Abstract
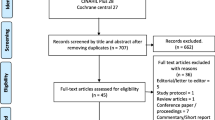
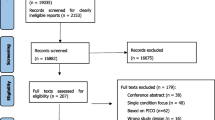
Background Multiple reviews have evaluated the impact of pharmacist-delivered patient care on health-related outcomes. However, it is unclear which of the pharmacist-delivered interventions in these services are the most effective. Aim of the review To gather the evidence of the impact of clinical pharmacy services on the medication use process or on patient outcomes using an overview of systematic reviews. Methods PubMed was searched to retrieve systematic reviews published between 2000 and 2010 that assessed the impact of clinical pharmacy services on the medication use process or patient outcomes. Two independent reviewers evaluated the study eligibility and one extracted the description and results of the services. The methodological quality of each review was assessed with the R-AMSTAR tool. Results Of the 343 potentially relevant records identified, 49 systematic reviews, comprising a total of 269 randomized controlled trials, met the selection criteria. Clinical pharmacy services that focused on specific medical conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes mellitus, revealed a positive impact of pharmacists’ interventions on patient outcomes. For other medical conditions, however, the results were inconclusive (e.g., dyslipidemia or thromboprophylaxis). Interventions that targeted medication adherence and assessed the impact of clinical pharmacy services in prescription appropriateness also produced inconclusive results because of the variability of methods used to assess both medication adherence and medication appropriateness. Conclusions Systematic reviews that assessed clinical pharmacy services targeting specific conditions were more conclusive given that the intervention was well defined, and the measured outcomes were unequivocal and tangible. Conversely, the results were inconclusive for interventions with a broader target and with monitoring parameters that were unclearly established or inconsistently assessed across studies. These findings emphasize the need to better define clinical pharmacy services and standardize methods that assess the impact of these services on patient health outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hepler CD. Clinical pharmacy, pharmaceutical care, and the quality of drug therapy. Pharmacotherapy. 2004;24(11):1491–8.
Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS. To err is human. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 2000.
Carter BL, Rogers M, Daly J, Zheng S, James PA. The potency of team-based care interventions for hypertension: a meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(19):1748–55.
Kaboli PJ, Hoth AB, McClimon BJ, Schnipper JL. Clinical pharmacists and inpatient medical care: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(9):955–64.
American College of Clinical Pharmacy. The definition of clinical pharmacy. Pharmacotherapy. 2008;28(6):816–7.
van Mil JW, Fernandez-Llimos F. What is ‘pharmaceutical care’ in 2013? Int J Clin Pharm. 2013;35(1):1–2.
Al-Rashed SA, Wright DJ, Roebuck N, Sunter W, Chrystyn H. The value of inpatient pharmaceutical counselling to elderly patients prior to discharge. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;54(6):657–64.
Chen Z, Ernst ME, Ardery G, Xu Y, Carter BL. Physician-pharmacist co-management and 24-hour blood pressure control. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013;15(5):337–43.
Koshman SL, Charrois TL, Simpson SH, McAlister FA, Tsuyuki RT. Pharmacist care of patients with heart failure: a systematic review of randomized trials. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(7):687–94.
Chisholm-Burns MA, Kim Lee J, Spivey CA, Slack M, Herrier RN, Hall-Lipsy E, et al. US pharmacists’ effect as team members on patient care: systematic review and meta-analyses. Med Care. 2010;48(10):923–33.
Salgado TM, Moles R, Benrimoj SI, Fernandez-Llimos F. Pharmacists’ interventions in the management of patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(1):276–92.
Saez-Benito L, Fernandez-Llimos F, Feletto E, Gastelurrutia MA, Martinez-Martinez F, Benrimoj SI. Evidence of the clinical effectiveness of cognitive pharmaceutical services for aged patients. Age Ageing. 2013;42(4):442–9.
Melchiors AC, Correr CJ, Venson R, Pontarolo R. An analysis of quality of systematic reviews on pharmacist health interventions. Int J Clin Pharm. 2012;34(1):32–42.
Viswanathan M, Kahwati LC, Golin CE, Blalock SJ, Coker-Schwimmer E, Posey R, et al. Medication therapy management interventions in outpatient settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(1):76–87.
Souza TT, Saez-Benito L, Correr CJ, Fernandez-Llimos F. Critical assessment of the systematic review on hospitalization resulting from medicine related problems. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;78(6):1465–6.
Kennie NR, Schuster BG, Einarson TR. Critical analysis of the pharmaceutical care research literature. Ann Pharmacother. 1998;32(1):17–26.
