Abstract
Background and aims
Soil hydraulic properties drive water distribution and availability in soil. There exists limited knowledge of how plant species diversity might influence soil hydraulic properties.
Methods
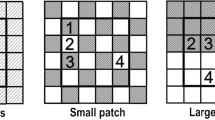
We quantified the change in infiltration capacity affected by soil structural variables (soil bulk density, porosity and organic carbon content) along a gradient of soil texture, plant species richness (1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 60) and functional group composition (grasses, legumes, small herbs, tall herbs). We conducted two infiltration measurement campaigns (May and October 2012) using a hood infiltrometer.
Results
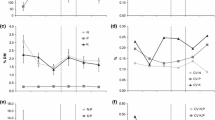
Plant species richness significantly increased infiltration capacity in the studied grasslands. Both soil porosity (or inversely bulk density) and organic carbon played an important role in mediating the plant species richness effect. Soil texture did not correlate with infiltration capacity. In spring 2012, earthworm biomass increased infiltration capacity, but this effect could not be attributed to changes in soil structural variables.
Conclusions
We experimentally identified important ecological drivers of infiltration capacity, suggesting complex interactions between plant species richness, earthworms, and soil structural variables, while showing little impact of soil texture. Changes in plant species richness may thus have significant effects on soil hydraulic properties with potential consequences for surface run-off and soil erosion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaoui A, Lipiec J, Gerke HH (2011) A review of the changes in the soil pore system due to soil deformation: a hydrodynamic perspective. Soil Tillage Res 115–116:1–15
Allan E, Weisser W, Weigelt A, Roscher C, Fischer M, Hillebrand H (2011) More diverse plant communities have higher functioning over time due to turnover in complementary dominant species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:17034–17039
Angers DA, Caron J (1998) Plant-induced changes in soil structure: processes and feedbacks. Biogeochemistry 42:55–72
Azooz RH, Arshad MA (1996) Soil infiltration and hydraulic conductivity under long-term no-tillage and conventional tillage systems. Can J Soil Sci 76:143–152
Barley KP (1954) Effects of root growth and decay on the permeability of a synthetic sandy loam. Soil Sci 78:205–210
Berglund ER, Ahyoud A, Tayaa MH (1980) Comparison of soil and infiltration properties of range and afforested sites in northern Morocco. For Ecol Manage 3:295–306
Beven K (1981) Micro-, meso-, macroporosity and channeling flow phenomena in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45:1245–1245
Beven K, Germann P (2013) Macropores and water flow in soils revisited. Water Resour Res 49:3071–3092
Bissinger V, Kolditz O (2008) Helmholtz Interdisciplinary Graduate School for Environmental Research (HIGRADE). GAIA 1:71–73
Bouché MB (1977) Strategies lombriciennes. Ecol Bull 25:122–132
Bouché MB, Al-Addan F (1996) Earthworms, water infiltration and soil stability: some new assessments. Soil Biol Biochem 29:441–452
Bouma J, Anderson JL (1973) Relationships between soil structure characteristics and hydraulic conductivity. In: Bruce RR (ed) Field soil water regime. SSSA Spec. Pupl. No. 5. Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison
Caldeira MC, Ryel RJ, Lawton JH, Pereira JS (2001) Mechanisms of positive biodiversity–production relationships: insights provided by δ13C analysis in experimental Mediterranean grassland plots. Ecol Lett 4:439–443
Cong W-F, van Ruijven J, Mommer L, De Deyn GB, Berendse F, Hoffland E (2014) Plant species richness promotes soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in grasslands without legumes. J Ecol 102:1163–1170
De Boeck H, Lemmens C, Bossuyt H, Malchair S, Carnol M, Merckx R, Nijs I, Ceulemans R (2006) How do climate warming and plant species richness affect water use in experimental grasslands? Plant Soil 288:249–261
