Abstract
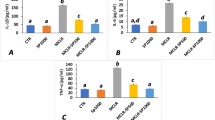
Nostoc sp. BHU001, a planktonic cyanobacterium isolated from an agricultural pond in India, was examined for its toxicity. Mice, administered intraperitoneally with Nostoc sp. BHU001 crude extract (50 mg kg−1 body weight) died at 4.5 h. Examination of liver and spleen showed microcystin (MC)-like symptoms. Serum enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities increased by 1.6–1.8 and 2.6–3.0-folds, respectively at 50 and 100 mg crude extract kg−1 body weight. Thin layer chromatography of the crude extract produced five bands (N-1 to N-5). UV absorption maxima of band N-4 corresponded to that of standard microcystin-LR. Further analysis of the band N-4 by high-performance liquid chromatography gave a retention time (R t ) of 4.61 min similar to that of standard microcystin–LR (LR stands for lysine and arginine). Total MC content was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and was 189.9 μg g−1 of crude extract, 9.8 μg l−1 of spent medium and 5.5 μg l−1 of pond water. Exposure of rice (Oryza sativa var. Sonam) seeds to the crude extract did not affect their germination, but inhibited the root and shoot growth of seedlings by 27.3 and 42.89 folds at 3 mg ml−1 crude extract, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MB, Arnon DI (1955) Studies on nitrogen-fixing blue-green algae. I. Growth and nitrogen fixation by Anabaena cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol 30:366–372. doi:10.1104/pp.30.4.366
APHA (1995) Biological examination. In: Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (eds) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 19th edn edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, pp 13–16
Bajpai R, Sharma NK, Lawton LA et al (2009) Microcystin producing cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. BHU001 from a pond in India. Toxicon 53:587–590. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.01.023
Banack SA, Johnson HE, Cheng R et al (2007) Production of the neurotoxin BMAA by a marine cyanobacterium. Mar Drugs 5:180–196
Beattie KA, Kaya K, Sano T et al (1998) Three dehydrobutyrine containing microcystins from Nostoc. Phytochemistry 47:1289–1292. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00769-3
Bibo L, Yan G, Bangding X et al (2008) A laboratory study on risk assessment of microcystin-RR in cropland. J Environ Manag 86:556–574. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.12.040
Briand JF, Jacket S, Bernard C et al (2003) Health hazards for terrestrial vertebrates from toxic cyanobacteria in surface water ecosystems. Vet Res 34:361–377. doi:10.1051/vetres:2003019
Burja AM, Banaigs B, Abou-Mansour E et al (2001) Marine cyanobacteria—a prolific source of natural products. Tetrahedron 57:9347–9377. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)00931-0
Chen J, Son L, Dai J et al (2004) Effects of microcystins on the growth and the activity of superoxide dismutase and peroxidase of rape (Brassica napus L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.). Toxicon 43:393–400. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.01.011
Chorus I, Bartram J (1999) Toxic cyanobacteria in water, a guide of their public health consequences, monitoring, and management. E & FN Spoon and WHO, London
Codd GA (1995) Cyanobacterial toxins: occurrence, properties and biological significance. Water Sci Technol 32:149–156. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(95)00692-3
Codd GA, Morrison LF, Metcalf JS (2005) Cyanobacterial toxins: risk management for health protection. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:264–272. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2004.02.016
de Figueiredo DR, Azeiteiro UM, Esteves SM et al (2004) Microcystin-producing blooms-a serious global public health issues. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:151–163. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.04.006
Dembitsky VM, Řezanka T (2005) Metabolites produced by nitrogen-fixing Nostoc species. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 50:363–391. doi:10.1007/BF02931419
Dodds WK, Gudder DA, Mollenhauer D (1995) The ecology of Nostoc. J Phycol 31:2–18. doi:10.1111/j.0022-3646.1995.00002.x
Edwards C, Graham D, Fowler N et al (2008) Biodegradation of microcystins and nodularin in freshwaters. Chemosphere 73:1315–1321. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.015
Falconer IR (2001) Toxic cyanobacteria bloom problems in Australian waters: risks and impacts on human health. Phycologia 40:228–233
Fawell JK, James CP, James HA (1993) Toxins from blue-green algae: toxicological assessement of microcystin-LR and a method for its determination in water. Foundation for water research, Marlow
Funari E, Testai E (2008) Human health risk assessment related to cyanotoxins exposure. Crit Rev Toxicol 38:97–125. doi:10.1080/10408440701749454
Harada K-I (1996) Chemistry and detection of microcystins. In: Watanabe MF, Harada K-I, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (eds) Toxic Microcystis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 103–148
Harada K-I, Kondo F, Lawton L (1999) Laboratory analysis of cyanotoxins. In: Chorus I, Bartram J (eds) Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. E & FN Spoon and WHO, London, pp 369–405
Hirata K, Yoshitomi S, Dwi S et al (2003) Bioactivities of nostocine A produced by a freshwater cyanobacterium Nostoc spongiaeforme TISTR 8169. J Biosci Bioeng 95:512–517
