Abstract
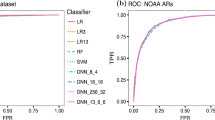
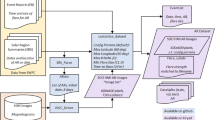
The precise physical process that triggers solar flares is not currently understood. Here we attempt to capture the signature of this mechanism in solar-image data of various wavelengths and use these signatures to predict flaring activity. We do this by developing an algorithm that i) automatically generates features in 5.5 TB of image data taken by the Solar Dynamics Observatory of the solar photosphere, chromosphere, transition region, and corona during the time period between May 2010 and May 2014, ii) combines these features with other features based on flaring history and a physical understanding of putative flaring processes, and iii) classifies these features to predict whether a solar active region will flare within a time period of \(T\) hours, where \(T = 2 \mbox{ and }24\). Such an approach may be useful since, at the present time, there are no physical models of flares available for real-time prediction. We find that when optimizing for the True Skill Score (TSS), photospheric vector-magnetic-field data combined with flaring history yields the best performance, and when optimizing for the area under the precision–recall curve, all of the data are helpful. Our model performance yields a TSS of \(0.84 \pm0.03\) and \(0.81 \pm0.03\) in the \(T = 2\)- and 24-hour cases, respectively, and a value of \(0.13 \pm0.07\) and \(0.43 \pm0.08\) for the area under the precision–recall curve in the \(T=2\)- and 24-hour cases, respectively. These relatively high scores are competitive with previous attempts at solar prediction, but our different methodology and extreme care in task design and experimental setup provide an independent confirmation of these results. Given the similar values of algorithm performance across various types of models reported in the literature, we conclude that we can expect a certain baseline predictive capacity using these data. We believe that this is the first attempt to predict solar flares using photospheric vector-magnetic field data as well as multiple wavelengths of image data from the chromosphere, transition region, and corona, and it points the way towards greater data integration across diverse sources in future work.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, O.W., Qahwaji, R., Colak, T., Higgins, P.a., Gallagher, P.T., Bloomfield, D.S.: 2013, Solar flare prediction using advanced feature extraction, machine learning, and feature selection. Solar Phys. 283, 157. DOI .
Barnes, G., Leka, K.D.: 2008, Evaluating the performance of solar flare forecasting methods. Astrophys. J. Lett. 688, L107. DOI . ADS .
Benz, A.O.: 2017, Flare observations. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 14(1), 2. DOI .
Bishop, C.M.: 2006, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Springer, New York.
Bloomfield, D.S., Higgins, P.a., McAteer, R.T.J., Gallagher, P.T.: 2012, Toward reliable benchmarking of solar flare forecasting methods. Astrophys. J. 747, L41. DOI .
Bobra, M.G., Couvidat, S.: 2015, Solar flare prediction using SDO/HMI vector magnetic field data and a machine learning algorithm. Astrophys. J. 798, 135. DOI .
Bobra, M.G., Sun, X., Hoeksema, J.T., Turmon, M., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., Barnes, G., Leka, K.D.: 2014, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: SHARPs – space-weather HMI active region patches. Solar Phys. 289(9), 3549. DOI .
Boucheron, L.E., Al-Ghraibah, A., McAteer, R.T.J.: 2015, Prediction of solar flare size and time-to-flare using support vector machine regression. Astrophys. J. 812, 51. DOI . ADS .
Canfield, R.C., Hudson, H.S., McKenzie, D.E.: 1999, Sigmoidal morphology and eruptive solar activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26(6), 627. DOI .
Cho, Y., Saul, L.K.: 2009, Kernel methods for deep learning. In: Bengio, Y., Schuurmans, D., Lafferty, J.D., Williams, C.K.I., Culotta, A. (eds.) Adv Neural Info Proc Sys, 342.
Crown, M.D.: 2012, Validation of the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center’s solar flare forecasting look-up table and forecaster-issued probabilities. Space Weather 10, S06006. DOI . ADS .
Falconer, D.A., Moore, R.L., Barghouty, A.F., Khazanov, I.: 2012, Prior flaring as a complement to free magnetic energy for forecasting solar eruptions. Astrophys. J. 757, 32. DOI . ADS .
Fisher, G.H., Bercik, D.J., Welsch, B.T., Hudson, H.S.: 2012, Global forces in eruptive solar flares: the Lorentz force acting on the solar atmosphere and the solar interior. Solar Phys. 277, 59. DOI . ADS .
