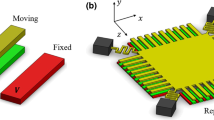
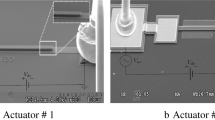
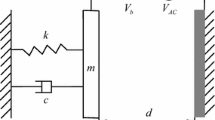
Abstract
An efficient electrostatic resonator is designed by adding a low voltage controller to an electrostatic actuator. The closed loop actuator shows stable, and bi-sable behaviors with bounded chaotic oscillations as large as 117% of the capacitor gap. The controller voltage is decreased from a previously designed resonator to less than 9 V thereby reducing the load on the controller circuit components. Bifurcation diagrams are obtained showing the frequency and magnitude of AC voltage required for chaotic oscillations to develop. The information entropy, a measure of chaotic characteristic, is calculated for the micro-resonator and is found to be 0.732.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epureanu, B.I., Tang, L.S., Paidoussis, M.P.: Exploiting chaotic dynamics for detecting parametric variations in aeroelastic systems. AIAA J. 42(4), 728–735 (2004)
Epureanu, B.I., Yin, S.-H.: Identification of damage in an aeroelastic system based on attractor deformations. Comput. Struct. 82(31–32), 2743–2751 (2004)
Epureanu, B.I., Yin, S.H., Derriso, M.M.: High-sensitivity damage detection based on enhanced nonlinear dynamics. Smart Mater. Struct. 14(2), 321–327 (2005)
Ghafari, S.: A fault diagnosis system for rotary machinery supported by rolling element bearings. PhD thesis, University of Waterloo (2007)
Yin, S.-H., Epureanu, B.I.: Experimental enhanced nonlinear dynamics and identification of attractor morphing modes for damage detection. J. Sound Acoust. 129(6), 763–770 (2007)
Cuomo, K.M., Oppenheim, A.V., Strogatz, S.H.: Synchronization of Lorenz-based chaotic circuits with applications to communications. In: IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, vol. 40, pp. 626–633 (1993)
Park, K., Chen, Q., Lai, Y.C.: Energy enhancement and chaos control in microelectromechanical systems. Phys. Rev. 77, 026210-1-6 (2008)
Buks, E., Yurke, B.: Mass detection with a nonlinear nanomechanical resonator. Phys. Rev. E 74(4), 46619-461-9 (2006)
Conley, W.G., Raman, A., Krousgrill, C.M., Mohammadi, S.: Nonlinear and nonplanar dynamics of suspended nanotube and nanowire resonators. Nano Lett. 8(6), 1590–1595 (2008)
Chen, Q., Huang, L., Lai, Y.C., Grebogi, C., Dietz, D.: Extensively chaotic motion in electrostatically driven nanowires and applications. Nano Lett. 10(2), 406–413 (2010)
Basso, M., Giarré, L., Dahleh, M., Mezic, I.: Numerical analysis of complex dynamics in atomic force microscopes. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Trieste, Italy, pp. 1026–1030 (1998)
Ashhab, M., Salapaka, M.V., Dahleh, M., Mezic, I.: Melnikov-based dynamical analysis of microcantilevers in scanning probe microscopy. Nonlinear Dyn. 20(3), 197–220 (1999)
Ashhab, M., Salapaka, M.V., Dahleh, M., Mezic, I.: Dynamical analysis and control of microcantilevers. Automatica 35(10), 1663–1670 (1999)
Lee, S.I., Howell, S.W., Raman, A., Reifenberger, R.: Nonlinear dynamics of microcantilevers in tapping mode atomic force microscopy: A comparison between theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. B, Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 66(11), 115409/1-10 (2002)
Raman, A., Hu, S.: Chaos in dynamic atomic force microscopy. In: 2006 International Symposium on Nonlinear Theory and Its Applications, Bologna, Italy, pp. 911–914 (2006)
Jamitzky, F., Stark, M., Bunk, W., Heckl, W.M., Stark, R.W.: Chaos in dynamic atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 17(7), S213–S220 (2006)
Bienstman, J., Vandewalle, J., Puers, R.: Autonomous impact resonator: A new operating principle for a silicon resonant strain gauge. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 66(1–3), 40–49 (1998)
Wang, Y.C., Adams, S.G., Thorp, J.S., MacDonald, N.C., Hartwell, P., Bertsch, F.: Chaos in MEMS, parameter estimation and its potential application. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Fundam. Theory Appl. 45(10), 1013–1020 (1998)
De, S.K., Aluru, N.R.: Complex nonlinear oscillations in electrostatically actuated microstructures. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 15(2), 355–369 (2006)
