Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to apply an analogue of bombesin, NOTA-AMBA, labeled with Co-55 or Ga-68, for preclinical imaging of prostate cancer.
Procedures
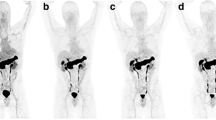
The peptide NOTA-AMBA was labeled with Ga-68 or Co-55 by microwave irradiation. Biodistribution in xenograft mice (PC3) was performed at 1, 4, and 24 h (only cobalt at 24 h) using a fixed amount of peptide. Four weeks post-inoculation, xenograft mice were positron emission tomography/X-ray computed tomography scanned after tail vein injection of [68Ga]NOTA-AMBA or [55Co]NOTA-AMBA.
Results
Labeling with Ga-68 and Co-55/57 was achieved in yields greater than 90 %. A radiochemical purity (RCP) of 95 and 90 % were obtained for Ga-68 and Co-55, respectively. Both radiopeptides showed high uptake in the intestines, stomach, pancreas, and in the tumor ([68Ga]NOTA-AMBA, 10.3 %ID/g at 1 h to 6.4 %ID/g at 4 h; [57Co]NOTA-AMBA, 8.2 %ID/g at 1 h to 5.3%ID/g at 24 h). Normal tissue cleared over time improving tumor-to-background ratios.
Conclusions
NOTA-AMBA was labeled in high yields and RCP with Ga-68 and Co-55/57. High tumor uptake in a subcutaneous mouse prostate cancer model was observed. At 24 h, [55/57Co]NOTA-AMBA showed better tumor-to-organ ratios than [68Ga]NOTA-AMBA at both 1 and 4 h post-injection. Hence, for imaging, [55Co]NOTA-AMBA was found to be superior compared to [68Ga]NOTA-AMBA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananias H, de Jong I, Dierckx R et al (2008) Nuclear imaging of prostate cancer with gastrin-releasing-peptide- receptor targeted radiopharmaceuticals. Curr Pharm Des 14:3033–3047
Fani M, Maecke HR, Okarvi SM (2012) Radiolabeled peptides: valuable tools for the detection and treatment of cancer. Theranostics 2:481–501
Fani M, Maecke HR (2012) Radiopharmaceutical development of radiolabelled peptides. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39(Suppl 1):S11–S30
Schottelius M, Wester H-J (2009) Molecular imaging targeting peptide receptors. Methods 48:161–177
Schroeder RPJ, van Weerden WM, Bangma C et al (2009) Peptide receptor imaging of prostate cancer with radiolabelled bombesin analogues. Methods 48:200–204
Smith CJ, Volkert WA, Hoffman TJ (2005) Radiolabeled peptide conjugates for targeting of the bombesin receptor superfamily subtypes. Nucl Med Biol 32:733–740
Varasteh Z, Velikyan I, Lindeberg G et al (2013) Synthesis and characterization of a high-affinity NOTA-conjugated bombesin antagonist for GRPR-targeted tumor imaging. Biocojugate Chem 24:1144–1153
Gourni E, Mansi R, Jamous M et al (2014) N-terminal modifications improve the receptor affinity and pharmacokinetics of radiolabeled peptidic gastrin-releasing peptide receptor antagonists: examples of 68Ga- and 64Cu-labeled peptides for PET imaging. J Nucl Med 55:1719–1725
Kroll C, Mansi R, Braun F et al (2013) Hybrid bombesin analogues: combining an agonist and an antagonist in defined distances for optimized tumor targeting. J Am Chem Soc 135:16793–16796
Mansi R, Wang X, Forrer F et al (2009) Evaluation of a 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-conjugated bombesin-based radioantagonist for the labeling with single-photon emission computed tomography, positron emission tomography, and therapeutic radionuclides. Clin Cancer Res 15:5240–5249
Mansi R, Wang X, Forrer F et al (2011) Development of a potent DOTA-conjugated bombesin antagonist for targeting GRPr-positive tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:97–107
Breeman WA, Hofland LJ, de Jong M et al (1999) Evaluation of radiolabelled bombesin analogues for receptor-targeted scintigraphy and radiotherapy. Int J Cancer 81:658–665
Liu Y, Hu X, Liu H et al (2013) A comparative study of radiolabeled bombesin analogs for the PET imaging of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med 54:2132–2138
Asti M, Iori M, Capponi PC et al (2014) Influence of different chelators on the radiochemical properties of a 68-gallium labelled bombesin analogue. Nucl Med Biol 41:24–35
Koumarianou E, Loktionova NS, Fellner M et al (2012) 44Sc-DOTA-BN[2-14]NH2 in comparison to 68Ga-DOTA-BN[2-14]NH2 in pre-clinical investigation. Is 44Sc a potential radionuclide for PET? Appl Radiat Isot 70:2669–2676
