Abstract
Aim
Ambrosia trifida L. is designated as an invasive exotic plants in South Korea. Despite its widespread distribution in South Korea, research on A. trifida is limited. Organic matter input by A. trifida litter decomposition is predicted to change the soil environment. In this study, we investigated the effects of A. trifida litter decomposition on soil nutrient status.
Methods
We used the litterbag method to investigate the decomposition rate, decay constant (k), carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio, and nutrient dynamics of A. trifida litter during decomposition.
Results
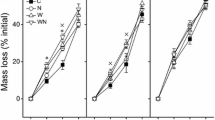
The decay constants (k) of leaf, stem, and root litter after 11 months of decomposition were 1.93, 1.47, and 1.28, respectively. After 22 months of decomposition, the decay constants (k) of leaf, stem, and root litter were 1.01, 0.99 and 1.84, respectively. After 22 months, approximately 85% of organic matter, 79% of nitrogen (N), 98% of phosphorus (P), 96% of potassium (K), 96% of magnesium (Mg), and 69% of calcium (Ca) were returned to the soil.
Conclusion
Our results provide key insights into the nutrients exchange between A. trifida and soil. Given the biological characteristics of A. trifida, the input of a large amount of organic matter to the soil and the nutrients released through the decomposition of this organic matter are expected to enhance the growth and nutrient absorption of A. trifida in invaded areas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abul-Fatih H, Bazzaz F, Hunt R (1979a) The biology of Ambrosia trifida L. III. Growth and biomass allocation. New Phytol 83:829–838
Abul-Fatih HA, Bazzaz FA, Hunt R (1979b) The biology of Ambrosia trifida L. I. Influence of species removal on the organizatioin of the plant community. New Phytol 83:829–838. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1979.tb02314.x
Aerts R (1997) Climate, leaf litter chemistry and leaf litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: a triangular relationship. Oikos 79:439–449. https://doi.org/10.2307/3546886
Alhamd L, Arakaki S, Hagihara A (2004) Decomposition of leaf litter of four tree species in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, Okinawa Island, Japan. For Ecol Manag 202:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.02.062
Allison SD, Vitousek PM (2004) Rapid nutrient cycling in leaf litter from invasive plants in Hawai’i. Oecologia 141:612–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-004-1679-z
Aponte C, García LV, Marañón T (2012) Tree species effect on litter decomposition and nutrient release in Mediterranean oak forests changes over time. Ecosystems 15:1204–1218
Asplund J, Hustoft E, Nybakken L, Ohlson M, Lie MH (2018) Litter impair spruce seedling emergence in beech forests: a litter manipulation experiment. Scand J For Res 33:332–337. https://doi.org/10.1080/02827581.2017.1388440
Austin AT, Ballaré CL (2010) Dual role of lignin in plant litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci:20090936. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909396107
Baker TT, Lockaby BG, Conner WH, Meier CE, Stanturf JA, Burke MK (2001) Leaf litter decomposition and nutrient dynamics in four southern forested floodplain communities. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:1334–1347
Balogh L, Botta-Dukát Z, Dancza I (2003) What kind of plants are invasive in Hungary. Plant invasions: ecological threats and management solutions. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, pp 131–146
Barnett KA, Steckel LE (2013) Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) competition in cotton. Weed Sci 61:543–548. https://doi.org/10.1614/WS-D-12-00169.1
Baruch Z, Goldstein G (1999) Leaf construction cost, nutrient concentration, and net CO2 assimilation of native and invasive species in Hawaii. Oecologia 121:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050920
Bending GD, Read DJ (1995) The structure and function of the vegetative mycelium of ectomycorrhizal plants. New Phytol 130:401–409
Bennett AE, Thomsen M, Strauss SY (2011) Multiple mechanisms enable invasive species to suppress native species. Am J Bot 98:1086–1094
Berg B (2000) Litter decomposition and organic matter turnover in northern forest soils. For Ecol Manag 133:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(99)00294-7
