Abstract
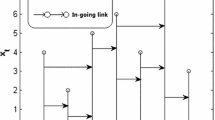
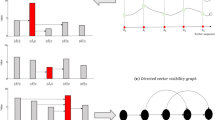
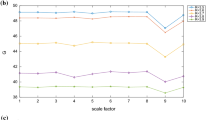
In this paper, we suggest a new measure for testing reversibility of time series which combines two different tools: the visibility algorithm and the inversion number. First, the visibility algorithm maps the time series to the network according to a geometric criterion. After that, the degree of irreversibility of the time series can be estimated by the relative asynchronous index (RAI), based on the inverse number, between out and \(\hbox {out}^*\) degree sequences of the network (out and \(\hbox {out}^*\) represent the outgoing sequence of forward time series and reverse time series, respectively). This method does not need to rely on additional parameters, so it can avoid the error caused by parameter estimation. In addition, we also study the multiscale RAI and find that the optimal scale selection for detection time irreversibility is 1–4. Different types of time series are used to confirm the validity of this metric. Finally, we apply the method to financial time series and find that the financial crisis can be detected by RAI.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamilton, J.D.: Time Series Analysis, vol. 2. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1994)
Dickey, D.A., Fuller, W.A.: Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 74, 427–431 (1979)
Priestley, M.B.: Spectral analysis and time series. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 79, 385 (1981)
Marwan, N., Romano, M.C., Thiel, M., Kurths, J.: Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems. Phys. Rep. 438, 237–329 (2007)
Eckmann, J.P., Kamphorst, S.O., Ruelle, D.: Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 4, 973 (1987)
Schreiber, T.: Measuring information transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 461 (2000)
Costa, M., Goldberger, A.L., Peng, C.K.: Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 068102 (2002)
Peng, C.K., Havlin, S., Stanley, H.E., Goldberger, A.L.: Quantification of scaling exponents and crossover phenomena in nonstationary heartbeat time series. Chaos 5, 82–87 (1995)
Gao, Z.K., Yang, Y.X., Fang, P.C., Zou, Y., Xia, C.Y., Du, M.: Multiscale complex network for analyzing experimental multivariate time series. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 109, 30005 (2015)
Gao, Z.K., Zhang, S.S., Dang, W.D., Li, S., Cai, Q.: Multilayer network from multivariate time series for characterizing nonlinear flow behavior. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 1750059 (2017)
Lobier, M., Siebenhühner, F., Palva, S., Palva, J.M.: Phase transfer entropy: a novel phase-based measure for directed connectivity in networks coupled by oscillatory interactions. Neuroimage 85, 853–872 (2014)
Yang, P., Shang, P.: Recurrence quantity analysis based on matrix eigenvalues. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 59, 15–29 (2018)
Diks, C., Van Houwelingen, J., Takens, F., DeGoede, J.: Reversibility as a criterion for discriminating time series. Phys. Lett. A 201, 221–228 (1995)
Van der Heyden, M., Diks, C., Pijn, J., Velis, D.: Time reversibility of intracranial human EEG recordings in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Phys. Lett. A 216, 283–288 (1996)
Yang, A.C.C., Hseu, S.S., Yien, H.W., Goldberger, A.L., Peng, C.K.: Linguistic analysis of the human heartbeat using frequency and rank order statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 108103 (2003)
Costa, M., Goldberger, A.L., Peng, C.K.: Broken asymmetry of the human heartbeat: loss of time irreversibility in aging and disease. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 198102 (2005)
Costa, M.D., Peng, C.K., Goldberger, A.L.: Multiscale analysis of heart rate dynamics: entropy and time irreversibility measures. Cardiovasc. Eng. 8, 88–93 (2008)
Cammarota, C., Rogora, E.: Time reversal, symbolic series and irreversibility of human heartbeat. Chaos Solitons Fract. 32, 1649–1654 (2007)
Broder, G., Weil, M.H.: Excess lactate: an index of reversibility of shock in human patients. Science 143, 1457–1459 (1964)
Weiss, G.: Time-reversibility of linear stochastic processes. J. Appl. Probab. 12, 831–836 (1975)
Cheng, Q.: On time-reversibility of linear processes. Biometrika 86, 483–486 (1999)
Hinich, M.J.: Testing for Gaussianity and linearity of a stationary time series. J. Time Ser. Anal. 3, 169–176 (1982)
Sharifdoust, M., Mahmoodi, S.: On time reversibility of linear time series. J. Math. Ext. 6, 33–47 (2013)
Kawai, R., Parrondo, J., Van den Broeck, C.: Dissipation: the phase-space perspective. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 080602 (2007)
Parrondo, J.M., Van den Broeck, C., Kawai, R.: Entropy production and the arrow of time. New J. Phys. 11, 073008 (2009)
Chen, Y.T., Chou, R.Y., Kuan, C.M.: Testing time reversibility without moment restrictions. J. Econom. 95, 199–218 (2000)
Tong, H.: Non-linear Time Series: A Dynamical System Approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1990)