Dekker LW, Ritsema CJ (1994) How water moves in a water repellent sandy soil: 1. Potential and actual water repellency. Water Resour Res 30:2507–2517
Dimitrakopoulos PG, Schmid B (2004) Biodiversity effects increase linearly with biotope space. Ecol Lett 7:574–583
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1996) The biology and ecology of earthworms. Chapman and Hall, London
Eisenhauer N, Scheu S (2008a) Earthworms as drivers of the competition between grasses and legumes. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2650–2659
Eisenhauer N, Straube D, Scheu S (2008b) Efficiency of two widespread non-destructive extraction methods under dry soil conditions for different ecological earthworm groups. Eur J Soil Biol 44:141–145
Eisenhauer N, Milcu A, Sabais ACW, Bessler H, Weigelt A, Engels C, Scheu S (2009a) Plant community impacts on the structure of earthworm communities depend on season and change with time. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2430–2443
Eisenhauer N, Milcu A, Nitschke N, Sabais A, Scherber C, Scheu S (2009b) Earthworm and belowground competition effects on plant productivity in a plant diversity gradient. Oecologia 161:291–301
Eisenhauer N, Beßler H, Engels C, Gleixner G, Habekost M, Milcu A, Partsch S, Sabais ACW, Scherber C, Steinbeiss S, Weigelt A, Weisser WW, Scheu S (2010) Plant diversity effects on soil microorganisms support the singular hypothesis. Ecol 91:485–496
Ellenberg H, Leuschner C (2010) Vegetation Mitteleuropas mit den Alpen: In ökologischer, dynamischer und historischer Sicht. Ulmer Verlag, Stuttgart
FAO (2006) Guidelines for soil description. FAO, Rome
FAO-Unesco (1997) Soil map of the world. Revised legend with corrections and update. ISRIC, Wageningen
Fischer C, Roscher C, Jensen B, Eisenhauer N, Baade J, Attinger S, Scheu S, Weisser WW, Schumacher J, Hildebrandt A (2014) How do earthworms, soil texture and plant composition affect infiltration along an experimental plant diversity gradient in grassland? PLoS One 9:e98987
Fonte SJ, Winsome T, Six J (2009) Earthworm populations in relation to soil organic matter dynamics and management in California tomato cropping systems. Appl Soil Ecol 41:206–214
Fornara DA, Tilman D (2008) Plant functional composition influences rates of soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation. J Ecol 96:314–322
Franzluebbers AJ (2002) Water infiltration and soil structure related to organic matter and its stratification with depth. Soil Tillage Res 66:197–205
Germann P, Beven K (1981) Water flow in soil macropores I. An experimental approach. J Soil Sci 32:1–13
Gish TJ, Jury WA (1983) Effect of plant root channels on solute transport. Trans Am Soc Agric Eng 26:440–444
Grace J (2006) Structural equation modeling and natural systems. Cambridge Univ, Press
Haynes RJ, Naidu R (1998) Influence of lime, fertilizer and manure applications on soil organic matter content and soil physical conditions: a review. Nut Cyc Agroecosyst 51:123–137
Hillel D (1998) Environmental soil physics. CA Academic Press, New York
IPCC (2012) Summary for policemakers. In: managing the risks of extrem events and disaster in advance climate change adaption. In: CB Field, Barros V, Stocker TF, Qin D, Dokken DJ, Ebi KL, Mastrandrea MD, Mach K., PJ, G.-K, Allen SK, Tignor M & Midgley PM) (eds) A special report of working groups I and II of the intergovernmental panel on climate change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, NY, USA
Isselstein J, Jeangros B, Pavlu V (2005) Agronomic aspects of biodiversity targeted management of temperate grasslands in Europe–a review. Agron Res 3:139–151
Jarvis NJ, Leeds-Harrison PB, Dosser JM (1987) The use of tension infiltrometers to assess routes and rates of infiltration in a clay soil. J Soil Sci 38:633–640
Kahmen A, Perner J, Buchmann N (2005) Diversity-dependent productivity in semi-natural grasslands following climate perturbations. Funct Ecol 19:594–601