Berg B (2006) Litter decomposition : a guide to carbon and nutrient turnover/ by Bjorn Berg, Ryszard Laskowski. Academic, Amsterdam
Berg B, Staaf H (1981) Leaching, accumulation and release of nitrogen in decomposing forest litter. Ecol Bull 33:163–178
Cadotte MW, Hamilton MA, Murray BR (2009) Phylogenetic relatedness and plant invader success across two spatial scales. Divers Distrib 15:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2009.00560.x
Carson WP, Peterson CJ (1990) The role of litter in an old-field community: impact of litter quantity in different seasons on plant species richness and abundance. Oecologia 85:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00317337
Chen B-M, D’Antonio CM, Molinari N, Peng S-L (2018) Mechanisms of influence of invasive grass litter on germination and growth of coexisting species in California. Biol Invasions 20:1881–1897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-018-1668-5
Choi H-J, Lim S-H, Kim K-H, Kim S (2007) Distribution of Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) at northwest of Gangwon, Korea. Kor J Weed Sci 27:241–247
Corbin JD, D’Antonio CM (2012) Gone but not forgotten? Invasive plants' legacies on community and ecosystem properties. Invasive Plant Sci Manag 5:117–124
Cornelissen JHC, Thompson K (1997) Functional leaf attributes predict litter decomposition rate in herbaceous plants. New Phytol 135:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00628.x
Cotrufo MF, Soong JL, Horton AJ, Campbell EE, Haddix Michelle L, Wall DH, Parton WJ (2015) Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat Geosci 8:776. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2520. https://www.nature.com/articles/ngeo2520#supplementary-information
Coûteaux M-M, Bottner P, Berg B (1995) Litter decomposition, climate and liter quality. Trends Ecol Evol 10:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(00)88978-8
D’Antonio C, Meyerson LA (2002) Exotic plant species as problems and solutions in ecological restoration: a synthesis. Restor Ecol 10:703–713. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1526-100X.2002.01051.x
Damasceno G, Souza L, Pivello VR, Gorgone-Barbosa E, Giroldo PZ, Fidelis A (2018) Impact of invasive grasses on Cerrado under natural regeneration. Biol Invasions 20:3621–3629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-018-1800-6
Davies KW (2011) Plant community diversity and native plant abundance decline with increasing abundance of an exotic annual grass. Oecologia 167:481–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-011-1992-2
Davis MA, Grime JP, Thompson K (2000) Fluctuating resources in plant communities: a general theory of invasibility. J Ecol 88:528–534. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2745.2000.00473.x
Dickson TL, Hopwood JL, Wilsey BJ (2012) Do priority effects benefit invasive plants more than native plants? An experiment with six grassland species. Biol Invasions 14:2617–2624
Djukic I, Kepfer-Rojas S, Schmidt IK, Larsen KS, Beier C, Berg B, Verheyen K, Caliman A, Paquette A, Gutiérrez-Girón A, Humber A, Valdecantos A, Petraglia A, Alexander H, Augustaitis A, Saillard A, Fernández ACR, Sousa AI, Lillebø AI, da Rocha GA, Francez A-J, Fischer A, Bohner A, Malyshev A, Andrić A, Smith A, Stanisci A, Seres A, Schmidt A, Avila A, Probst A, Ouin A, Khuroo AA, Verstraeten A, Palabral-Aguilera AN, Stefanski A, Gaxiola A, Muys B, Bosman B, Ahrends B, Parker B, Sattler B, Yang B, Juráni B, Erschbamer B, Ortiz CER, Christiansen CT, Carol Adair E, Meredieu C, Mony C, Nock CA, Chen C-L, Wang C-P, Baum C, Rixen C, Delire C, Piscart C, Andrews C, Rebmann C, Branquinho C, Polyanskaya D, Delgado DF, Wundram D, Radeideh D, Ordóñez-Regil E, Crawford E, Preda E, Tropina E, Groner E, Lucot E, Hornung E, Gacia E, Lévesque E, Benedito E, Davydov EA, Ampoorter E, Bolzan FP, Varela F, Kristöfel F, Maestre FT, Maunoury-Danger F, Hofhansl F, Kitz F, Sutter F, Cuesta F, de Almeida LF, de Souza FL, Berninger F, Zehetner F, Wohlfahrt G, Vourlitis G, Carreño-Rocabado G, Arena G, Pinha GD, González G, Canut G, Lee H, Verbeeck H, Auge H, Pauli H, Nacro HB, Bahamonde HA, Feldhaar H, Jäger H, Serrano HC, Verheyden H, Bruelheide H, Meesenburg H, Jungkunst H, Jactel H, Shibata H, Kurokawa H, Rosas HL, Rojas Villalobos HL, Yesilonis I, Melece I, Van