Fletcher, L., Dennis, B.R., Hudson, H.S., Krucker, S., Phillips, K., Veronig, A., Battaglia, M., Bone, L., Caspi, A., Chen, Q., Gallagher, P., Grigis, P.T., Ji, H., Liu, W., Milligan, R.O., Temmer, M.: 2011, An observational overview of solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 19. DOI . ADS .
Gabor, D.: 1947, Theory of communication. J. Inst. Electr. Eng., Part I, Gen. 94(73), 58. DOI .
Garcia, H.A.: 1994, Temperature and emission measure from GOES soft X-ray measurements. Solar Phys. 154, 275. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K., Rust, D.M.: 2007, Quantitative forecasting of major solar flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 661, L109. DOI . ADS .
Hanser, F.A., Sellers, F.B.: 1996, Design and calibration of the goes-8 solar X-ray sensor: the XRS. Proc. SPIE 2812, 344. DOI .
Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., Sun, X., Schou, J., Couvidat, S., Norton, A., Bobra, M., Centeno, R., Leka, K.D., Barnes, G., Turmon, M.: 2014, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: overview and performance. Solar Phys. 289, 3483. DOI .
Jing, J., Song, H., Abramenko, V., Tan, C., Wang, H.: 2006, The statistical relationship between the photospheric magnetic parameters and the flare productivity of active regions. Astrophys. J. 644, 1273. DOI . ADS .
Jonas, E., Pu, Q., Venkataraman, S., Stoica, I., Recht, B.: 2017, Occupy the cloud: distributed computing for the 99%. In: Proc. 2017 Symp. Cloud Computing, 445. ACM, New York.
Kamarainen, J.K., Kyrki, V., Kälviäinen, H.: 2006, Invariance properties of Gabor filter-based features – overview and applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(5), 1088. DOI .
Leka, K.D., Barnes, G.: 2003, Photospheric magnetic field properties of flaring versus flare-quiet active regions. II. Discriminant analysis. Astrophys. J. 595(2), 1296. DOI .
Leka, K.D., Barnes, G.: 2007, Photospheric magnetic field properties of flaring versus flare-quiet active regions. IV. A statistically significant sample. Astrophys. J. 656, 1173. DOI . ADS .
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., Friedlaender, F.M., Heyman, G.F., Hurlburt, N.E., Katz, N.L., Kushner, G.D., Levay, M., Lindgren, R.W., Mathur, D.P., McFeaters, E.L., Mitchell, S., Rehse, R.A., Schrijver, C.J., Springer, L.A., Stern, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Wuelser, J.-P., Wolfson, C.J., Yanari, C., Bookbinder, J.A., Cheimets, P.N., Caldwell, D., Deluca, E.E., Gates, R., Golub, L., Park, S., Podgorski, W.A., Bush, R.I., Scherrer, P.H., Gummin, M.A., Smith, P., Auker, G., Jerram, P., Pool, P., Soufli, R., Windt, D.L., Beardsley, S., Clapp, M., Lang, J., Waltham, N.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 17. DOI . ADS .
Mairal, J., Koniusz, P., Harchaoui, Z., Schmid, C.: 2014, Convolutional kernel networks. In: Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Weinberger, K.Q. (eds.) Adv. Neural Info. Proc. Sys., 27, 2627.
Mason, J.P., Hoeksema, J.T.: 2010, Testing automated solar flare forecasting with 13 years of Michelson Doppler Imager magnetograms. Astrophys. J. 723(1), 634. DOI .
Metcalf, T.R.: 1994, Resolving the 180-degree ambiguity in vector magnetic field measurements: the ‘minimum’ energy solution. Solar Phys. 155, 235. DOI . ADS .
SunPy Community, Mumford, S.J., Christe, S., Pérez-Suárez, D., Ireland, J., Shih, A.Y., Inglis, A.R., Liedtke, S., Hewett, R.J., Mayer, F., Hughitt, K., Freij, N., Meszaros, T., Bennett, S.M., Malocha, M., Evans, J., Agrawal, A., Leonard, A.J., Robitaille, T.P., Mampaey, B., Campos-Rozo, J.I., Kirk, M.S.: 2015, SunPy – Python for solar physics. Comput. Sci. Discov. 8(1), 014009. DOI . ADS .
