Abstract
Background
Previous studies have investigated the connection between diabetic nephropathy and smoking, and reported widely varying rates. This study aimed to systematically analyze the impact of smoking on diabetic nephropathy.
Methods
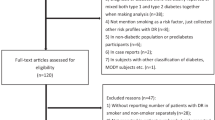
We searched the PubMed and EMBASE electronic databases to identify relevant English-language studies published up to March 2016. Eligible studies were selected using inclusion and exclusion criteria. Data for each study were extracted independently by two authors. The homogeneity of the effect size across the studies was tested. Odds ratio (OR) was calculated by using the random-effect model. Sensitivity analysis was performed to reduce heterogeneity, and publication biases were examined.
Results
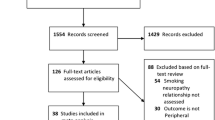
A total of 21 eligible studies were selected and pooled analyzed. No significant differences in demographic characteristics were found between patients with diabetic nephropathy and those with non-diabetic nephropathy. Significant heterogeneity across studies was found except those of diabetes mellitus controls. The aggregate OR of smoking in the patients with diabetic nephropathy in comparison with those with non-diabetic nephropathy was 1.70 (95% confidence interval 1.48–1.95). No evidence of publication bias was found.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that smoking is a significant risk factor for diabetic nephropathy in diabetic patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duran-Salgado MB, Rubio-Guerra AF (2014) Diabetic nephropathy and inflammation. World J Diabetes 5(3):393–398
Sun Y-M, Su Y, Li J et al (2013) Recent advances in understanding the biochemical and molecular mechanism of diabetic nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 433(4):359–361
Clair C, Cohen MJ, Eichler F et al (2015) The effect of cigarette smoking on diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med 30(8):1193–1203
Phisitkul K, Hegazy K, Chuahirun T et al (2008) Continued smoking exacerbates but cessation ameliorates progression of early type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Am J Med Sci 335(4):284–291
Byun S-H, Ma SH, Jun JK et al (2013) Screening for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with diabetes: a nationwide survey in Korea. PLoS ONE 8(5):e62991. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062991
Obert DM, Hua P, Pilkerton ME et al (2011) Environmental tobacco smoke furthers progression of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Med Sci 341(2):126–130
Hua P, Feng W, Ji S et al (2010) Nicotine worsens the severity of nephropathy in diabetic mice: implications for the progression of kidney disease in smokers. Am J Physiol-Renal Physiol 299(4):F732–F739
Tarnow L, Groop P-H, Hadjadj S et al (2008) European rational approach for the genetics of diabetic complications—EURAGEDIC: patient populations and strategy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23(1):161–168. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm501
Li H, Feng S-J, Zhang G-Z et al (2014) Correlation of lower concentrations of hydrogen sulfide with atherosclerosis in chronic hemodialysis patients with diabetic nephropathy. Blood Purif 38(3–4):188–194. doi:10.1159/000368883
Afkarian M, Sachs MC, Kestenbaum B et al (2013) Kidney disease and increased mortality risk in type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol: ASN. 2012070718
Hovind P, Rossing P, Tarnow L et al (2003) Smoking and progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 26(3):911–916
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH (1997) Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med 127(9):820–826
Feng RN, Zhao C, Sun CH et al (2011) Meta-analysis of TNF 308 G/A polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18480. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018480
Afkarian M, Sachs MC, Kestenbaum B et al (2013) Kidney disease and increased mortality risk in type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 24(2):302–308. doi:10.1681/ASN.2012070718
Ahluwalia TS, Lindholm E, Groop L et al (2011) Uromodulin gene variant is associated with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Hypertens 29(9):1731–1734. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e328349de25
Ahmed MA, Kishore G, Khader HA et al (2013) Risk factors and management of diabetic nephropathy. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 24(24):1242–1247
Baum L, Ng MC, So WY, Lam VK et al (2005) Effect of hepatic lipase -514C- > T polymorphism and its interactions with apolipoprotein C3–482C- > T and apolipoprotein E exon 4 polymorphisms on the risk of nephropathy in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 28(7):1704–1709