Kluge G, Müller-Westermeier G (2000) Das Klima ausgewählter Orte der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Berichte des Deutschen Wetterdienstes 213. Offenbach/ Main, Jena
Lado M, Paz A, Ben-Hur M (2004) Organic matter and aggregate-size interactions in saturated hydraulic conductivity contribution from the agricultural research organization, The Volcani Center, No. 623/02, 2002 series. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:234–242
Lavelle P (1997) Faunal activities and soil processes: adaptive strategies that determine ecosystem function. Adv Ecol Res Vol 27:93–132
Leimer S, Kreutziger Y, Rosenkranz S, Beßler H, Engels C, Hildebrandt A, Oelmann Y, Weisser WW, Wirth C, Wilcke W (2014) Plant diversity effects on the water balance of an experimental grassland. Ecohydrol 7:1378–1391
Marquard E, Weigelt A, Temperton VM, Roscher C, Schumacher J, Buchmann N, Fischer M, Weisser WW, Schmid B (2009) Plant species richness and functional composition drive overyielding in a 6-year grassland experiment. Ecol 90:3290–3302
Meek BD, Rechel ER, Carter LM, DeTar WR, Urie AL (1992) Infiltration rate of a sandy loam soil: effects of traffic, tillage, and plant roots. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:908–913
Messing I, Jarvis NJ (1990) Seasonal variation in field-saturated hydraulic conductivity in two swelling clay soils in Sweden. J Soil Sci 41:229–237
Messing I, Jarvis NJ (1993) Temporal variation in the hydraulic conductivity of a tilled clay soil as measured by tension infiltrometers. J Soil Sci 44:11–24
Mitchell AR, Ellsworth TR, Meek BD (1995) Effect of root systems on preferential flow in swelling soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:2655–2666
Oades JM (1993) The role of biology in the formation, stabilization and degradation of soil structure. Geoderma 56:377–400
Ortlepp S (2004) Holozäne fluviale Dynamik im mittleren Saaletal. Sedimentologische Untersuchungen in der Unteraue. Friedrich-Schiller-Universität FSU Jena, Jena
Pérès G, Cluzeau D, Menasseri S, Soussana JF, Bessler H, Engels C, Habekost M, Gleixner G, Weigelt A, Weisser WW, Scheu S, Eisenhauer N (2013) Mechanisms linking plant community properties to soil aggregate stability in an experimental grassland plant diversity gradient. Plant Soil 373:285–299
Périé C, Ouimet R (2008) Organic carbon, organic matter and bulk density relationships in boreal forest soils. Can J Soil Sci 88:315–325
Pinheiro JC, Bates DM (2000) Mixed-effects models in S and S-Plus. Springer, New York
Ravenek JM, Bessler H, Engels C, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Gessler A, Gockele A, De Luca E, Temperton VM, Ebeling A, Roscher C, Schmid B, Weisser WW, Wirth C, de Kroon H, Weigelt A, Mommer L (2014) Long-term study of root biomass in a biodiversity experiment reveals shifts in diversity effects over time. Oikos. doi:10.1111/oik.01502
Rawls WJ, Brakensiek DL, Saxto KE (1982) Estimation of soil water properties. Trans ASAE 25:1316–1320
Richard G, Cousin I, Sillon JF, Bruand A, Guérif J (2001) Effect of compaction on the porosity of a silty soil: influence on unsaturated hydraulic properties. Eur J Soil Sci 52:49–58
Roscher C, Schumacher J, Baade J, Wilcke W, Gleixner G, Weisser WW, Schmid B, Schulze E-D (2004) The role of biodiversity for element cycling and trophic interactions: an experimental approach in a grassland community. Basic Appl Ecol 5:107–121
Roscher C, Temperton VM, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schumacher J, Schmid B, Buchmann N, Weisser WW, Schulze E-D (2005) Overyielding in experimental grassland communities– irrespective of species pool or spatial scale. Ecol Lett 8:419–429
Salehi A, Ghorbanzadeh N, Kahneh E (2013) Earthworm biomass and abundance, soil chemical and physical properties under different poplar plantations in the north of Iran. J For Sci 59:223–229
Schaap MG, Leij FJ (1998) Using neural networks to predict soil water retention and soil hydraulic conductivity. Soil Tillage Res 47:37–42
