Abstract
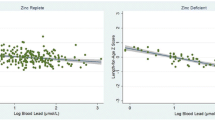
Many studies indicate that lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) exposure may alter bone development through both direct and indirect mechanisms, increasing the risk of osteoporosis later in life. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between Pb and Cd exposure, physical growth, and bone and calcium metabolism in children of an electronic waste (e-waste) processing area. We recruited 246 children (3–8 years) in a kindergarten located in Guiyu, China. Blood lead levels (BLLs) and blood cadmium levels (BCLs) of recruited children were measured as biomarkers for exposure. Serum calcium, osteocalcin, bone alkaline phosphatase, and urinary deoxypyridinoline were used as biomarkers for bone and calcium metabolism. Physical indexes such as height, weight, and head and chest circumference were also measured. The mean values of BLLs and BCLs obtained were 7.30 μg/dL and 0.69 μg/L, respectively. The average of BCLs increased with age. In multiple linear regression analysis, BLLs were negatively correlated with both height and weight, and positively correlated with bone resorption biomarkers. Neither bone nor calcium metabolic biomarkers showed significant correlation with cadmium. Childhood lead exposure affected both physical development and increased bone resorption of children in Guiyu. Primitive e-waste recycling may threaten the health of children with elevated BLL which may eventually cause adult osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfvén T, Elinder CG, Carlsson MD, Grubb A, Hellström L, Persson B, Pettersson C, Spang G, Schütz A, Järup L (2000) Low-level cadmium exposure and osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 15:1579–1586
Alfvén T, Järup L, Elinder C (2002) Cadmium and lead in blood in relation to low bone mineral density and tubular proteinuria. Environ Health Perspect 110:699–702
Barry P (1975) A comparison of concentrations of lead in human tissues. Br J Ind Med 32:119–139
Barry PSI, Mossman DB (1970) Lead concentration in human tissues. Br J Ind Med 27:339–351
Berglund M, Akesson A, Bjellerup P, Vahter M (2000) Metal–bone interactions. Toxicol Lett 112:219–225
Campbell J, Rosier R, Novotny L, Puzas J (2004) The association between environmental lead exposure and bone density in children. Environ Health Perspect 112:12001203
Carmouche JJ, Puzas JE, Zhang X, Tiyapatanaputi P, Cory-Slechta DA, Gelein R, Zuscik M, Rosier RN, Boyce BF, O'Keefe RJ, Schwarz EM (2005) Lead exposure inhibits fracture healing and is associated with increased chondrogenesis, delay in cartilage mineralization, and a decrease in osteoprogenitor frequency. Environ Health Perspect 113:749–755
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2005) Preventing lead poisoning in young children. CDC, Atlanta
Chalkley SR, Richmond J, Barltrop D (1998) Measurement of vitamin D3 metabolites in smelter workers exposed to lead and cadmium. Occup Environ Med 55:446–452
De Burbure C, Buchet JP, Leroyer A, Nisse C, Haguenoer JM, Mutti A, Smerhovsky Z, Cikrt M, Trzcinka-Ochocka M, Razniewska G, Jakubowski M, Bernard A (2006) Renal and neurologic effects of cadmium, lead, mercury, and arsenic in children: evidence of early effects and multiple interactions at environmental exposure levels. Environ Health Perspect 114:584–590
Deng WJ, Louie PKK, Liu WK, Bi XH, Fu JM, Wong MH (2006) Atmospheric levels and cytotoxicity of PAHs and heavy metals in TSP and PM2.5 at an electronic waste recycling site in southeast China. Atmos Environ 40:6945–6955
Escribano A, Revilla M, Hernandez ER, Seco C, González-Riola J, Villa LF, Rico H (1997) Effect of lead on bone development and bone mass: a morphometric, densitometric, and histomorphometric study in growing rats. Calcif Tissue Int 60:200–203
Finkelstein Y, Markowitz ME, Rosen JF (1998) Low-level lead-induced neurotoxicity in children: an update on central nervous system effects. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 27:168–176
Frisancho A, Ryan A (1991) Decreased stature associated with moderate blood lead concentrations in Mexican-American children. Am J Clin Nutr 54:516–519
Goyer R, Epstein S, Bhattacharyya M, Korach KS, Pounds J (1994) Environmental risk factors for osteoporosis. Environ Health Perspect 102:390–394
Gruber H, Gonick H, Khalil-Manesh F, Sanchez TV, Motsinger S, Meyer M, Sharp CF (1997) Osteopenia induced by long-term, low-and high-level exposure of the adult rat to lead. Miner Electrolyte Metab 23:65–73
Guo Y, Huo X, Li Y, Wu K, Liu J, Huang J, Zheng G, Xiao Q, Yang H, Wang Y, Chen A, Xu X (2010) Monitoring of lead, cadmium, chromium and nickel in placenta from an e-waste recycling town in China. Sci Total Environ 408:3113–3117
Hu H, Rabinowitz M, Smith D (1998) Bone lead as a biological marker in epidemiologic studies of chronic toxicity: conceptual paradigms. Environ Health Perspect 106:1–8
Huo X, Peng L, Xu X, Zheng L, Qiu B, Qi Z, Zhang B, Han D, Piao Z (2007) Elevated blood lead levels of children in Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling town in China. Environ Health Perspect 115:1113–1117
Järup L, Alfvén T (2004) Low level cadmium exposure, renal and bone effects—the OSCAR study. Biometals 17:505–509
Järup L, Kesson A (2009) Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:201–208
Kim R, Hu H, Rotnitzky A, Bellinger D, Needleman H (1995) A longitudinal study of chronic lead exposure and physical growth in Boston children. Environ Health Perspect 103:952–957
