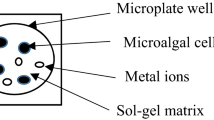
Abstract
Anthropic activities generate contaminants, as pesticides and other pollutants, in the aquatic environment which present a real threat to ecosystems and human health. Thus, monitoring tools become essential for water managers to detect these chemicals before the occurrence of adverse effects. In this aim, algal cell biosensors, based on photosystem II activity measurement, have been designed for several years in previous studies. In this work, we study a new immobilization technique of algal cells in the aim of improving the performance of these biosensors. Immobilization was here achieved by encapsulation in a hybrid alginate/silica translucid hydrogel. The feasibility of this process was here assessed, and the biosensor designed was tested on the detection of chemicals in urban rainwaters.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalderink RH, Van Duin EHS, Peels CE, Scholten MJM (1990) Some characteristics of run-off quality from a separated sewer system in Leleystad, the Netherlands. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Urban Storm Drainage, Osaka, Japan, pp 427–432
AFNOR (1980) Détermination de l’inhibition de croissance de Scenedesmus subspicatus par une substance. Norme experimentale NT90-304; Association Française de Normalisation, Paris, France
Angerville R (2009) Evaluation des risques écotoxicologiques liés au déversement de Rejets Urbains par Temps de Pluie (RUTP) dans les cours d’eau: Application à une ville française et à une ville haïtienne. Thèse de doctorat, Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Lyon, 479 p
Armstrong JW, Thom RM, Chew KK (1980) Impact of a combined sewer overflow on the abundance, distribution and community structure of subtidal benthos. Mar Environ Res 4:3–23
Aryal R, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, Naidu R (2010) Urban stormwater quality and treatment. Korean J Chem Eng 27:1343–1359
Aubertot JN (2005) Pesticides, agriculture et environment. Rapport, INRA et Cemagref, France, p 64
Ban-Dar H, Yuh-Shein L, Yuh-Ren J (1989) A method for analysis of fluorescence curve from DCMU-poisoned chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 975:44–49
Bertrand-Krajewski JL, Becouze C, Dembélé A, Coquery M, Cren-Olivé C, Barillon B, Dauthuille P, Chapgier J, Grenier-Loustalot MF, Marin P (2008) Priority pollutants in stormwater: the ESPRIT project. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Edinburgh, UK, 31 augt-5 sept 2008
Chouteau C, Dzyadevych S, Chovelon JM, Durrieu C (2004) Development of novel conductometric biosensors based on immobilised whole cell Chlorella vulgaris microalgae. Biosens Bioelectron 19(9):1089–1096
Chouteau C, Dzyadevych S, Durrieu C, Chovelon JM (2005) A bi-enzymatic whole cell conductometric biosensor for heavy metal ions and pesticides detection in water sample. Biosens Bioelectron 21(2):273–281
Ciucu A, Lupu A, Pirvutoi S, Palleschi G (2001) Biosensors for heavy metals determination based on enzyme inhibition. Chem Mater Sci 63:33–44
Directive 2009/128/CE, Règlement (CE) n°1107/2009, Directive 2009/127/CE et Règlement (CE n°1185/2009)
Draber W, Tietjen K, Kluth JF, Trebst A (1991) Herbicides in photosynthesis research. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 30:1621–1633
Dubois A, Lacouture L (2011) Rapport du commissariat général du développement durable, MEDDTL
Dzyadevych SV, Soldatkin AP, Korpan YI, Arkhypova VN, EL’skaya AV, Chovelon JM, Martelet C, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2003) Biosensors based on enzyme field-effect transistors for determination of some substrates and inhibitors. Anal BioanalChem 377:496–506
Fai PB, Grant A, Reid B (2007) Chlorophyll-a fluorescence as a biomarker for rapid toxicity assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(7):1520–1531
Ferro Y, Perulloni M, Jobbagy M, Bilmes SA, Durrieu C (2012) Development of a biosensor for environmental monitoring based on microalgae immobilized in silica hydrogel. Sensors 12:16879–16891
Giardi MT, Koblizek M, Masojidek J (2001) Photosystem II based biosensors for the detection of pollutants. Biosens Bioelectron 16:1027–1033
Gorman DS, Levine RP (1965) Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 54:1665–1669
Moreland DE (1980) Mechanisms of action of herbicides. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:597–638
Perullini M, Jobbágy M, Soler-Illia GJAA, Bilmes SA (2005) Cell growth at cavities created inside silica monoliths synthesized by sol-gel. Chem Mater 78:3806–3808
Perullini M, Rivero MM, Jobbágy M, Mentaberry A, Bilmes SA (2007) Plant cell proliferation inside an inorganic host. J Biotechnol 127:542–548
Samson G, Popovic R (1988) Use of algal fluorescence for determination of phytotoxicity of heavy metals and pesticides as environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 16:272–278
Sicard C, Perullini M, Spedalieri C, Coradin T, Brayner R, Livage J, Jobbagy M, Bilmes SA (2011) CeO2 nanoparticles for the protection of photosynthetic organisms immobilized in silica gels. Chem Mater 23:1374–1378
Tran-Minh C (1993) Biosensors. Chapman & Hall, London
Acknowledgments
This work has been financially supported by ECOS SUD (University of Paris 13), MINCYT (Argentina), L’Office national de l’eau et des milieux aquatiques (France), and CONICET (GI-PIP 11220110101020, UBACyT 20020130100048BA, ANPCyT-PICT 2012-1167 and 2013-2045) from Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durrieu, C., Ferro, Y., Perullini, M. et al. Feasibility of using a translucid inorganic hydrogel to build a biosensor using immobilized algal cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 9–13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5023-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5023-4