Gourni E, Del Pozzo L, Kheirallah E et al (2015) Copper-64 labeled macrobicyclic sarcophagine coupled to a GRP receptor antagonist shows great promise for PET imaging of prostate cancer. Mol Pharm 12:2781–2790. doi:10.1021/mp500671j
Pan D, Xu YP, Yang RH et al (2014) A new (68)Ga-labeled BBN peptide with a hydrophilic linker for GRPR-targeted tumor imaging. Amino Acids 46:1481–1489
Schroeder RPJ, Müller C, Reneman S et al (2010) A standardised study to compare prostate cancer targeting efficacy of five radiolabelled bombesin analogues. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:1386–1396
Heppeler A, André JP, Buschmann I et al (2008) Metal-ion-dependent biological properties of a chelator-derived somatostatin analogue for tumour targeting. Chemistry 14:3026–3034
Braad PEN, Hansen SB, Thisgaard H, Høilund-Carlsen PF (2015) PET imaging with the non-pure positron emitters: 55Co, 86Y and 124I. Phys Med Biol 60:3479–3497
Thisgaard H, Olesen ML, Dam JH (2011) Radiosynthesis of 55Co- and 58mCo-labelled DOTATOC for positron emission tomography imaging and targeted radionuclide therapy. J Label Compd Radiopharm 54:758–762
Thisgaard H, Olsen BB, Dam JH et al (2014) Evaluation of cobalt-labeled octreotide analogs for molecular imaging and auger electron-based radionuclide therapy. J Nucl Med 55:1311–1316
Waser B, Eltschinger V, Linder K et al (2007) Selective in vitro targeting of GRP and NMB receptors in human tumours with the new bombesin tracer 177Lu-AMBA. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34:95–100
Schroeder RPJ, van Weerden WM, Krenning EP et al (2011) Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-based targeting using bombesin analogues is superior to metabolism-based targeting using choline for in vivo imaging of human prostate cancer xenografts. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:1257–1266
Reubi JC, Wenger S, Schmuckli-maurer J et al (2002) Bombesin receptor subtypes in human cancers: detection with the universal radioligand 125I-[d-TYR6, β-ALA11, PHE13, NLE14] bombesin (6–14). Clin Cancer Res 8:1139–1146
Cornelio DB, Roesler R, Schwartsmann G (2007) Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor as a molecular target in experimental anticancer therapy. Ann Oncol 18:1457–1466
Cagnolini A, Chen J, Ramos K et al (2010) Automated synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of [(68)Ga]Ga-AMBA, and the synthesis and characterization of (nat)Ga-AMBA and [(67)Ga]Ga-AMBA. Appl Radiat Isot 68:2285–2292
Lantry LE, Cappelletti E, Maddalena ME et al (2006) 177Lu-AMBA: synthesis and characterization of a selective 177Lu-labeled GRP-R agonist for systemic radiotherapy of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med 47:1144–1152
Liu I, Chang C-H, Ho C et al (2010) Multimodality imaging and preclinical evaluation of 177Lu-AMBA for human prostate tumours in a murine model. Anticancer Res 30:4039–4048
Ho C-L, Liu I-H, Wu Y-H, et al. (2011) Molecular imaging, pharmacokinetics, and dosimetry of In-AMBA in human prostate tumor-bearing mice. J Biomed Biotechnol 1
Wild D, Frischknecht M, Zhang H et al (2011) Alpha- versus beta-particle radiopeptide therapy in a human prostate cancer model (213Bi-DOTA-PESIN and 213Bi-AMBA versus 177Lu-DOTA-PESIN). Cancer Res 71:1009–1018
De Blois E, Schroeder RPJ, de Ridder CMA, van Weerden WM, Breeman WAP, de Jong M (2013) Improving radiopeptide pharmacokinetics by adjusting experimental conditions for bombesin receptor-mediated imaging of prostate cancer. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 57:1–9
Ciatto S, Zappa M, Bonardi R, Gervasi G (2000) Prostate cancer screening: the problem of overdiagnosis and lessons to be learned from breast cancer screening. Eur J Cancer 36:1347–1350
Acknowledgments
The bioimaging experiments reported in this paper were performed at DaMBIC, a bioimaging research core facility, at the University of Southern Denmark. DaMBIC was established by an equipment grant from the Danish Agency for Science Technology and Innovation and by internal funding from the University of Southern Denmark.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dam, J.H., Olsen, B.B., Baun, C. et al. In Vivo Evaluation of a Bombesin Analogue Labeled with Ga-68 and Co-55/57. Mol Imaging Biol 18, 368–376 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-015-0911-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-015-0911-z