Charrois TL, Durec T, Tsuyuki RT. Systematic reviews of pharmacy practice research: methodologic issues in searching, evaluating, interpreting, and disseminating results. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43(1):118–22.
Correr CJ, Melchiors AC, de Souza TT, Rotta I, Salgado TM, Fernandez-Llimos F. A tool to characterize the components of pharmacist interventions in clinical pharmacy services: the DEPICT project. Ann Pharmacother. 2013;47(7–8):946–52.
Rotta I, Salgado TM, Felix DC, de Souza TT, Correr CJ, Fernandez-Llimos F. Ensuring consistent reporting of clinical pharmacy services to enhance reproducibility in practice: an improved version of DEPICT. J Eval Clin Pract. 2015. doi:10.1111/jep.12339. [Epub ahead of print].
Salgado TM, Correr CJ, Moles R, Benrimoj SI, Fernandez-Llimos F. Assessing the implementability of clinical pharmacist interventions in patients with chronic kidney disease: an analysis of systematic reviews. Ann Pharmacother. 2013;47(11):1498–506.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The cochrane collaboration. 2011.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336–41.
Kung J, Chiappelli F, Cajulis OO, Avezova R, Kossan G, Chew L, et al. From systematic reviews to clinical recommendations for evidence-based health care: validation of revised assessment of multiple systematic reviews (R-AMSTAR) for grading of clinical relevance. Open Dent J. 2010;4:84–91.
Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, Boers M, Andersson N, Hamel C, et al. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7:10.
Kozma CM, Reeder CE, Schulz RM. Economic, clinical, and humanistic outcomes: a planning model for pharmacoeconomic research. Clin Ther. 1993;15(6):1121–32.
Babinec PM, Rock MJ, Lorenzetti DL, Johnson JA. Do researchers use pharmacists’ communication as an outcome measure? A scoping review of pharmacist involvement in diabetes care. Int J Pharm Pract. 2010;18(4):183–93.
Blenkinsopp A, Anderson C, Armstrong M. Systematic review of the effectiveness of community pharmacy-based interventions to reduce risk behaviours and risk factors for coronary heart disease. J Public Health Med. 2003;25(2):144–53.
Fahey T, Schroeder K, Ebrahim S. Educational and organisational interventions used to improve the management of hypertension in primary care: a systematic review. Br J Gen Pract. 2005;55(520):875–82.
Gallagher H, de Lusignan S, Harris K, Cates C. Quality-improvement strategies for the management of hypertension in chronic kidney disease in primary care: a systematic review. Br J Gen Pract. 2010;60(575):e258–65.
Glynn LG, Murphy AW, Smith SM, Schroeder K, Fahey T. Self-monitoring and other non-pharmacological interventions to improve the management of hypertension in primary care: a systematic review. Br J Gen Pract. 2010;60(581):e476–88.
Glynn LG, Murphy AW, Smith SM, Schroeder K, Fahey T. Interventions used to improve control of blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; (3):CD005182.
Machado M, Bajcar J, Guzzo GC, Einarson TR. Sensitivity of patient outcomes to pharmacist interventions. Part II: systematic review and meta-analysis in hypertension management. Ann Pharmacother. 2007;41(11):1770–81.
Machado M, Bajcar J, Guzzo GC, Einarson TR. Sensitivity of patient outcomes to pharmacist interventions. Part I: systematic review and meta-analysis in diabetes management. Ann Pharmacother. 2007;41(10):1569–82.
Machado M, Nassor N, Bajcar JM, Guzzo GC, Einarson TR. Sensitivity of patient outcomes to pharmacist interventions. Part III: systematic review and meta-analysis in hyperlipidemia management. Ann Pharmacother. 2008;42(9):1195–207.
Renders CM, Valk GD, Griffin S, Wagner EH, Eijk JT, Assendelft WJ. Interventions to improve the management of diabetes mellitus in primary care, outpatient and community settings. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001; (1):CD001481.
Saokaew S, Permsuwan U, Chaiyakunapruk N, Nathisuwan S, Sukonthasarn A. Effectiveness of pharmacist-participated warfarin therapy management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(11):2418–27.
Sinclair HK, Bond CM, Stead LF. Community pharmacy personnel interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004; (1):CD003698.
Wubben DP, Vivian EM. Effects of pharmacist outpatient interventions on adults with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Pharmacotherapy. 2008;28(4):421–36.
Banning M. A review of interventions used to improve adherence to medication in older people. Int J Nurs Stud. 2009;46(11):1505–15.
