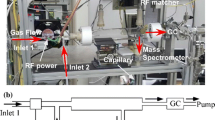
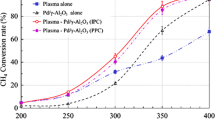
Abstract
The chemical kinetic effects of RF plasma on the pyrolysis and oxidation of methane were studied experimentally and computationally in a laminar flow reactor at 100 Torr and 373 K with and without oxygen addition into He/CH4 mixtures. The formation of excited species as well as intermediate species and products in the RF plasma reactor was measured with optical emission spectrometer and Gas Chromatography and the data were used to validate the kinetic model. The kinetic analysis was performed to understand the key reaction pathways. The experimental results showed that H2, C2 and C3 hydrocarbon formation was the major pathways for plasma assisted pyrolysis of methane. In contrast, with oxygen addition, C2 and C3 formation dramatically decreased, and syngas (H2 and CO) became the major products. The above results revealed oxygen addition significantly modified the chemistry of plasma assisted fuel pyrolysis in a RF discharge. Moreover, an increase of E/n was found to be more beneficial for the formation of higher hydrocarbons while a small amount of oxygen was presented in a He/CH4 mixture. A reaction path flux analysis showed that in a RF plasma, the formation of active species such as CH3, CH2, CH, H, O and O (1D) via the electron impact dissociation reactions played a critical role in the subsequent processes of radical chain propagating and products formation. The results showed that the electronically excitation, ionization, and dissociation processes as well as the products formation were selective and strongly dependent on the reduced electric field.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petitpasa G, Rollier J-D, Darmon A, Gonzalez-Aguilar J, Metkemeijer R, Fulcheri L (2007) A comparative study of non-thermal plasma assisted reforming technologies-a review. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:2848–2867
Jamal Y, Wyszynski ML (1994) On-board generation of hydrogen-rich gaseous fuels-a review. Int J Hydrogen Energy 19:557–572
Yiguang J, Sun W (2015) Plasma assisted combustion: dynamics and chemistry. Prog Energy Combust 48:21–83
Nozaki T, Okazaki K (2013) Non-thermal plasma catalysis of methane: principles, energy efficiency, and applications. Catal Today 211:29–38
Guo X, Fang G, Li G (2014) Direct, nonoxidative conversion of methane to ethylene, aromatics, and hydrogen. Science 344:616–619
Liu H, Wierzbicki D, Debek R, Motak M, Grzybek T, Da Costa P, Gálvez ME (2016) La-promoted Ni-hydrotalcite-derived catalysts for dry reforming of methane at low temperatures. Fuel 182:8–16
Zhu T, Yang Z, Han M (2015) Performance evaluation of solid oxide fuel cell with in-situ methane reforming. Fuel 161:168–173
Arp DJ, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Hommes NG (2002) Molecular biology and biochemistry of ammonia oxidation by Nitrosomonas europaea. Arch Microbiol 178:250–255
Balasubramanian R, Rosenzweig AC (2007) Structural and mechanistic insights into methane oxidation by particulate methane monooxygenase. Acc Chem Res 40:573–580
Yang E-C, Hao J-K, Tang T-H, Wang B-W, Cao Y-Y (2003) The theoretical study of reaction paths and transition states on coupling reaction of methane through plasma. J Mol Struct 626:121–126
Ren ZF, Huang ZP, Xu JW, Wang JH et al (1998) Synthesis of large arrays of well-aligned carbon nanotubes on glass. Science 282:1105–1107
Mitura S (1987) Nucleation of diamond powder particles in an RF methane plasma. J. Cryst Growth 80:417–424
Katayama K, Fukada S, Nishikawa M (2010) Direct decomposition of methane using helium RF plasma. Fusion Eng Des 85:1381–1385
Patino P, Perez Y, Caetano M (2005) Coupling and reforming of methane by means of low pressure radio-frequency plasmas. Fuel 84:2008–2014
Tsai C-H, Hsieh T-H (2004) New approach for methane conversion using an rf discharge reactor. 1. Influences of operating conditions on syngas production. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:4043–4047
Iskenderova K, Porshnev P, Gutsol A, Saveliev A, Fridman A, Kennedy L (2001) Methane conversion into syn-gas in gliding arc discharge. In: 15th international symposium on plasma chemistry, Orleans
Kalra CS, Gutsol AF, Fridman AA (2005) Gliding arc discharges as a source of intermediate plasma for methane partial oxidation. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 33(1):32–41
Czernikowski A (2001) Glidarc assisted preparation of the synthesis gas from natural gas and waste hydrocarbons gases. Oil Gas Sci Technol Rev IFP 2(56):181–198
Jasinski M, Dors M, Mizeraczyk J (2009) Destruction of Freon HFC-134a using a nozzleless microwave plasma source. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 29:363–372
Shen C, Sun D, Yang H (2011) Methane coupling in microwave plasma under atmospheric pressure. J Nat Gas Chem 20:449–456
Rusanov VD, Babaritskii AI, Geramisov EN, Deminskii MA, Demkin SA, Zhivotov VK (2003) Stimulation of the partial oxidation of methane in a microwave discharge. Dokl Phys 48(3):119–122
Babararistkii I, Baranov IR, Bibikov MB, Demkin SA, Zhivotov VK, Konovalov GM (2004) Partial hydrocarbon oxidation processes induced by atmospheric-pressure microwave-discharge plasma. High Energy Chem 38(6):407–410
Sun W, Uddi M, Won SH, Ombrello T, Carter C, Yiguang J (2012) Kinetic effects of non-equilibrium plasma-assisted methane oxidation on diffusion flame extinction limits. Combust Flame 159:221–229