Halder I, Quirós IG, Makelele I, Senou I, Fekete I, Mihal I, Ostonen I, Borovská J, Roales J, Shoqeir J, Lata J-C, Theurillat J-P, Probst J-L, Zimmerman J, Vijayanathan J, Tang J, Thompson J, Doležal J, Sanchez-Cabeza J-A, Merlet J, Henschel J, Neirynck J, Knops J, Loehr J, von Oppen J, Þorláksdóttir JS, Löffler J, Cardoso-Mohedano J-G, Benito-Alonso J-L, Torezan JM, Morina JC, Jiménez JJ, Quinde JD, Alatalo J, Seeber J, Stadler J, Kriiska K, Coulibaly K, Fukuzawa K, Szlavecz K, Gerhátová K, Lajtha K, Käppeler K, Jennings KA, Tielbörger K, Hoshizaki K, Green K, Yé L, Pazianoto LHR, Dienstbach L, Williams L, Yahdjian L, Brigham LM, van den Brink L, Rustad L, Zhang L, Morillas L, Xiankai L, Carneiro LS, Di Martino L, Villar L, Bader MY, Morley M, Lebouvier M, Tomaselli M, Sternberg M, Schaub M, Santos-Reis M, Glushkova M, Torres MGA, Giroux M-A, de Graaff M-A, Pons M-N, Bauters M, Mazón M, Frenzel M, Didion M, Wagner M, Hamid M, Lopes ML, Apple M, Schädler M, Weih M, Gualmini M, Vadeboncoeur MA, Bierbaumer M, Danger M, Liddell M, Mirtl M, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Růžek M, Carbognani M, Di Musciano M, Matsushita M, Zhiyanski M, Pușcaș M, Barna M, Ataka M, Jiangming M, Alsafran M, Carnol M, Barsoum N, Tokuchi N, Eisenhauer N, Lecomte N, Filippova N, Hölzel N, Ferlian O, Romero O, Pinto OB, Peri P, Weber P, Vittoz P, Turtureanu PD, Fleischer P, Macreadie P, Haase P, Reich P, Petřík P, Choler P, Marmonier P, Muriel P, Ponette Q, Guariento RD, Canessa R, Kiese R, Hewitt R, Rønn R, Adrian R, Kanka R, Weigel R, Gatti RC, Martins RL, Georges R, Meneses RI, Gavilán RG, Dasgupta S, Wittlinger S, Puijalon S, Freda S, Suzuki S, Charles S, Gogo S, Drollinger S, Mereu S, Wipf S, Trevathan-Tackett S, Löfgren S, Stoll S, Trogisch S, Hoeber S, Seitz S, Glatzel S, Milton SJ, Dousset S, Mori T, Sato T, Ise T, Hishi T, Kenta T, Nakaji T, Michelan TS, Camboulive T, Mozdzer TJ, Scholten T, Spiegelberger T, Zechmeister T, Kleinebecker T, Hiura T, Enoki T, Ursu T-M, di Cella UM, Hamer U, Klaus VH, Rêgo VM, Di Cecco V, Busch V, Fontana V, Piscová V, Carbonell V, Ochoa V, Bretagnolle V, Maire V, Farjalla V, Zhou W, Luo W, McDowell WH, Hu Y, Utsumi Y, Kominami Y, Zaika Y, Rozhkov Y, Kotroczó Z, Tóth Z (2018) Early stage litter decomposition across biomes. Sci Total Environ 628-629:1369–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.012
Dukes JS, Mooney HA (1999) Does global change increase the success of biological invaders? Trends Ecol Evol 14:135–139
Dziadowiec H (1987) The decomposition of plant litter fall in an oak-linden-hornbeam forest and an oak-pine mixed forest of the Białowieża National Park. Acta Soc Bot Pol 56:169–185
Early R, Bradley BA, Dukes JS, Lawler JJ, Olden JD, Blumenthal DM, Gonzalez P, Grosholz ED, Ibañez I, Miller LP, Sorte CJB, Tatem AJ (2016) Global threats from invasive alien species in the twenty-first century and national response capacities. Nat Commun 7:12485. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12485. https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms12485#supplementary-information
Ehrenfeld JG (2003) Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes. Ecosystems 6:503–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-002-0151-3
Enright NJ, Ogden J (1987) Decomposition of litter from common woody species of kauri (Agathis australis Salisb.) forest in northern New Zealand. Aust J Ecol 12:109–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.1987.tb00933.x
Facelli JM (1994) Multiple indirect effects of plant litter affect the establishment of Woody seedlings in old fields. Ecology 75:1727–1735. https://doi.org/10.2307/1939632
Facelli JM, Pickett STA (1991) Plant litter: its dynamics and effects on plant community structure. Bot Rev 57:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02858763
Farrer EC, Goldberg DE (2009) Litter drives ecosystem and plant community changes in cattail invasion. Ecol Appl 19:398–412. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-0485.1
Freschet GT, Aerts R, Cornelissen JHC (2012) A plant economics spectrum of litter decomposability. Funct Ecol 26:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2011.01913.x
Freschet GT, Cornwell WK, Wardle DA, Elumeeva TG, Liu W, Jackson BG, Onipchenko VG, Soudzilovskaia NA, Tao J, Cornelissen JHC (2013) Linking litter decomposition of above- and below-ground organs to plant–soil feedbacks worldwide. J Ecol 101:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12092