Scheinost AC, Sinowski W, Auerswald K (1997) Regionalization of soil water retention curves in a highly variable soilscape. I. Developing a new pedotransfer function. Geoderma 78:129–143
Schlichting E, Blume HP (1966) Bodenkundliches Praktikum: eine Einführung in pedologisches Arbeiten für Ökologen, insbesondere Land- und Forstwirte, und für Geowissenschaftler. Parey, Hamburg
Schumm SA, Lusby GC (1963) Seasonal variation of infiltration capacity and runoff on hillslopes in western Colorado. J Geophys Res 68:3655–3666
Schwärzel K, Punzel J (2007) Hood infiltrometer - a new type of tension infiltrometer. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1438–1447
Shipitalo MJ, Protz R (1988) Factors influencing the dispersibility of clay in worm casts. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:764–769
Shipitalo MJ, Nuutinen V, Butt KR (2004) Interaction of earthworm burrows and cracks in a clayey, subsurface-drained, soil. Appl Soil Ecol 26:209–217
Shipley B (2000) Cause and correlation in biology: a user’s guide to path analysis, structural equations and causal inference. Cambridge University Press, UK
Shukla MK, Lal R, Ebinger M (2006) Determining soil quality indicators by factor analysis. Soil Tillage Res 87:194–204
Six J, Bossuyt H, Degryze S, Denef K (2004) A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res 79:7–31
Slater CS (1957) Cylinder infiltrometers for determining rates of irrigation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 21:457–460
Smit HJ, Metzger MJ, Ewert F (2008) Spatial distribution of grassland productivity and land use in Europe. Agric Syst 98:208–219
Soil Survey Staff (2014) Keys to soil taxonomy, 12th edn. USDA-SCS, Washington
Soto B, Basanta R, Benito E, Perez R, Diaz-Fierros F (1994) Runoff and erosion from burnt soils in northwest Spain. In: Sala M, Rubio JL (eds) Soil erosion and degradation as a consequence of forest fires. Geoforma, Logroño
Spehn E, Joshi J, Schmid B, Alphei J, Körner C (2000) Plant diversity effects on soil heterotrophic activity in experimental grassland ecosystems. Plant Soil 224:217–230
Spehn EM, Hector A, Joshi J, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmid B, Bazeley-White E, Beierkuhnlein C, Caldeira MC, Diemer M, Dimitrakopoulos PG, Finn JA, Freitas H, Giller PS, Good J, Harris R, Högberg P, Huss-Danell K, Jumpponen A, Koricheva J, Leadley PW, Loreau M, Minns A, Mulder CPH, O’Donovan G, Otway SJ, Palmborg C, Pereira JS, Pfisterer AB, Prinz A, Read DJ, Schulze ED, Siamantziouras ASD, Terry AC, Troumbis AY, Woodward FI, Yachi S, Lawton JH (2005) Ecosystem effects of biodiversity manipulations in european grasslands. Ecol Monogr 75:37–63
Steinbeiss S, Beßler H, Engels C, Temperton VM, Buchmann N, Roscher C, Kreutziger Y, Baade J, Habekost M, Gleixner G (2008) Plant diversity positively affects short-term soil carbon storage in experimental grasslands. Global Chang Biol 14:2937–2949
Thielemann U (1986) The octet-method for sampling earthworm populations. Pedobiologia 29:296–302
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops J, Wedin D, Mielke T, Lehman C (2001) Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Sci 294:843–845
van Peer L, Nijs I, Reheul D, De Cauwer B (2004) Species richness and susceptibility to heat and drought extremes in synthesized grassland ecosystems: compositional vs physiological effects. Funct Ecol 18:769–778
van Schaik L, Palm J, Klaus J, Zehe E, Schröder B (2014) Linking spatial earthworm distribution to macropore numbers and hydrological effectiveness. Ecohydrology 7:401–408
Vereecken H (1995) Estimating the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity from theoretical models using simple soil properties. Geoderma 65:81–92
Vereecken H, Weynants M, Javaux M, Pachepsky Y, Schaap MG, Genuchten MTV (2010) Using pedotransfer functions to estimate the van Genuchten–Mualem soil hydraulic properties: A Review. Vadose Zone J 9:795–820