Lefkowitz J, Uddi M, Windom BC, Lou G, Yiguang J (2014) In situ species diagnostics and kinetic study of plasma activated ethylene dissociation and oxidation in a low temperature flow reactor. Proc Combust Inst 35:3505–3512
Khalifeh O, Mosallanejad A, Taghvaei H, Rahimpour MR (2016) Decomposition of methane to hydrogen using nanosecond pulsed plasma reactor with different active volumes, voltages and frequencies. Appl Energy 169:585–596
Jemmer P (1999) Mathematical modeling and interpretation of reactive plasma chemistry. Math Comput Model 30:61–76
Ropcke J, Mechold L, Kaning M, Fan WY, Davies PB (1999) Tunable diode laser diagnostic studies of H(2)–Ar–O(2) microwave plasmas containing methane or methanol. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 19:395–419
Nair SA, Pemen AJM, Yan K, van Heesch EJM, Ptasinski KJ, Drinkenburg AAH (2004) Tar removal from biomass derived fuel gas by pulsed corona discharges—a chemical kinetic study. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:1649–1658
Nair SA, Nozaki T, Okazaki K (2007) Methane oxidative conversion pathways in a dielectric barrier discharge reactor—investigation of gas phase mechanism. Chem Eng J 132:85–95
Lee DH, Kim K-T, Cha MS, Song Y-H (2010) Plasma-controlled chemistry in plasma reforming of methane. Int J Hydrogen 35:10967–10976
Kraus M, Egli W, Haffner K, Eliasson B, Kogelschatz U, Wokaun A (2002) Investigation of mechanistic aspects of the catalytic CO2 reforming of methane in a dielectric-barrier discharge using optical emission spectroscopy and kinetic modeling. Phys Chem Chem Phys 4:668–675
Benilov MS, Naidis GV (2006) Modelling of hydrogen-rich gas production by plasma reforming of hydrocarbon fuels. Int J Hydrogen Energy 31:769–774
Hughes KJ, Turanyi T, Clague AR, Pilling MJ (2001) Development and testing of a comprehensive chemical mechanism for the oxidation of methane. Int J Chem Kinet 33:513–538
Indarto A, Choi JW, Lee H, Song HK (2005) Kinetic modelling of plasma methane conversion using gliding arc. J Nat Gas Chem 14:13–21
Luche Jocelyn, Aubry Olivier, Khacef Ahmed, Cormier Jean-Marie (2009) Syngas production from methane oxidation using a non-thermal plasma: experiments and kinetic modeling. Chem Eng J 149:35–41
Lee DH, Kim K-T, Song Y-H, Kang WS, Jo S (2013) Mapping plasma chemistry in hydrocarbon fuel processing processes. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33:249–269
Fincke JR, Anderson RP, Hyde T, Detering BA (2002) Plasma thermal conversion of methane to acetylene. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 22(1):395–408
Bourig A, Lago V, Martin JP, Pliavaka K, Pliavaka F, Gorbatov S, Chernukho A, Naumov V (2007) Generation of singlet oxygen in HV pulsed + DC crossed discharge at atmospheric pressure for oxygen-enhanced combustion. Int J Plasma Environ Sci Technol (IJEST) V1(1):57–63
Straub HC, Lin D, Lindsay BG, Smith KA, Stebbings RF (1997) Absolute partial cross sections for electron-impact ionization of CH4 from threshold to 1000 eV. J Chem Phys 106(11):4430–4435
Janev RK, Reiter D (2002) Collision processes of CHy and CHy hydrocarbons with plasma electrons and protons. Phys Plasmas 9(9):4071–4081
LAPLACE database (2016). http://www.lxcat.net. Accessed 29 Sept 2016
Shen X, Yang X, Santner J, Sun J, Ju Y (2015) Experimental and kinetic studies of acetylene flames at elevated pressures. Proc Combust Inst 35:721–728. http://engine.princeton.edu/mechanism.html
Goulay F, Trevitt AJ, Meloni G, Selby TM et al (2009) Cyclic versus linear lsomers produced by reaction of the methylidyne radical (CH) with small unsaturated hydrocarbons. J Am Chem Soc 131(3):993–1005
Galland N, Caralp F, Hannachi Y et al (2003) Experimental and theoretical studies of the methylidyne CH (X2Π) radical reaction with ethane (C2H6): overall rate constant and product channels. J Phys Chem A 107(28):5419–5426
Holroyd RA, Noyes WA Jr (1956) Photochemical studies. L. The ketene-oxygen system at higher temperatures. J Am Chem Soc 78(19):4831–4836
Wang H, You X, Joshi AV, Davis SG, Laskin A, Egolfopoulos F, Law CK (2007) USC mech version II. High-temperature combustion reaction model of H2/CO/C1–C4 compounds. http://ignis.usc.edu/USC_MechII.htm
Halberstadt ML, Crump J (1973) Insertion of methylene into the carbon–hydrogen bonds of the C1 to C4 alkanes. J Photochem 1(4):295–305
Revel J, Boettner JC, Cathonnet M, Bachman JS (1994) Derivation of a global chemical kinetic mechanism for methane ignition and combustion. J Chim Phys 91(4):365–382
Zyn VI (1998) Kinetic identification of a mechanism of complex plasma chemical reactions. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 18(3):395–408
Neyts EC, Ostrikov K, Sunkara MK, Bogaerts A (2015) Plasma catalysis: synergistic effects at the nanoscale. Chem Rev 115(24):13408–13446
Starikovskaia SM (2006) Plasma assisted ignition and combustion. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:R265–R299
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the ACEE grand challenge grants, the Exxon Mobile research grant, the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science (DE-SC0015735),and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51373021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Yang, X., Sun, J. et al. Pyrolysis and Oxidation of Methane in a RF Plasma Reactor. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 37, 1551–1571 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-017-9844-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-017-9844-4