Hitzfeld B, Lampert C, Spath N et al (2000) Toxin production in cyanobacterial mats from ponds on the McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Toxicon 38:1731–1748. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(00)00103-3
Järvenpää S, Lundberg-Niinistö C, Spoof L et al (2007) Effects of microcystins on broccoli and mustard, and analysis of accumulated toxin by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Toxicon 49:865–874. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.12.008
Kaebernick M, Dittmann E, Börner T et al (2002) Multiple alternate transcripts direct the biosynthesis of microcystin, a cyanobacterial nonribosomal peptide. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:449–455. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.2.449-455.2002
Lawton LA, Edwards C, Codd GA (1994) Extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of microcystins in raw and treated waters. Analyst (Lond) 119:1525–1530. doi:10.1039/an9941901525
Lee ESJ, Gleason FK (1994) A second algicidal natural product from cyanobacterium, Scytonema hofmanni. Plant Sci 103:155–160. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(94)90203-8
MacKintosh C, Beattie KA, Klumpp S et al (1990) Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett 264:187–192. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-E
Martins R, Pereira P, Welker M et al (2005) Toxicity of culturable cyanobacterial strains isolated from the Portuguese coast. Toxicon 46:454–464. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.06.010
Oksanen I, Jokela J, Fewer P et al (2004) Discovery of rare and highly toxic microcystins from lichen-associated cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain IO-102-I. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5756–5763. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.10.5756-5763.2004
Oudra B, El Andaloussi DM, Vasconcelos VM (2009) Identification and quantification of microcystins from a Nostoc muscorum bloom occurring in Oukaïmeden River (High-Atlas mountains of Marrakech, Morocco). Environ Monit Assess 149:437–444. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0220-y
Ouellette AJA, Wilhelm SW (2003) Toxic cyanobacteria: the evolving molecular toolbox. Front Ecol Environ 1:359–366
Pearl HW, Fulton RSIII, Mosisander PH et al (2001) Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. Sci World 1:76–113
Peuthert A, Chakrabarti S, Pflugmacher S (2007) Uptake of microcystins-LR and -LF (cyanobacterial toxins) in seedlings of several important agricultural plant species and the correlation with cellular damage (lipid peroxidation). Environ Toxicol 22:436–442. doi:10.1002/tox.20266
Pflugmacher S, Hofmann J, Hübner B (2007) Effects on growth and physiological parameters in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in soil and irrigated with cyanobacterial toxin contaminated water. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:2710–2716. doi:10.1897/07-145.1
Porfirio Z, Ribeiro MP, Estevam CS et al (1999) Hepatosplenomegaly caused by an extract of cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa bloom collected in the Manguaba Lagoon, Alagoas - Brazil. Rev Microbiol 30:278–285. doi:10.1590/S0001-37141999000300016
Rao PVL, Gupta N, Jayaraj R et al (2005) Age dependent effects on biochemical variables and toxicity induced by cyclic peptide toxin microcystin- LR in mice. Comp Biochem Physiol 140:11–19
Rapala J, Sivonen K, Lyra C et al (1997) Variation of microcystins, cyanobacterial hepatotoxins, in Anabaena spp. as a function of growth stimuli. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2206–2212
Saqrane S, Ghazali IE, Oudra B et al (2008) Effects of cyanobacteria producing microcystins on seed germination and seedling growth of several agricultural plants. J Environ Sci Health B 43:443–451. doi:10.1080/03601230802062307
Sharma NK, Rai AK (2008) Allergenicity of air borne cyanobacteria Phormidium fragile and Nostoc muscorum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:158–162. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.08.006
Sotero-Santos RB, Carvalho EG, Dellamano-Oliveira MJ et al (2008) Occurrence and toxicity of an Anabaena bloom in a tropical reservoir (Southeast Brazil). Harmful Algae 7:590–598. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2007.12.017
Toivola DM, Eriksson JE (1999) Toxins affecting cell signaling and alternation of cytoskeletal structure. Toxicol In Vitro 13:521–530. doi:10.1016/S0887-2333(99)00024-7
Weng D, Lu Y, Wei Y et al (2007) The role of ROS in microcystin-LR-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury in mice. Toxicology 232:15–23. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2006.12.010
Zurawell RW, Chen H, Burke JM et al (2005) Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: a review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J Toxicol Environ Health 8:1–37
Acknowledgments
RB is grateful to CSIR, New Delhi, for providing Senior Research Fellowship (award no. 9/13 (45)/2004-EMR-I) and AKR to DST, New Delhi, for financial assistance in the form of a project (ref. no. SP/SO/A-11/99).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajpai, R., Sharma, N.K., Rai, A.K. et al. Hepatosplenomegaly and phytotoxicity of a planktonic cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. BHU001 isolated from agricultural pond. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25, 1995–2003 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0100-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0100-9