Bell S, McLachlan AJ, Aslani P, Whitehead P, Chen TF. Community pharmacy services to optimise the use of medications for mental illness: a systematic review. Aust N Z Health Policy. 2005;2:29.
Cutrona SL, Choudhry NK, Fischer MA, Servi A, Liberman JN, Brennan TA, et al. Modes of delivery for interventions to improve cardiovascular medication adherence. Am J Manag Care. 2010;16(12):929–42.
Desplenter FA, Simoens S, Laekeman G. The impact of informing psychiatric patients about their medication: a systematic review. Pharm World Sci. 2006;28(6):329–41.
George J, Elliott RA, Stewart DC. A systematic review of interventions to improve medication taking in elderly patients prescribed multiple medications. Drugs Aging. 2008;25(4):307–24.
Haynes RB, Ackloo E, Sahota N, McDonald HP, Yao X. Interventions for enhancing medication adherence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;2:CD000011.
Lindenmeyer A, Hearnshaw H, Vermeire E, Van Royen P, Wens J, Biot Y. Interventions to improve adherence to medication in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of the literature on the role of pharmacists. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2006;31(5):409–19.
Morrison A, Wertheimer AI. Evaluation of studies investigating the effectiveness of pharmacists’ clinical services. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2001;58(7):569–77.
Ogedegbe G, Schoenthaler A. A systematic review of the effects of home blood pressure monitoring on medication adherence. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2006;8(3):174–80.
Rueda S, Park-Wyllie LY, Bayoumi AM, Tynan AM, Antoniou TA, Rourke SB, et al. Patient support and education for promoting adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy for HIV/AIDS. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006; (3):CD001442.
Schlenk EA, Bernardo LM, Organist LA, Klem ML, Engberg S. Optimizing medication adherence in older patients: a systematic review. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2008;15(12):595–606.
Van Wijk BL, Klungel OH, Heerdink ER, de Boer A. Effectiveness of interventions by community pharmacists to improve patient adherence to chronic medication: a systematic review. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39(2):319–28.
Williams A, Manias E, Walker R. Interventions to improve medication adherence in people with multiple chronic conditions: a systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2008;63(2):132–43.
Bayoumi I, Howard M, Holbrook AM, Schabort I. Interventions to improve medication reconciliation in primary care. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43(10):1667–75.
Costello I, Wong IC, Nunn AJ. A literature review to identify interventions to improve the use of medicines in children. Child Care Health Dev. 2004;30(6):647–65.
Finley PR, Crismon ML, Rush AJ. Evaluating the impact of pharmacists in mental health: a systematic review. Pharmacotherapy. 2003;23(12):1634–44.
Hanlon JT, Lindblad CI, Gray SL. Can clinical pharmacy services have a positive impact on drug-related problems and health outcomes in community-based older adults? Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2004;2(1):3–13.
Holland R, Desborough J, Goodyer L, Hall S, Wright D, Loke YK. Does pharmacist-led medication review help to reduce hospital admissions and deaths in older people? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;65(3):303–16.
Kaur S, Mitchell G, Vitetta L, Roberts MS. Interventions that can reduce inappropriate prescribing in the elderly: a systematic review. Drugs Aging. 2009;26(12):1013–28.
LaMantia MA, Scheunemann LP, Viera AJ, Busby-Whitehead J, Hanson LC. Interventions to improve transitional care between nursing homes and hospitals: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58(4):777–82.
Marcum ZA, Handler SM, Wright R, Hanlon JT. Interventions to improve suboptimal prescribing in nursing homes: a narrative review. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2010;8(3):183–200.
Nkansah N, Mostovetsky O, Yu C, Chheng T, Beney J, Bond CM, et al. Effect of outpatient pharmacists’ non-dispensing roles on patient outcomes and prescribing patterns. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; (7):CD000336.
Robertson J, Walkom E, Pearson SA, Hains I, Williamsone M, Newby D. The impact of pharmacy computerised clinical decision support on prescribing, clinical and patient outcomes: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Pharm Pract. 2010;18(2):69–87.
Rollason V, Vogt N. Reduction of polypharmacy in the elderly: a systematic review of the role of the pharmacist. Drugs Aging. 2003;20(11):817–32.
Royal S, Smeaton L, Avery AJ, Hurwitz B, Sheikh A. Interventions in primary care to reduce medication related adverse events and hospital admissions: systematic review and meta-analysis. Qual Saf Health Care. 2006;15(1):23–31.