Gaertner M, Biggs R, Beest MT, Hui C, Molofsky J, Richardson DM (2014) Invasive plants as drivers of regime shifts: identifying high-priority invaders that alter feedback relationships. Divers Distrib 20:733–744. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12182
González G, Seastedt TR (2001) Soil fauna and plant litter decomposition in tropical and subalpine forests. Ecology 82:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[0955:Sfapld]2.0.Co;2
Gosz JR, Likens GE, Bormann FH (1973) Nutrient release from decomposing leaf and branch litter in the Hubbard brook Forest, New Hampshire. Ecol Monogr 43:173–191
Gulis V, Suberkropp K (2003) Leaf litter decomposition and microbial activity in nutrient-enriched and unaltered reaches of a headwater stream. Freshw Biol 48:123–134
Hättenschwiler S, Gasser P (2005) Soil animals alter plant litter diversity effects on decomposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:1519–1524. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0404977102
Heneghan L, Fatemi F, Umek L, Grady K, Fagen K, Workman M (2006) The invasive shrub European buckthorn (Rhamnus cathartica, L.) alters soil properties in Midwestern US woodlands. Appl Soil Ecol 32:142–148
Hess MC, Mesléard F, Buisson E (2019) Priority effects: emerging principles for invasive plant species management. Ecol Eng 127:48–57
Hobbie SE (2015) Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol Evol 30:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.03.015
Hobbie SE, Vitousek PM (2000) Nutrient limitation of decomposition in Hawaian forests. Ecology 81:1867–1877. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2000)081[1867:NLODIH]2.0.CO;2
Hobbie SE, Oleksyn J, Eissenstat DM, Reich PB (2010) Fine root decomposition rates do not mirror those of leaf litter among temperate tree species. Oecologia 162:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-009-1479-6
Holdredge C, Bertness MD (2011) Litter legacy increases the competitive advantage of invasive Phragmites australis in New England wetlands. Biol Invasions 13:423–433
Jia C, Huang Z, Miao H-T, Lu R, Li J, Liu Y, Shen W, He H, Wu G-L (2018) Litter crusts promote herb species formation by improving surface microhabitats in a desert ecosystem. Catena 171:245–250
Jiang L, Yue K, Yang Y, Wu Q (2016) Leaching and freeze-thaw events contribute to litter decomposition-a review. Sains Malaysiana 45:1041–1047
Jo I, Fridley JD, Frank DA (2017) Invasive plants accelerate nitrogen cycling: evidence from experimental woody monocultures. J Ecol 105:1105–1110. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12732
Johnson WG, Ott EJ, Gibson KD, Nielsen RL, Bauman TT (2007) Influence of nitrogen application timing on low density giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) interference in corn. Weed Technol 21:763–767. https://doi.org/10.1614/WT-06-171.1
Jung IW, Bae DH, Kim G (2011) Recent trends of mean and extreme precipitation in Korea. Int J Climatol 31:359–370
Kang BH, Shim SI, Lee SG, Kim KH, Chung IM (1998) Evaluation of Ambrosia artemisiifolia var. elatior, Ambrosia trifida, Rumex crispus for phytoremediation of Cu and Cd contaminated soil. Kor J Weed Sci 18:262–267
Keane RM, Crawley MJ (2002) Exotic plant invasions and the enemy release hypothesis. Trends Ecol Evol 17:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(02)02499-0
Keyport S, Carson BD, Johnson O, Lawrence BA, Lishawa SC, Tuchman NC, Kelly JJ (2019) Effects of experimental harvesting of an invasive hybrid cattail on wetland structure and function. Restor Ecol 27:389–398
Kil JH, Shim KC, Park SH, Koh KS, Suh MH, Ku YB, Suh SU, Oh HK, Kong HY (2004) Distributions of naturalized alien plants in South Korea. Weed Technol 18:1493–1495
Kim KD (2017) Distribution and management of the invasive exotic species Ambrosia trifida and Sicyos angulatus in the Seoul metropolitan area. Journal of Ecological Engineering 18:27–36. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/76216
Kim KH, Kang SH (2019) Flora of Western civilian control zone (CCZ) in Korea. Korean Journal of Plant Resources 32:565–588