DeMartini, B.E., Butterfield, H.E., Moehlis, J., Turner, K.L.: Chaos for a microelectromechanical oscillator governed by the nonlinear Mathieu equation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 16(6), 1314–1323 (2007)
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y.S., Li, Z.H., Huang, Y.B., Li, D.C.: Snap-through and pull-in instabilities of an arch-shaped beam under an electrostatic loading. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 16(3), 684–693 (2007)
Krylov, S.: Lyapunov exponents as a criterion for the dynamic pull-in instability of electrostatically actuated microstructures. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 42(4), 626–642 (2007)
Krylov, S., Ilic, B.R., Schreiber, D., Seretensky, S., Craighead, H.: The pull-in behavior of electrostatically actuated bistable microstructures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 18(5), 1–20 (2008)
Das, K., Batra, R.C.: Pull-in and snap-through instabilities in transient deformations of microelectromechanical systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 19(3), 1–19 (2009)
Rhoads, J.F., Shaw, S.W., Moehlis, J., Demartini, B.E., Turner, K.L., Zhang, W.: Nonlinear response of parametrically-excited MEMS. In: DETC2005: ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, vol. 1A, pp. 453–461 (2005)
Zhang, W.-M., Meng, G.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis of electrostatically actuated resonant MEMS sensors under parametric excitation. IEEE Sens. J. 7(3), 370–380 (2007)
Liu, S., Davidson, A., Lin, Q.: Simulation studies on nonlinear dynamics and chaos in a MEMS cantilever control system. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14(7), 1064–1073 (2004)
Younis, M.I., Ouakad, H., Alsaleem, F.M., Miles, R., Cui, W.: Nonlinear dynamics of MEMS arches under harmonic electrostatic actuation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 19(3), 647–656 (2010)
Ouakad, H., Younis, M.I.: The dynamic behavior of MEMS arch resonators actuated electrically. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 45(7), 704–713 (2010)
Lu, M.S.-C., Fedder, G.K.: Position control of parallel-plate microactuators for probe-based data storage. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 13(5), 759–769 (2004)
Alsaleem, F.M., I Younis, M.: Integrity analysis of electrostatically actuated resonators with delayed feedback controller. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 133(3), 031011 (2011) (8 pages)
Alsaleem, F.M., Younis, M.I.: Stabilization of electrostatic MEMS resonators using delayed feedback controller. Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 035016 (2010)
Towfighian, S., Heppler, G.R., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: Analysis of a chaotic electrostatic micro-oscillator. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 6(1), 011001-10 (2011)
Towfighian, S., Heppler, G.R., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: A low voltage controller for a chaotic micro resonator. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2010 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences. pp. DETC2010–28990, Montreal, QC, Canada (2010)
Towfighian, S.: A Large-stroke electrostatic micro-actuator. PhD thesis, University of Waterloo (2010)
Towfighian, S., Seleim, A., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Heppler, G.R.: A large stroke electrostatic micro-actuator. J. Micromech. Microeng. 21, 075023 (2011) (12 pages)
Younis, M.I., Alsaleem, F.: Exploration of new concepts for mass detection in electrostatically-actuated structures based on nonlinear phenomena. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 4(2), 021010-1-15 (2009)
Moon, F.C.: Chaotic Vibrations: An Introduction for Applied Scientists and Engineers. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Towfighian, S., Heppler, G.R. & Abdel-Rahaman, E.M. Low-voltage closed loop MEMS actuators. Nonlinear Dyn 69, 565–575 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0287-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0287-9