Abstract
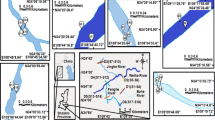
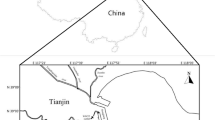
The levels of hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs) in the sediments from Haihe Plain, China, were measured by a gas chromatograph with a 63Ni microelectron capture detector. The spatial distributions, possible sources, and potential ecological risks of these compounds were analyzed. The residual level of total HCHs was 33.84 ± 173.37 ng g−1 dry weight (d.w.) with ranges of 0.13 ∼ 1,107.41 ng g−1 d.w. Much higher ΣHCH contents were found in the lower reaches of some rivers and in the mouth of the main stream receiving tributaries. The predominance of β-HCH (36 %) in the sediments was similar to that in the soils from Haihe Plain. The high percentages of γ-HCH (23–41 %) could be detected at 25 % of the sampling sites in the seven river systems. There were statistically significant positive relationships between the contents of HCHs and total organic carbon. Lindane was identified as the primary source of HCHs in the sediments, and it seemed that recent illegal lindane inputs still existed in some areas in Haihe Plain, as indicated by the α-/γ-HCH and β-/(α + γ)-HCH ratios. Severe potential ecological risks of γ-HCH to benthic organisms at some sampling sites were found based on the consensus-based sediment quality guidelines.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accardi-Dey A, Gschwend PM (2002) Assessing the combined roles of natural organic matter and black carbon as sorbents in sediments. Environ Sci Technol 36:21–29
Arias AH, Pereyra MT, Marcovecchio JE (2011) Multi-year monitoring of estuarine sediments as ultimate sink for DDT, HCH, and other organochlorinated pesticides in Argentina. Environ Monit Asses 172:17–32
Carvalho FP, Villeneuve JP, Cattini C, Tolosa I, Thuan DD, Nhan DD (2008) Agrochemical and polychlorobyphenyl (PCB) residues in the Mekong River delta, Vietnam. Marin Pollut Bull 56:1476–1485
Chau KW (2005) Characterization of transboundary POP contamination in aquatic ecosystems of Pearl River delta. Marin Pollut Bull 51:960–965
Chen JW, Liu C, Yang ZF, Wang JY (2008) Residues and characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in surface water in the suburb of Beijing. Earth Sci Front 15(5):242–247
Chessells MJ, Hawker DW, Connell DW (1988) Factors influencing the distribution of lindane and isomers in soil of an agricultural environment. Chemosphere 17:1741–1749
Gong ZM, Xu FL, Dawson R, Tao S (2004) Residues of Hexachlorocyclohexane isomers and their distribution characters in soils in Tianjin area, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:432–437
Hong H, Chen W, Xu L (1999) Distribution and fate of organochlorine pollutions in the Pearl River Estuary. Marin Pollut Bull 29:376–382
Isaacon PJ, Frinj CR (1984) Nonreversible sorption of phenolic com-pounds by sediments fractions: the role of sediment organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 18(1):43–48
Iwata H, Tanabe S, Tatsukawa R (1993) A new view on the divergence of HCH isomer compositions in oceanic air. Mar Pollut Bull 26:302–305
Iwata H, Tanabe S, Ueda K, Tatsukawa R (1995) Persistent organochlorine residues in air, water, sediments, and soils from the Lake Baikal region, Russia. Environ Sci Technol 29:792–801
Jeffrey WT, Upal G (2002) Particle-scale understanding of the bioavailability of PAHs in sediment. Environ Sci Technol 36(3):477–483
Jin XC (1991) Organic Pollutants in Sediments. Science Press, Bijing
Johnson WP, Amy GL (1995) Facilitated transport and enhanced de-sorption of PAHs by natural organic in aquifer sediments. Environ Sci Technol 29:807–817
Johnson MD, Huang W, Weber WJ (2001) A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments: 13. Simulated diagenesis of natural sediment organic matter and its impact on sorption/desorption equilibria. Environ Sci Technol 35(8):1680–1687
Karapanagioti HK, Kleineidam S (2000) Impacts of heterogeneous organic matter on phenanthrene sorption: equilibrium and kinetic studies with aqutifer material. Environ Sci Technol 34:406–414
Law SA, Diamond ML, Helm PA, Jantunen LM, Alaee M (2001) Factors affecting the occurrence and enantiomeric degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in northern and temperate aquatic systems. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2690–2698
Leppanen MT, Kukkonen JVK (2000) Effect of sediment-chemical contact time on availability of sediment-associated pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene to oligochaete worms and semi-permeable membrane devices. Aquat Toxicol 49(4):227–241
Li XH, Zhu YF, Liu XF (2006) Distribution of HCHs and DDTs in soils from Beijing City, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:329–336
Li J, Zhang G, Guo LL, Xu WH, Li XD, Lee CSL, Ding AJ, Wang T (2007) Organochlorine pesticides in the atmosphere of Guangzhou and Hong Kong: Regional sources and long-range atmospheric transport. Atmos Environ 41:3889–3903
Liu WX, Li Y, Zuo Q, Liu SZ, Tao S, Wang LG, Wang JF, Tian ZF, Ji ZG (2008) Residual characteristics of HCHs and DDTs in surface soils from the western zone of Bohai Bay. Acta Sci Circumst 28(1):142–149
Long ER, Macdonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manag 19:81–97
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Manz M, Wenzel KD, Dietze U (2001) Persistent organic pollutants in agricultural soils of central Germany. Sci Total Environ 277:187–198