Kim E, Kim M, Lee S, Hong YS, Lee E, Park J, Lee S, Cho K, You Y (2018) Impact of Ambrosia trifida L. (invasive plant) on the plant diversity and performance of Polygonatum stenophyllum maxim. (near threatended) and managmenet suggestion for the habitat conservation. Journal of Wetlands Research 20:249–255
Langley JA, Hungate BA (2003) Mycorrhizal controls on belowground litter quality. Ecology 84:2302–2312. https://doi.org/10.1890/02-0282
Lee IY, Park J, Oh SM, Park JE, Kwon O (2007) Selection of insects for potential biological control of Ambrosia trifida. Kor J Weed Sci 27:309–317
Lee CS, Cho YC, Shin HC, Kim GS, Pi JH (2010) Control of an invasive alien species, Ambrosia trifida with restoration by introducing willows as a typical riparian vegetation. Journal of Ecology and Field Biology 33:157–164. https://doi.org/10.5141/JEFB.2010.33.2.157
Lee SH, Choi SS, Lee DB, Hwang SH, Ahn JK (2016) The Flora of vascular plants in the west side of DMZ area. Korean Journal of Environment and Ecology 30:1–18
Liu Y, Liu M, Xu X, Tian Y, Zhang Z, van Kleunen M (2018) The effects of changes in water and nitrogen availability on alien plant invasion into a stand of a native grassland species. Oecologia. 188:441–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-018-4216-1
Lu XR, Liu T, Wang R, Wang H, Duan YX (2016) Impacts of leaf litter decomposition of invasive plant Ambrosia trifida on soil nematode community structure. Chinese Journal of Ecology 35:2369–2378. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.201609.012
Mariotte P, Spotswood EN, Farrer EC, Suding KN (2017) Positive litter feedbacks of an introduced species reduce native diversity and promote invasion in Californian grasslands. Appl Veg Sci 20:28–39
Maron JL, Vilà M (2001) When do herbivores affect plant invasion? Evidence for the natural enemies and biotic resistance hypotheses. Oikos 95:361–373. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0706.2001.950301.x
Medina-Villar S, Castro-Díez P, Alonso A, Cabra-Rivas I, Parker IM, Pérez-Corona E (2015) Do the invasive trees, Ailanthus altissima and Robinia pseudoacacia, alter litterfall dynamics and soil properties of riparian ecosystems in Central Spain? Plant Soil 396:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2592-4
Meier CL, Bowman WD (2008) Links between plant litter chemistry, species diversity, and below-ground ecosystem function. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:19780–19785. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805600105
Meisner A, De Boer W, Cornelissen JH, van der Putten WH (2012) Reciprocal effects of litter from exotic and congeneric native plant species via soil nutrients. PLoS One 7:e31596
Melillo JM, Aber JD, Muratore JF (1982) Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 63:621–626
Mfilinge P, Atta N, Tsuchiya M (2002) Nutrient dynamics and leaf litter decomposition in a subtropical mangrove forest at Oura Bay, Okinawa, Japan. Trees 16:172–180
Montagnani C, Gentili R, Smith M, Guarino M, Citterio S (2017) The worldwide spread, success, and impact of ragweed (Ambrosia spp.). Crit Rev Plant Sci 36:139–178
Moore JC, Berlow EL, Coleman DC, Ruiter PC, Dong Q, Hastings A, Johnson NC, McCann KS, Melville K, Morin PJ, Nadelhoffer K, Rosemond AD, Post DM, Sabo JL, Scow KM, Vanni MJ, Wall DH (2004) Detritus, trophic dynamics and biodiversity. Ecol Lett 7:584–600. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00606.x
Moro MJ, Domingo F (2000) Litter decomposition in four Woody species in a Mediterranean climate: weight loss, N and P dynamics. Ann Bot 86:1065–1071. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.2000.1269
Morris KA, Stark JM, Bugbee B, Norton JM (2016) The invasive annual cheatgrass releases more nitrogen than crested wheatgrass through root exudation and senescence. Oecologia 181:971–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-015-3544-7
Olson JS (1963) Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44:322–331. https://doi.org/10.2307/1932179
Olson BE, Wallander RT (2002) Effects of invasive forb litter on seed germination, seedling growth and survival. Basic Appl Ecol 3:309–317
Osono T, Takeda H (2004) Potassium, calcium, and magnesium dynamics during litter decomposition in a cool temperate forest. J For Res 9:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-003-0047-x
Park EJ, Nam MA (2013) Changes in land cover and the cultivation area of ginseng in the civilian control zone -Paju city and Yeoncheon county. Korean Journal of Environment and Ecology 27:507–515
