Abstract
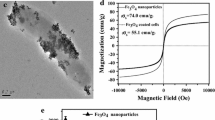
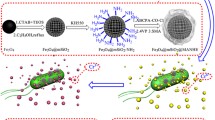
Biodesulfurization activity can be enhanced by assembling nano-γ-Al2O3 particles on the magnetic immobilized Rhodococcus erythropolis LSSE8-1-vgb. The cells can be collected and reused conveniently by an external magnetic field. Firstly, cells were magnetic immobilized by coating with Fe3O4 nano-particles. The optimal ratio of cells to magnetic Fe3O4 nano-particles was determined to be 50:1 (g/g). Then nano-γ-Al2O3 adsorbents were assembled onto the cells to enhance the desulfurization activity. The nano-γ-Al2O3 adsorbent had the largest pore volume as well as specific surface area, and the strongest electrostatics interaction with microbial cell, and cells assembled with this nano-adsorbent performed the highest desulfurization activity. The activity of magnetic immobilized cells assembled with adsorbents was tested in desulfurization of model oil. The desulfurization rate was raised by nearly 20% when the amount ratio of magnetic particles to adsorbents was 1:5 (g/g). These cells can be reused. The activity decreased less than 10% through out three desulfurization-activation-reuse recycles.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herna’ndez-Maldonado AJ, Yang RT (2003) Desulfurization of liquid fuels by adsorption via π-complexation with Cu (I)-Y and Ag-Y zeolites. Ind Eng Chem Res 42:123–129
Herna’ndez-Maldonado AJ, Yang RT (2004a) Desulfurization of diesel fuels by adsorption via π-complexation with vapor-phase exchanged Cu (I)-Y zeolites. J Am Chem Soc 126:992–993
Herna’ndez-Maldonado AJ, Yang RT (2004b) Desulfurization of transportation fuels by adsorption. Catal Rev 46:111–150
Herna’ndez-Maldonado AJ, Stamatis SD, Yang RT (2004) New sorbents for desulfurization of diesel fuels via π complexation: layered beds and regeneration. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:769–776
John JK (2006) Microbial biocatalyst developments to upgrade fossil fuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:305–314
Konishi J, Ishii Y, Onaka T, Okumura K, Suzuki M (1997) Thermophilic carbon-sulfur bond targeted biodesulfurization. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3164–3169
Li WL, Tang H, Liu QF, Xing JM, Li Q, Wang D, Yang MH, Li X, Liu HZ (2009) Deep desulfurization of diesel by integrating adsorption and microbial method. Biochem Eng J 44:297–301
Liu X, Kaminski MD, Guan Y, Chen H, Liu H, Rosengart AJ (2006) Preparation and characterization of hydrophobic superparamagnetic magnetite gel. J Magn Magn Mater 306:248–253
Lzumi Y, Ohsjiro T, Ogino H, Hine Y, Shimao M (1994) Selective desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:223–226
Mikhail S, Zaki T, Khalil L (2002) Desulfurization by an economically adsorption technique. Appl Catal A-Gen 227:265–278
Morio K, Keizo H, Osamu Y, Kazuaki H, Yoshitaka I, Kazuhito F, Hiroshi S, Kenji M (2001) Kinetics analysis of microbial desulfurization of model and light gas oil containing multiple alkyldibenzothiophene. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:298–304
Nekodzuka S, Toshiaki N, Nakajima-Kambe T, Nobura N, Lu J, Nakahura Y (1997) Specific desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Mycobecterium strain G3. Biocatal Biotransform 15:21–27
Salem AS, Hamid HS (1997) Removal of sulfur compounds from naphtha solutions using solid adsorbents. Chem Eng Technol 20:342–347
Scott GM, Robert JA (2003) Deep desulfurization by selective adsorption of dibenzothiophenes on Ag+/SBA-15 and Ag+/SiO2. Chem Commun 2003:2620–2621
Setti L, Farinelli P, Martino SD, Frassinetti S, Lanzarini G, Pifferi PG (1999) Developments in destructive and non-destructive pathways for selective desulfurization in oil-biorefining processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:111–117
Shan GB, Xing JM, Zhang HY, Liu HZ (2005a) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by microbial cells coated with magnetic nano-particles. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4497–4502
Shan GB, Zhang HY, Cai WQ, Xing JM, Liu HZ (2005b) Improvement of biodesulfurization rate by assembling nanosorbents on the surfaces of microbial cells. Biophys J 89:L58–L60
Shan GB, Zhang HY, Xing JM, Li WL, Liu HZ (2006) Biodesulfurization of hydrodesulfurized diesel oil with Pseudomonas delafieldii R-8 from high density culture. Biochem Eng J 27:305–309
Song CS, Ma XL (2003) New design approaches to ultra-clean diesel fuels by deep desulfurization and deep dearomatization. Appl Catal B-Environ 41:207–238
Tailleur RG, Ravigli J, Quenza S, Valencia N (2005) Catalyst for ultra-low sulfur and aromatic diesel. Appl Catal A-Gen 282:227–235
Takahashi A, Yang FH, Yang RT (2002) New sorbents for desulfurization by π-complexation: thiophene/benzene adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:2487–2496
Vicas B, Anand G, Subrata K, Catherine JM, Ravi FS (2005) Deposition of CTAB terminated nanorods on bacteria to form highly conducting hybrid system. J Am Chem Soc 127:17600–17601
Xiong XC, Xing JM, Li X, Bai XJ, Li WL, Li YG, Liu HZ (2007) Enhancement of biodesulfurization in two-liquid system by heterogeneous expression of vitreoscilla hemoglobin. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2394–2397
Yang RT, Herna’ndez-Maldonado AJ, Cannella W (2003) Desulfurization of transportation fuels with zeolites under ambient conditions. Science 301:79–80
Zhang HY, Liu QF, Li YG, Li WL, Xiong XC, Xing JM, Liu HZ (2007) Selection of adsorbents for in situ coupling technology of adsorptive desulfurization and biodesulfurization. Sci China Ser B 37:506–513
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial supports by the State Major Basic Research Development Program of China (Grant No. 2006CB202507) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30970046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Li, WL., Chen, XX. et al. Enhanced biodesulfurization by magnetic immobilized Rhodococcus erythropolis LSSE8-1-vgb assembled with nano-γ-Al2O3 . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 299–305 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0459-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0459-7