Nishizuka, N., Sugiura, K., Kubo, Y., Den, M., Watari, S., Ishii, M.: 2017, Solar flare prediction model with three machine-learning algorithms using ultraviolet brightening and vector magnetograms. Astrophys. J. 835, 156. DOI . ADS .
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 3. DOI . ADS .
Priest, E.R., Forbes, T.G.: 2002, The magnetic nature of solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 10, 313. DOI . ADS .
Rahimi, A., Recht, B.: 2008, Random features for large-scale kernel machines. In: Platt, J.C., Koller, D., Singer, Y., Roweis, S.T. (eds.) Adv. Neural Information Processing Systems, 20, 1177.
Schou, J., Scherrer, P.H., Bush, R.I., Wachter, R., Couvidat, S., Rabello-Soares, M.C., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Akin, D.J., Allard, B.A., Miles, J.W., Rairden, R., Shine, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A.M., Wolfson, C.J., Elmore, D.F., Norton, A.A., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, Design and ground calibration of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 229. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J.: 2007, A characteristic magnetic field pattern associated with all major solar flares and its use in flare forecasting. Astrophys. J. Lett. 655, L117. DOI . ADS .
Schwenn, R.: 2006, Space weather: the solar perspective. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 3, 2. DOI . ADS .
Song, H., Tan, C., Jing, J., Wang, H., Yurchyshyn, V., Abramenko, V.: 2009, Statistical assessment of photospheric magnetic features in imminent solar flare predictions. Solar Phys. 254, 101. DOI .
Su, Y., Golub, L., Van Ballegooijen, A.A.: 2007, A statistical study of shear motion of the footpoints in two-ribbon flares. Astrophys. J. 655, 606. DOI . ADS .
Sudol, J.J., Harvey, J.W.: 2005, Longitudinal magnetic field changes accompanying solar flares. Astrophys. J. 635, 647. DOI . ADS .
Sun, X.: 2013, On the coordinate system of Space-Weather HMI Active Region Patches (SHARPs): a technical note. arXiv . ADS .
Turmon, M., Jones, H.P., Malanushenko, O.V., Pap, J.M.: 2010, Statistical feature recognition for multidimensional solar imagery. Solar Phys. 262, 277. DOI . ADS .
Welsch, B.T., Li, Y., Schuck, P.W., Fisher, G.H.: 2009, What is the relationship between photospheric flow fields and solar flares? Astrophys. J. 705, 821. DOI . ADS .
Wheatland, M.S.: 2004, A Bayesian approach to solar flare prediction. Astrophys. J. 609(2), 17. DOI .
Woodcock, F.: 1976, The evaluation of yes/no forecasts for scientific and administrative purposes. Mon. Weather Rev. 104, 1209. DOI . ADS .
Yu, D., Huang, X., Wang, H., Cui, Y.: 2009, Short-term solar flare prediction using a sequential supervised learning method. Solar Phys. 255, 91. DOI . ADS .
Yuan, Y., Shih, F.Y., Jing, J., Wang, H.-M.: 2010, Automated flare forecasting using a statistical learning technique. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 10, 785. DOI . ADS .
Zirin, H., Wang, H.: 1993, Narrow lanes of transverse magnetic field in sunspots. Nature 363, 426. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
The data used here are courtesy of the GOES team and the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) and Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) science teams of the NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory. This work was supported by NASA Grant NAS5-02139 (HMI), and in part by DHS Award HSHQDC-16-3-00083, NSF CISE Expeditions Award CCF-1139158, DOE Award SN10040 DE-SC0012463, and DARPA XData Award FA8750-12-2-0331, and gifts from Amazon Web Services, Google, IBM, SAP, The Thomas and Stacey Siebel Foundation, Apple Inc., Arimo, Blue Goji, Bosch, Cisco, Cray, Cloudera, Ericsson, Facebook, Fujitsu, HP, Huawei, Intel, Microsoft, Mitre, Pivotal, Samsung, Schlumberger, Splunk, State Farm and VMware. B. Recht is supported by NSF award CCF-1359814, ONR awards N00014-14-1-0024 and N00014-17-1-2191, the DARPA Fundamental Limits of Learning (Fun LoL) Program, a Sloan Research Fellowship, and a Google Faculty Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonas, E., Bobra, M., Shankar, V. et al. Flare Prediction Using Photospheric and Coronal Image Data. Sol Phys 293, 48 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1258-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1258-9