Furukawa S, Yamamoto S, Todo Y et al (2014) Association between subclinical hypothyroidism and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J 61(10):1011–1018
Hyvonen ME, Ihalmo P, Forsblom C et al (2012) INPPL1 is associated with the metabolic syndrome in men with type 1 diabetes, but not with diabetic nephropathy. Diabet Med 29(12):1589–1595. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2012.03668.x
Khalid AR, Youssef AM, Subhani SN et al (2014) Diabetic nephropathy and its risk factors in a society with a type 2 diabetes epidemic: a Saudi National Diabetes Registry-based study. PLoS ONE 9(2):e88956
Korpinen E, Groop PH, Rautio A et al (1999) N-acetyltransferase-2 polymorphism, smoking and type 1 diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacogenet Genomics 9(5):627–633
Lajer M, Jorsal A, Tarnow L et al (2010) Plasma growth differentiation factor-15 independently predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality as well as deterioration of kidney function in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Diabetes Care 33(7):1567–1572. doi:10.2337/dc09-2174
Liu L, Zheng T, Wang F et al (2010) Pro12Ala polymorphism in the PPARG gene contributes to the development of diabetic nephropathy in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 33(1):144–149. doi:10.2337/dc09-1258
Mollsten A, Marklund SL, Wessman M et al (2007) A functional polymorphism in the manganese superoxide dismutase gene and diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 56(1):265–269. doi:10.2337/db06-0698
Ngarmukos C, Bunnag P, Kosachunhanun N et al (2006) Thailand diabetes registry project: prevalence, characteristics and treatment of patients with diabetic nephropathy. J Med Assoc Thai 89(Suppl 1):S37–S42
Ozaki R, Cheung KKT, Wu E et al (2011) A new tool to detect kidney disease in Chinese type 2 diabetes patients: comparison of EZSCAN with standard screening methods. Diabetes Technol Ther 13(9):937–943. doi:10.1089/dia.2011.0023
Rossing P, Hougaard P, Parving HH (2002) Risk factors for development of incipient and overt diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients: a 10-year prospective observational study. BMJ 25(5):859–864
Sawicki PT (1994) Smoking and diabetic nephropathy. Springer, US
Teratani G, Awano S, Soh I et al (2013) Oral health in patients on haemodialysis for diabetic nephropathy and chronic glomerulonephritis. Clin Oral Investig 17(2):483–489. doi:10.1007/s00784-012-0741-1
Theilade S, Lajer M, Jorsal A et al (2012) Evaluation of placental growth factor and soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 as predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 1 diabetes with and without diabetic nephropathy. Diabet Med 29(3):337–344. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03482.x
Zhang W, Yang Z, Li X et al (2015) The functional Q84R polymorphism of TRIB3 gene is associated with diabetic nephropathy in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Gene 555(2):357–361. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.031
Zheng S, Powell DW, Zheng F et al (2016) Diabetic Nephropathy: Proteinuria, Inflammation, and Fibrosis. J Diabetes Res 2016
Kanwar YS, Wada J, Sun L et al (2008) Diabetic nephropathy: mechanisms of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med 233(1):4–11
Ritz E, Ogata H, Orth S (2008) Smoking: a factor promoting onset and progression of diabetic nephropathy
Voulgari C, Katsilambros N, Tentolouris N (2011) Smoking cessation predicts amelioration of microalbuminuria in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 1-year prospective study. Metabolism 60(10):1456–1464
Scott LJ, Warram JH, Hanna LS et al (2001) A nonlinear effect of hyperglycemia and current cigarette smoking are major determinants of the onset of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 50(12):2842–2849
Prince CT, Secrest AM, Mackey RH et al (2010) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, HDL cholesterol, and smoking correlate with arterial stiffness markers determined 18 years later in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 33(3):652–657
Chakkarwar VA (2012) Smoking in diabetic nephropathy: sparks in the fuel tank? World J diabetes 3(12):186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, S., Wang, W., Sun, T. et al. Smoking as a risk factor for diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 1801–1807 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1638-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1638-3