Li Y, Huo X, Liu J, Peng L, Li W, Xu X (2011) Assessment of cadmium exposure for neonates in Guiyu, an electronic waste pollution site of China. Environ Monit Assess 177:343–351
Li Y, Xu X, Wu K, Chen G, Liu J, Chen S, Gu C, Zhang B, Zheng L, Zheng M, Huo X (2008) Monitoring of lead load and its effect on neonatal behavioral neurological assessment scores in Guiyu, an electronic waste recycle town in China. J Environ Monit 10:1233–1238
Liu J, Xu X, Wu K, Piao Z, Huang J, Guo Y, Li W, Zhang Y, Chen A, Huo X (2011) Association between lead exposure from electronic waste recycling and child temperament alterations. Neurotoxicology 32:458–464
Min KB, Min JY, Cho SI, Kim R, Kim H, Paek D (2008) Relationship between low blood lead levels and growth in children of white-collar civil servants in Korea. Int Hyg Environ Health 211:82–87
Miyahara T, Komiyama H, Miyanishi A, Takata M, Nagai M, Kozuka H, Hayashi T, Yamamoto M, Ito Y, Odake H et al (1995) Stimulative effects of lead on bone resorption in organ culture. Toxicology 97:191–197
Moncrieff AA, Koumides OP, Clayton BE, Patrick AD, Renwick AGC, Roberts GE (1964) Lead poisoning in children. Arch Dis Childh 39:1–13
Nash D, Magder LS, Sherwin R, Rubin RJ, Silbergeld EK (2004) Bone density-related predictors of blood lead level among peri- and postmenopausal women in the United States: the third national health and nutrition examination survey, 1988–1994. Am J Epidemiol 160:901–911
Ohta H, Ichikawa M, Seki Y (2002) Effects of cadmium intake on bone metabolism of mothers during pregnancy and lactation. Tohoku J Exp Med 196:33–42
Olympio KP, Gonçalves C, Günther WM, Bechara EJ (2009) Neurotoxicity and aggressiveness triggered by low-level lead in children: a review. Rev Panam Salud Publica 26:266–275
Pounds J, Long G, Rosen J (1991) Cellular and molecular toxicity of lead in bone. Environ Health Perspect 91:17–32
Rignell-Hydbom A, Skerfving S, Lundh T, Lindh CH, Elmståhl S, Bjellerup P, Jünsson BA, Strümberg U, Akesson A (2009) Exposure to cadmium and persistent organochlorine pollutants and its association with bone mineral density and markers of bone metabolism on postmenopausal women. Environ Res 109:991–996
Rosen JF, Chesney RW, Hamstra A, DeLuca HF, Mahaffey KR (1980) Reduction in 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D in children with increased lead absorption. N Engl J Med 302:1128–1131
Schutte R, Nawrot TS, Richart T, Thijs L, Vanderschueren D, Kuznetsova T, Van Hecke E, Roels HA, Staessen JA (2008) Bone resorption and environmental exposure to cadmium in women: a population study. Environ Health Perspect 116:777–783
Shen X, Wu S, Yan C (2001) Impacts of low-level lead exposure on development of children: recent studies in China. Clin Chim Acta 313:217–220
Sughis M, Penders J, Haufroid V, Nemery B, Nawrot TS (2011) Bone resorption and environmental exposure to cadmium in children: a cross-sectional study. Environ Health 10:104
Trzcinka-Ochocka M, Jakubowski M, Szymczak W, Janasik B, Brodzka R (2010) The effects of low environmental cadmium exposure on bone density. Environ Res 110:286–293
WHO (1995) Inorganic lead. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wong CS, Wu SC, Duzgoren-Aydin NS, Aydin A, Wong MH (2007) Trace metal contamination of sediments in an e-waste processing village in China. Environ Pollut 145:434–442
Yu XZ, Gao Y, Wu SZ, Zhang HB, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2006) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils at Guiyu area of China, affected by recycling of electronic waste using primitive technologies. Chemosphere 65:1500–1509
Zahran S, Mielke HW, Weiler S, Berry KJ, Gonzales C (2009) Children's blood lead and standardized test performance response as indicators of neurotoxicity in metropolitan New Orleans elementary schools. Neurotoxicology 30:888–897
Zheng G, Xu X, Li B, Wu K, Yekeen TA, Huo X (2012) Association between lung function in school children and exposure to three transition metals from an e-waste recycling area. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. doi:10.1038/jes.2012.84
Zheng L, Wu K, Li Y, Qi Z, Han D, Zhang B, Gu C, Chen G, Liu J, Chen S, Xu X, Huo X (2008) Blood lead and cadmium levels and relevant factors among children from an e-waste recycling town in China. Environ Res 108:15–20
Zuscik MJ, Ma L, Buckley T, Puzas JE, Drissi H, Schwarz EM, O'Keefe RJ (2007) Lead induces chondrogenesis and alters transforming growth factor-beta and bone morphogenetic protein signaling in mesenchymal cell populations. Environ Health Perspectives 115:1276–1282
Zuscik MJ, Pateder DB, Puzas JE, Schwarz EM, Rosier RN, O'Keefe RJ (2002) Lead alters parathyroid hormone-related peptide and transforming growth factor-beta1 effects and AP-1 and NF-kappaB signaling in chondrocytes. J Orthop Res 20:811–818
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21177080). We wish to thank Dr. Stanley Li Lin for his constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Hui Yang and Xia Huo contributed equally to this work and are Co- First authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Huo, X., Yekeen, T.A. et al. Effects of lead and cadmium exposure from electronic waste on child physical growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 4441–4447 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1366-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1366-2