Weigelt A, Marquard E, Temperton VM, Roscher C, Scherber C, Mwangi PN, von Felten S, Buchmann N, Schmid B, Schulze E-D, Weisser WW (2010) The Jena experiment: 6 years of data from a grassland biodiversity experiment. Ecol 91:930–931
Weltzin JF, Loik ME, Schwinning S, Williams DG, Fay PA, Haddad BM, Harte J, Huxman TE, Knapp AK, Lin G, Pockman WT, Shaw MR, Small EE, Smith MD, Smith SD, Tissue DT, Zak JC (2003) Assessing the response of terrestrial ecosystems to potential changes in precipitation. Biosci 53:941–952
Wooding RA (1968) Steady infiltration from a shallow circular pond. Water Resour Res 4:1259–1273
Wösten JHM, van Genuchten MT (1988) Using texture and other soil properties to predict the unsaturated soil hydraulic functions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:1762–1770
Wösten J, Lilly A, Nemes A and Le Bas C (1998) Using existing soil data to derive hydraulic parameters for simulation models in enviromental studies and in land use planning. DLO-Staring Centre
Wösten JHM, Pachepsky YA, Rawls WJ (2001) Pedotransfer functions: bridging the gap between available basic soil data and missing soil hydraulic characteristics. J Hydrol 251:123–150
Yeates GW, Shepherd TG, Francis GS (1998) Contrasting response to cropping of populations of earthworms and predacious nematodes in four soils. Soil Tillage Res 48:255–264
Zacharias S, Wessolek G (2007) Excluding organic matter content from pedotransfer predictors of soil water retention. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:43–50
Zachmann JE, Linden DR, Clapp CE (1987) Macroporous infiltration and redistribution as affected by earthworms, tillage and residue. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1580–1586
Zehe E, Flühler H (2001) Slope scale variation of flow patterns in soil profiles. J Hydrol 247:116–132
Zhang GS, Chan KY, Oates A, Heenan DP, Huang GB (2007) Relationship between soil structure and runoff/soil loss after 24 years of conservation tillage. Soil Tillage Res 92:122–128
Zund PR, Pillai-McGarry U, McGarry D, Bray SG (1997) Repair of a compacted Oxisol by the earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae, Oligochaeta). Biol Fertil Soils 25:202–208
Acknowledgments
The Jena Experiment is funded by the German Science Foundation (DFG, FOR456) with additional support from the Max Planck Society and the University of Jena and coordinated by W.W. Weisser. We thank all the people involved in the maintenance of the experiment, infiltration measurements (in particular Franziska Guderle) and the gardeners. We thank Alexandra Weigelt, Sybille Steinbeiss, Maike Habekost, and Alexandru Milcu for providing raw data on plant community data, soil organic carbon content and earthworm biomass. We also thank the three anonymous reviewers for their insights which improved the manuscript. This work was kindly supported by Helmholtz Impulse and Networking Fund through Helmholtz Interdisciplinary Graduate School for Environmental Research (HIGRADE) (Bissinger and Kolditz 2008). Anke Hildebrandt was supported by AquaDiv@Jena, a project funded by the initiative “ProExzellenz” of the German federal state of Thuringia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kees Jan van Groenigen.
Awaiting commentary by Nikolaus Obojes
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Path analysis showing the relationships between plant species richness (SR), texture (sand in 0–10 cm depth), soil organic carbon content (SOC), porosity, belowground biomass (BM root in 0–5 cm depth), and infiltration capacity for the full model in a), and including earthworm biomass (only for May) in b).(GIF 47 kb)
ESM 2
(DOCX 16 kb)
ESM 3
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, C., Tischer, J., Roscher, C. et al. Plant species diversity affects infiltration capacity in an experimental grassland through changes in soil properties. Plant Soil 397, 1–16 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2373-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2373-5