Granger, C.W., Terasvirta, T., et al.: Modelling non-linear economic relationships. OUP Catalogue (1993)
Cox, D.R.: Long-range dependence, non-linearity and time irreversibility. J. Time Ser. Anal. 12, 329–335 (1991)
Roldán, É., Parrondo, J.M.: Estimating dissipation from single stationary trajectories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 150607 (2010)
Roldán, É., Parrondo, J.M.: Entropy production and Kullback–Leibler divergence between stationary trajectories of discrete systems. Phys. Rev. E 85, 031129 (2012)
Lin, A., Liu, K.K., Bartsch, R.P., Ivanov, P.C.: Delay-correlation landscape reveals characteristic time delays of brain rhythms and heart interactions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 374, 20150182 (2016)
Daw, C., Finney, C., Kennel, M.: Symbolic approach for measuring temporal irreversibility. Phys. Rev. E 62, 1912 (2000)
Kennel, M.B.: Testing time symmetry in time series using data compression dictionaries. Phys. Rev. E 69, 056208 (2004)
Gaspard, P.: Time-reversed dynamical entropy and irreversibility in Markovian random processes. J. Stat. Phys. 117, 599–615 (2004)
Andrieux, D., Gaspard, P., Ciliberto, S., Garnier, N., Joubaud, S., Petrosyan, A.: Entropy production and time asymmetry in nonequilibrium fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 150601 (2007)
Wang, Q., Kulkarni, S.R., Verdú, S.: Divergence estimation of continuous distributions based on data-dependent partitions. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 51, 3064–3074 (2005)
Thomas, J.A., Cover, T.M.: Elements of information theory. Wiley, Hoboken (2006)
Luque, B., Lacasa, L., Ballesteros, F., Luque, J.: Horizontal visibility graphs: exact results for random time series. Phys. Rev. E 80, 046103 (2009)
Lacasa, L., Luque, B., Ballesteros, F., Luque, J., Nuno, J.C.: From time series to complex networks: the visibility graph. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 4972–4975 (2008)
Lacasa, L., Luque, B., Luque, J., Nuno, J.C.: The visibility graph: a new method for estimating the Hurst exponent of fractional Brownian motion. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 86, 30001 (2009)
Lacasa, L., Toral, R.: Description of stochastic and chaotic series using visibility graphs. Phys. Rev. E 82, 036120 (2010)
Casali, K.R., Casali, A.G., Montano, N., Irigoyen, M.C., Macagnan, F., Guzzetti, S., Porta, A.: Multiple testing strategy for the detection of temporal irreversibility in stationary time series. Phys. Rev. E 77, 066204 (2008)
Lacasa, L., Nunez, A., Roldán, É., Parrondo, J.M., Luque, B.: Time series irreversibility: a visibility graph approach. Eur. Phys. J. B 85, 1–11 (2012)
Flanagan, R., Lacasa, L.: Irreversibility of financial time series: a graph-theoretical approach. Phys. Lett. A 380, 1689–1697 (2016)
Weisenfeld, N.L., Warfteld, S.: Normalization of joint image-intensity statistics in MRI using the Kullback-Leibler divergence. In: Biomedical Imaging: Nano to Macro, 2004. IEEE International Symposium on, pp. 101–104. IEEE (2004)
Hershey, J.R., Olsen, P.A.: Approximating the Kullback–Leibler divergence between Gaussian mixture models. In: Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2007. ICASSP 2007. IEEE International Conference on, vol. 4, pp. IV–317. IEEE (2007)
Gao, Z.K., Cai, Q., Yang, Y.X., Dong, N., Zhang, S.S.: Visibility graph from adaptive optimal kernel time-frequency representation for classification of epileptiform EEG. Int. J. Neural Syst. 27, 1750005 (2017)
Costa, M., Peng, C.K., Goldberger, A.L., Hausdorff, J.M.: Multiscale entropy analysis of human gait dynamics. Physica A 330, 53–60 (2003)
Liu, Q., Wei, Q., Fan, S.Z., Lu, C.W., Lin, T.Y., Abbod, M.F., Shieh, J.S.: Adaptive computation of multiscale entropy and its application in EEG signals for monitoring depth of anesthesia during surgery. Entropy 14, 978–992 (2012)
Yin, Y., Shang, P., Feng, G.: Modified multiscale cross-sample entropy for complex time series. Appl. Math. Comput. 289, 98–110 (2016)
Wu, S.D., Wu, C.W., Lin, S.G., Wang, C.C., Lee, K.Y.: Time series analysis using composite multiscale entropy. Entropy 15, 1069–1084 (2013)
Sprott, J.C., Rowlands, G.: Improved correlation dimension calculation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 11, 1865–1880 (2001)
Ivanov, P.C., Liu, K.K., Bartsch, R.P.: Focus on the emerging new fields of network physiology and network medicine. New J. Phys. 18, 100201 (2016)
Bartsch, R.P., Liu, K.K., Bashan, A., Ivanov, P.C.: Network physiology: how organ systems dynamically interact. PLoS ONE 10, e0142143 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The financial supports from the Funds of the China National Science (61771035) and the Beijing National Science (4162047) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, P., Shang, P. Relative asynchronous index: a new measure for time series irreversibility. Nonlinear Dyn 93, 1545–1557 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4275-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4275-1