Perminova IV, Gerchishcheva NY (1999) Relationships between structure and binding affinity of humic substances for polycyclic aro-matic hydrocarbons: relevance of molecular descriptors. Environ Sci Technol 33(21):3781–3787
Persaud D, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Water Resources Branch. Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Toronto, p 27
Qiu YW, Zhang G, Guo LL, Cheng HR, Wang WX, Li XD, Wai OWH (2009) Current status and historical trends of organochlorine pesticides in the ecosystem of Deep Bay, South China. Estuarine Coast and Shelf Sci 85:265–272
Shi Y, Meng F, Guo F (2005) Residues of organic chlorinated pesticides in agricultural soils of Beijing, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 49:37–43
Song J, Peng P, Huang W (2002) Black carbon and kerogen in soils and sediments: 1. Quantification and characterization. Environ Sci Technol 36:3960–3967
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (SCPOPs) (2009) Guidance material on new POPs. http://chm.pops.int/Programmes/NewPOPs/Publications/tabid/695/ctl/Download/mid/2-784/language/en-US/Default.aspx?id = 1. Accessed 2011
Sun JH, Feng JL, Liu Q, Li QL (2010) Distribution and sources of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sediments from upper reach of Huaihe River, East China. J Hazard Mater 184:141–146
Tang ZW, Yang ZF, Shen ZY, Niu JF, Liao RF (2007) Distribution and sources of organochlorine pesticides in sediments from typical catchment of the Yangtze River, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53:303–312
Tao S, Xu FL, Wang XJ, Liu WX, Gong ZM, Fang JY, Zhu LZ, Luo YM (2005) Organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soil and vegetables from Tianjin, China. Environ Sci Technol 39:2494–2499
Tao S, Liu WX, Li Y, Yang Y, Zuo Q, Li BG, Cao J (2008) Organochlorine pesticides contaminated surface soil as reemission source in the Haihe Plain, China. Environ Sci Technol 42:8395–8400
Upal G, Jeffrey WT (2001) Particle-scale investigation of PAH desorption kinetics and thermodynamics from sediments. Environ Sci Technol 35(17):3468–3475
Walker K, Vallero AD, Lewis GR (1999) Factors influence the distribution of lidane and other hexachlorocyclohexance in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 33(24):4372–4378
Wan Y, Hu JY, Liu JL, An W, Tao S, Jia ZB (2005) Fate of DDT-related compounds in Bohai Bay and its adjacent Haihe Basin, North China. Mari Pollut Bull 50:439–445
Wang LS (1990) Organic Pollutant Chenmistry. Science Press, Bijing
Wang ZY, Yan W, Chi JS, Zhang G (2008) Spatial and vertical distribution of organochlorine pesticides in sediments from Daya Bay, South China. Mari Pollut Bull 56:1578–1585
Willett KL, Ulrich EM, Hites RA (1998) Differential toxicity and environmental fates of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers. Environ Sci Technol 32:2197–2207
Wu Y, Zhang J, Zhou Q (1999) Persistent organochlorine residues in sediments from Chinese river/estuary systems. Environ Pollut 10:143–150
Wurl O, Obbard JP (2005) Organochlorine pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in Singapore’s coastal marine sediments. Chemosphere 58:925–933
Xing BS, Pignatello JJ (1998) Competitive sorption between 1,3-dichlorobenzene or 2,4-dichlorophenol and natural aromatic acids in soil organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 32:614–619
Xu D, Deng L, Chai Z (2004) Organohalogenated compounds in pine needles from Beijing City, China. Chemosphere 57:1343–1353
Xu D, Dan M, Song Y (2005) Concentration characteristics of extractable organohalogens in PM2. 5 and PM10 in Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 39:4119–4412
Xu GF, Ma LL, Xu DD, Li SZ, Yao DX, Shi WQ (2009) Characteristics and sources of dissolved organochlorine pesticides in the rainwater in Beijing. China Environ Sci 29(11):1153–1157
Yang RQ, Lv AH, Shi JB, Jiang GB (2005) The levels and distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sediments from the Haihe River, China. Chemosphere 61:347–354
Yu H, Zhu Z, Zhao X (2003) Levels of organochlorine pesticides in Beijing human milk. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:193–197
Yu G, Niu JF, Huang J (2005) Persistant organic pollutants—new gloable environmental problems. Science Press, Bijing
Zhang ZL, Huang J, Yu G (2004) Occurrence of PAH, PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in Tonghui River of Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 130:249–261
Zhao ZH, Zhang L, Wu JL, Fan CX (2009) Distribution and bioaccumulation of organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments and benthic organisms from Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 77:1191–1198
Zhao L, Hou H, Zhou YY, Xue ND, Li HY, Li FS (2010) Distribution and ecological risk of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments from Haihe River and Haihe Estuary Area, China. Chemosphere 78:1285–1293
Acknowledgments
Funding was provided by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (no. 40725004), the Key Project of the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (41030529), the Ministry of Environmental Protection (201009032), and the Ministry of Education (20100001110035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, FL., Kong, XZ., He, W. et al. Distributions, sources, and ecological risks of hexachlorocyclohexanes in the sediments from Haihe Plain, Northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 2009–2019 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1226-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1226-0