Filho JD, José de Carvalho J, de Luna MDG, Rosa ACP (2008) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC) strains enter and survive within cultured intestinal epithelial cells. Microb Pathog 45:310–314. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2008.07.001
Ratchtrachenchai O, Subpasu S, Hayashi H, Ba-thein W (2004) Prevalence of childhood diarrhoea-associated Escherichia coli in Thailand. J Med Microbiol 53(Pt 3):237–243. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.05413-0
Robins-Browne RM, Hartland EL (2002) Escherichia coli as a cause of diarrhea. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:467–475. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02769.x
Scaletsky ICA, Fabbricotti SH, Rozane LB et al (2002) Diffusely adherent Escherichia coli as a cause of acute diarrhea in young children in northeast Brazil : a case-control study. J Clin Microbiol 40:645–648. doi:10.1128/JCM.40.2.645
Schierack P, Steinrück H, Kleta S, Vahjen W (2006) Virulence factor gene profiles of Escherichia coli isolates from clinically healthy pigs. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6680–6. doi:10.1128/AEM.02952-05
Schneider E, O’Mullan GD (2013) Investigation of estuarine sediment as a reservoir for sewage associated bacteria. Section II: 1–22 pp. In: S.H. Fernald, D.J. Yozzo and H. Andreyko (eds.), Final reports of the Tibor T. Polgar Fellowship Program 2012. Hudson River Foundation, Staatsburg, New York
Sidhu JPS, Ahmed W, Hodgers L, Toze S (2013) Occurrence of virulence genes associated with diarrheagenic pathotypes in Escherichia coli isolates from surface water. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:328–335. doi:10.1128/AEM.02888-12
Tahamtan Y, Hayati M, Mm N (2010) Prevalence and distribution of the stx1, stx2 genes in Shiga toxin producing E. coli (STEC) isolates from cattle. Iran J Microbiol 2:8–13
Tallon P, Magajna B, Lofranco C, Leung KT (2005) Microbial indicators of faecal contamination in water: a current perspective. Water Air Soil Pollut 116:139–166
Tiefenthaler L, Stein ED, Schiff KC (2011) Levels and patterns of fecal indicator bacteria in stormwater runoff from homogenous land use sites and urban watersheds. J Water Health 9:279–290. doi:10.2166/wh.2010.056
Trachman JD, Maas WK (1998) Temperature regulation of heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) synthesis in Escherichia coli is mediated by an interaction of H-NS protein with the LT A-subunit DNA. J Bacteriol 180:3715–3718
Viazis S, Diez-Gonzalez F (2011) Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. The twentieth century’s emerging foodborne pathogen: a review, 1st edn. Adv Agron. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-387689-8.00006-0
Wang G, Clark CG, Rodgers FG (2002) Detection in Escherichia coli of the genes encoding the major virulence factors, the genes defining the O157:H7 serotype and components of the type 2 Shiga toxin family by multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol 40:3613–3619
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. W. Khan of the Department of Microbiology, Stellenbosch University, South Africa, and Dr. T. G. Barnard of the Water and Health Research Group, University of Johannesburg, South Africa, for providing them with the reference strained for this work. This work received financial support from the Water Research Commission (WRC), South Africa (Project Nos. K5/2169 and K5/2147), the National Research Foundation (NRF) and the Tshwane University of Technology (TUT). However, opinions expressed and conclusions arrived at are those of the authors and are not necessarily to be attributed to the WRC, NRF or TUT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abia, A.L.K., Ubomba-Jaswa, E. & Momba, M.N.B. Occurrence of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli virulence genes in water and bed sediments of a river used by communities in Gauteng, South Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 15665–15674 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6762-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6762-6