Abstract
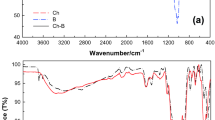
The preparation, characterization, and environmental application of crosslinked chitosan-coated bentonite (CCB) beads for tartrazine adsorption have been investigated. CCB beads were characterized by using Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometer (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) pore size distribution analyses were also determined. The values of pH of the aqueous slurry and pH of zero point charge (pHZPC) were almost equal. The adsorption at equilibrium of tartrazine was found to be a function of pH of the solution, stirring rate, contact time, and tartrazine concentration. The optimum conditions for tartrazine adsorption were pH 2.5, stirring rate of 400 rpm and contact time of 80 min. Pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models were used to analyze the kinetics of adsorption with the latter found to agree well with the kinetics data, suggesting that the rate determining step may be chemisorption. The two most common isotherm models, Langmuir and Freundlich, were used to describe the adsorption equilibrium data. On the basis of Langmuir isotherm model, the maximum adsorption capacities were determined to be 250.0, 277.8, and 294.1 mg g−1 at 300, 310, and 320 K, respectively. Desorption studies were carried out at different concentrations of EDTA, H2SO4, and NaOH. All desorbing solutions showed poor recovery of tartrazine.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Degs, Y. S., El-Barghouthi, M. I., El-Shiekh, A. H., & Walker, G. M. (2008). Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dyes and Pigments, 77, 16–23. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.03.001.
Bekçi, Z., Özveri, C., Seki, Y., & Yurdakoç, K. (2008). Sorption of malachite green on chitosan bead. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154, 254–261. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.021.
Boddu, V. M., Abburi, K., Tallbott, J. L., & Smith, E. D. (2003). Removal of hexavalent chromium from wastewater using a new composite chitosan biosorbent. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 4449–4456. doi:10.1021/es021013a.
Boddu, V. M., Abburi, K., Talbott, J. L., Smith, E. D., & Haasch, R. (2008). Removal of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) from aqueous medium using chitosan-coated biosorbent. Water Research, 43, 633–642. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.08.014.
Chang, M. Y., & Juang, R. S. (2004). Adsorption of tannic acid, humic acid and dyes from water using the composite of chitosan and activated clay. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 278, 18–25. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.05.029.
Chen, J. P., Wu, S., & Chong, K. (2003). Surface modification of a granular activated carbon by citric acid for enhancement of copper adsorption. Carbon, 41, 1979–1986. doi:10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00197-0.
Crini, G. (2008). Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the removal dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto cyclodextrin polymer. Dyes and Pigments, 77, 415–426. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.07.001.
Eren, E., & Afsin, B. (2008). Investigation of a basic dye adsorption from aqueous solution onto raw and pre-treated bentonite surfaces. Dyes and Pigments, 76, 220–225. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.08.019.
Fan, D., Zhu, X., Xu, M., & Yan, J. (2006). Adsorption properties of chromium (VI) by chitosan coated montmorillonite. The Journal of Biological Sciences, 6, 941–945. doi:10.3923/jbs.2006.941.945.
Gecol, H., Miakatsindila, P., Ergican, E., & Hiibel, S. R. (2006). Biopolymer coated clay particles for the adsorption of tungsten from water. Desalination, 197, 165–178. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2006.01.016.
Gregg, S. J., & Sing, K. S. W. (1982). Adsorption, surface area and porosity (2nd ed.). London: Academic.
Guibal, E., Vincent, T., & Mendoza, R. N. (2000). Synthesis and characterization of thiourea derivative of chitosan for platinum recovery. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 75, 119–134. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(20000103)75:1<119::AID-APP14>3.0.CO;2-E.
Hameed, B. H., Ahmad, A. L., & Latiff, K. N. A. (2007). Adsorption of basic dye (methylene blue) onto activated carbon prepared from rattan sawdust. Dyes and Pigments, 75, 143–149. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.05.039.