Park HC, Lim JC, Lee JH, Lee GG (2017) Predicting the potential distributions of invasive species using the landsat imagery and Maxent: Focused on "Ambrosia trifida L. var. " in Korean Demilitarized Zone. Journal of Korean Envrionmental Restoration Technology 20:1–12
Petersen RC, Cummins KW (1974) Leaf processing in a woodland stream. Freshw Biol 4:343–368
Pickett B, Irvine IC, Bullock E, Arogyaswamy K, Aronson E (2019) Legacy effects of invasive grass impact soil microbes and native shrub growth. Invasive Plant Sci Manag 12:22–35
Pimentel D, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2005) Update on the environmental and economic costs associated with alien-invasive species in the United States. Ecol Econ 52:273–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.10.002
Plaster E (2013) Soil science and management. Cengage learning, Melbourne
Pyšek P, Jarošík V, Hulme PE, Pergl J, Hejda M, Schaffner U, Vilà M (2012) A global assessment of invasive plant impacts on resident species, communities and ecosystems: the interaction of impact measures, invading species' traits and environment. Glob Chang Biol 18:1725–1737. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02636.x
R Core Team (2016) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Reich PB, Oleksyn J, Modrzynski J, Mrozinski P, Hobbie SE, Eissenstat DM, Chorover J, Chadwick OA, Hale CM, Tjoelker MG (2005) Linking litter calcium, earthworms and soil properties: a common garden test with 14 tree species. Ecol Lett 8:811–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00779.x
Ruhland CT, Remund AJ, Tiry CM, Secott TE (2018) Litter decomposition of three lignin-deficient mutants of Sorghum bicolor during spring thaw. Acta Oecol 91:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actao.2018.05.009
Rutigliano FA, Alfani A, Bellini L, De Santo AV (1998) Nutrient dynamics in decaying leaves of Fagus sylvatica L. and needles of Abies alba mill. Biol Fertil Soils 27:119–126
Salamanca EF, Kaneko N, Katagiri S, Nagayama Y (1998) Nutrient dynamics and lignocellulose degradation in decomposing Quercus serrata leaf litter. Ecol Res 13:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1703.1998.00258.x
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2012) The role of plants in the effects of global change on nutrient availability and stoichiometry in the plant-soil system. Plant Physiol 160:1741–1761. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.208785
Sardans J, Bartrons M, Margalef O, Gargallo-Garriga A, Janssens IA, Ciais P, Obersteiner M, Sigurdsson BD, Chen HY, Peñuelas J (2017) Plant invasion is associated with higher plant–soil nutrient concentrations in nutrient-poor environments. Glob Chang Biol 23:1282–1291
Setälä H, Huhta V (1990) Evaluation of the soil fauna impact on decomposition in a simulated coniferous forest soil. Biol Fertil Soils 10:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00336130
Simberloff D, Von Holle B (1999) Positive interactions of nonindigenous species: Invasional meltdown? Biol Invasions 1:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010086329619
Smith SD, Huxman TE, Zitzer SF, Charlet TN, Housman DC, Coleman JS, Fenstermaker LK, Seemann JR, Nowak RS (2000) Elevated CO2 increases productivity and invasive species success in an arid ecosystem. Nature 408:79–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/35040544
Swift MJ, Heal OW, Anderson JM, Anderson J (1979) Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Univ of California Press, Berkeley
Taylor BR, Parkinson D (1988) Does repeated freezing and thawing accelerate decay of leaf litter? Soil Biol Biochem 20:657–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(88)90150-2
Taylor BR, Parkinson D, Parsons WFJ (1989) Nitrogen and lignin content as predictors of litter decay rates: a microcosm test. Ecology 70:97–104. https://doi.org/10.2307/1938416
Theodore MW, Mark ML, Emilie ER, Harrison SK (1994) Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) canopy architecture and interference studies in soybean (Glycine max). Weed Technol 8:559–564
Tilman D (1980) Resources: a graphical-mechanistic approach to competition and predation. Am Nat 116:362–393. https://doi.org/10.1086/283633