Tonna AP, Stewart D, West B, Gould I, McCaig D. Antimicrobial optimisation in secondary care: the pharmacist as part of a multidisciplinary antimicrobial programme–a literature review. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008;31(6):511–7.
Tully MP, Seston EM. Impact of pharmacists providing a prescription review and monitoring service in ambulatory care or community practice. Ann Pharmacother. 2000;34(11):1320–31.
Verrue CL, Petrovic M, Mehuys E, Remon JP, Vander Stichele R. Pharmacists’ interventions for optimization of medication use in nursing homes: a systematic review. Drugs Aging. 2009;26(1):37–49.
von Gunten V, Reymond JP, Beney J. Clinical and economic outcomes of pharmaceutical services related to antibiotic use: a literature review. Pharm World Sci. 2007;29(3):146–63.
Ellitt GR, Brien JA, Aslani P, Chen TF. Quality patient care and pharmacists’ role in its continuity–a systematic review. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43(4):677–91.
Naik Panvelkar P, Saini B, Armour C. Measurement of patient satisfaction with community pharmacy services: a review. Pharm World Sci. 2009;31(5):525–37.
Stemer G, Lemmens-Gruber R. Clinical pharmacy services and solid organ transplantation: a literature review. Pharm World Sci. 2010;32(1):7–18.
Kitsiou S, Pare G, Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. J Med Internet Res. 2013;15(7):e150.
Farris KB, Kirking DM. Assessing the quality of pharmaceutical care. II. Application of concepts of quality assessment from medical care. Ann Pharmacother. 1993;27(2):215–23.
Mohler R, Bartoszek G, Kopke S, Meyer G. Proposed criteria for reporting the development and evaluation of complex interventions in healthcare (CReDECI): guideline development. Int J Nurs Stud. 2012;49(1):40–6.
Burney KD, Krishnan K, Ruffin MT, Zhang D, Brenner DE. Adherence to single daily dose of aspirin in a chemoprevention trial. An evaluation of self-report and microelectronic monitoring. Arch Fam Med. 1996;5(5):297–300.
Calvert SB, Kramer JM, Anstrom KJ, Kaltenbach LA, Stafford JA, Allen LaPointe NM. Patient-focused intervention to improve long-term adherence to evidence-based medications: a randomized trial. Am Heart J. 2012; 163(4):657–65 e1.
Grymonpre RE, Didur CD, Montgomery PR, Sitar DS. Pill count, self-report, and pharmacy claims data to measure medication adherence in the elderly. Ann Pharmacother. 1998;32(7–8):749–54.
Liu H, Golin CE, Miller LG, Hays RD, Beck CK, Sanandaji S, et al. A comparison study of multiple measures of adherence to HIV protease inhibitors. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134(10):968–77.
Friedman RH, Kazis LE, Jette A, Smith MB, Stollerman J, Torgerson J, et al. A telecommunications system for monitoring and counseling patients with hypertension. Impact on medication adherence and blood pressure control. Am J Hypertens. 1996; 9(4 Pt 1):285–92.
Volume CI, Farris KB, Kassam R, Cox CE, Cave A. Pharmaceutical care research and education project: patient outcomes. J Am Pharm Assoc (Wash). 2001;41(3):411–20.
Gallagher P, Barry P, O’Mahony D. Inappropriate prescribing in the elderly. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2007;32(2):113–21.
Steinman MA, Rosenthal GE, Landefeld CS, Bertenthal D, Sen S, Kaboli PJ. Conflicts and concordance between measures of medication prescribing quality. Med Care. 2007;45(1):95–9.
Carollo A, Rieutord A, Launay-Vacher V. European Society of Clinical Pharmacy (ESCP) glossary of scientific terms: a tool for standardizing scientific jargon. Int J Clin Pharm. 2012;34(2):263–8.
Pintor-Marmol A, Baena MI, Fajardo PC, Sabater-Hernandez D, Saez-Benito L, Garcia-Cardenas MV, et al. Terms used in patient safety related to medication: a literature review. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21(8):799–809.
Shultz M. Comparing test searches in PubMed and Google Scholar. J Med Libr Assoc. 2007;95(4):442–5.
Funding
Postgraduate Program in Pharmaceutical Sciences of the Federal University of Parana, Brazil and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Highly Educated Personnel).
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest to disclose that could affect the study results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rotta, I., Salgado, T.M., Silva, M.L. et al. Effectiveness of clinical pharmacy services: an overview of systematic reviews (2000–2010). Int J Clin Pharm 37, 687–697 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-015-0137-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-015-0137-9