Hasan, S., Krishnaiah, A., Ghosh, T. K., Viswanath, D. S., Boddu, V. M., & Smith, E. D. (2006). Adsorption of divalent cadmium (Cd(II)) from aqueous solutions onto chitosan-coated perlite beads. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 45, 5066–5077. doi:10.1021/ie0402620.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1998). A comparison of chemisorption kinetics models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 76, 332–340. doi:10.1205/095758298529696.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (2000). The kinetics of sorption of divalent metal ions onto spaghnum moss peat. Water Research, 34, 735–742. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00232-8.
Kalyani, S., Priya, J. A., Rao, P. S., & Krishnaiah, A. (2005). Removal of copper and nickel from aqueous using chitosan coated on perlite as biosorbent. Separation Science and Technology, 40, 1483–1495. doi:10.1081/SS-200055940.
Mane, V. S., Mall, I. D., & Srivastava, V. C. (2007). Use of fly ash as an adsorbent for the removal of brilliant green dye from aqueous solution. Dyes and Pigments, 73, 269–278. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.12.006.
Mittal, A., Krishnan, L., & Gupta, V. K. (2005). Removal and recovery of malachite green from wastewater using an agricultural waste material, de-oiled soya. Separation and Purification Technology, 43, 125–133. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2004.10.010.
Mittal, A., Kurup, L., & Mittal, J. (2006). Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and column operations for the removal of hazardous dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions using waste materials—bottom ash and de-oiled soya, as adsorbents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136, 567–578. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.037.
Mittal, A., Kurup, L., & Mittal, J. (2007). Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherms and kinetics for the removal of tartrazine from aqueous solutions using hen feathers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146, 243–248. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.012.
Monser, L., & Adhoum, N. (2008). Tartrazine modified activated carbon for the removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161, 263–269. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.120.
Morais, L. C., Freitas, O. M., Goncalves, E. P., Vasconcelos, L. T., & González Beça, C. G. (1999). Reactive dyes removal from wastewaters by adsorption on eucalyptus bark: variables that define the process. Water Research, 33, 979–988. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00294-2.
Ofomaja, A. E., & Ho, Y. S. (2007). Equilibrium sorption of anionic dye from aqueous solution by palm kernel fibre as sorbent. Dyes and Pigments, 72, 60–66. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.01.014.
Ravikumar, K., Krishnan, S., Ramalingam, S., & Balu, K. (2007). Optimization of process variables by the application of response surface methodology for dye removal using a novel biosorbent. Dyes and Pigments, 72, 66–74. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.07.018.
Vijaya, Y., Popuri, S. R., Boddu, V. M., & Krisnaiah, A. (2008). Modified chitosan and calcium alginate biopolymer sorbents for removal of nickel (II) through adsorption. Carbohydrate Polymers, 72, 261–271. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.08.010.
Wan Ngah, W. S., & Fathinathan, S. (2008). Adsorption of Cu(II) ions in aqueous solution using chitosan beads, chitosan-GLA beads and chitosan-alginate beads. Chemical Engineering Journal, 143, 62–72. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2007.12.006.
Wan Ngah, W. S., & Hanafiah, M. A. K. M. (2008). Adsorption of copper on rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) leaf powder: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 39, 521–530. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2007.11.006.
Wan Ngah, W. S., Ghani, S. A., & Kamari, A. (2005). Adsorption behaviour of Fe(II) and Fe(III) ions in aqueous solution on chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. Bioresource Technology, 96, 443–450. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2004.05.022.
Wang, L., & Wang, A. (2007). Adsorption characteristic of congo red onto the chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 979–985. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.145.
Wawrzkiewicz, M., & Hubicki, Z. (2009). Removal of tartrazine from aqueous solutions by strongly basic polystyrene anion exchange resins. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 502–509. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.021.
Yang, Z., & Yuan, Y. (2001). Studies on the synthesis and properties of hydroxyl azacrown ether-grafted chitosan. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 82, 1838–1843. doi:10.1002/app.2026.
Acknowledgement
The authors are very grateful to the Universiti Sains Malaysia (Grant No. 304/229/PKIMIA/638166) for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan Ngah, W.S., Ariff, N.F.M. & Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Preparation, Characterization, and Environmental Application of Crosslinked Chitosan-Coated Bentonite for Tartrazine Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 206, 225–236 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0098-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0098-5