Twilley RR, Pozo M, Garcia VH, Rivera-Monroy VH, Zambrano R, Bodero A (1997) Litter dynamics in riverine mangrove forests in the Guayas River estuary, Ecuador. Oecologia 111:109–122
Veen C, Fry E, ten Hooven F, Kardol P, Morriën E, De Long JR (2019) The role of plant litter in driving plant-soil feedbacks. Front Environ Sci 7:168
Vilà M, Espinar JL, Hejda M, Hulme PE, Jarošík V, Maron JL, Pergl J, Schaffner U, Sun Y, Pyšek P (2011) Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: a meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecol Lett 14:702–708. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01628.x
Vitousek PM, D’Antonio CM, Loope LL, RejmÁNek M, Westbrooks R (1997) Introduced species: a significant component of humna-caused global change. N Z J Ecol 21:1–16
Wang J, You Y, Tang Z, Liu S, Sun OJ (2014) Variations in leaf litter decomposition across contrasting forest stands and controlling factors at local scale. J Plant Ecol 8:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtu019
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setälä H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304:1629–1633. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094875
Williams LK, Shaw JD, Sindel BM, Wilson SC, Kristiansen P (2018) Longevity, growth and community ecology of invasive Poa annua across environmental gradients in the subantarctic. Basic Appl Ecol 29:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2018.02.003
Williamson MH, Fitter A (1996) The characters of successful invaders. Biol Conserv 78:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3207(96)00025-0
Wohler JR, Robertson DB, Laube HR (1975) Studies on the decomposition of Potamogeton diversifolius. Bull Torrey Bot Club 102:76–78. https://doi.org/10.2307/2484417
Wolkovich EM, Bolger DT, Cottingham KL (2009) Invasive grass litter facilitates native shrubs through abiotic effects. J Veg Sci 20:1121–1132
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee T, Lee W, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas M-L, Niinemets Ü, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov VI, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 428:821–827. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02403
Xiong S, Nilsson C (1999) The effects of plant litter on vegetation: a meta-analysis. J Ecol 87:984–994. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2745.1999.00414.x
Xiong Y, Xia H, Za L, Cai Xa FS (2008) Impacts of litter and understory removal on soil properties in a subtropical Acacia mangium plantation in China. Plant Soil 304:179–188
Xu X, Hirata E (2005) Decomposition patterns of leaf litter of seven common canopy species in a subtropical forest: N and P dynamics. Plant Soil 273:279–289
Xu X, Hirata E, Enoki T, Tokashiki Y (2004) Leaf litter decomposition and nutrient dynamics in a subtropical forest after typhoon disturbance. Plant Ecol 173:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:Vege.0000029319.05980.70
Xu J, Tang C, Chen ZL (2006) The role of plant residues in pH change of acid soils differing in initial pH. Soil Biol Biochem 38:709–719
Zhang D, Hui D, Luo Y, Zhou G (2008) Rates of litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: global patterns and controlling factors. J Plant Ecol 1:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtn002
Zhang L, Wang H, Zou J, Rogers WE, Siemann E (2014) Non-native plant litter enhances soil carbon dioxide emissions in an invaded annual grassland. PLoS ONE 9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092301
Zhang P, Li B, Wu J, Hu S (2019) Invasive plants differentially affect soil biota through litter and rhizosphere pathways: a meta-analysis. Ecol Lett 22:200–210
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the anonymous referees whose valuable suggestions and comments significantly improved the quality of this paper. This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2017R1A2B4006761).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alfonso Escudero.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mun, S., Lee, E.J. Litter decomposition rate and nutrient dynamics of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) in the non-native habitat of South Korea. Plant Soil 449, 373–388 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04502-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04502-7