Abstract
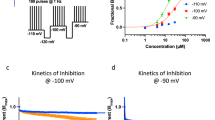
Spinal cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) and purinergic P2X receptors (P2XR) play a critical role in the process of pathological pain. Both CB1R and P2XR are expressed in spinal dorsal horn (DH) neurons. It is not clear whether CB1 receptor activation modulates the function of P2X receptor channels within dorsal horn. For this reason, we observed the effect of CP55940 (cannabinoid receptor agonist) on ATP-induced Ca2+ mobilization in cultured rat DH neurons. The changes of intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) were detected with confocal laser scanning microscopy using fluo-4/AM as a calcium fluorescent indicator. 100 μM ATP caused [Ca2+]i increase in cultured DH neurons. ATP-evoked [Ca2+]i increase in DH neurons was blocked by chelating extracellular Ca2+ and P2 purinoceptor antagonist PPADS. At the same time, ATP-γ-S (a non-hydrolyzable ATP analogue) mimicked the ATP action, while P2Y receptor agonist ADP failed to evoke [Ca2+]i increase in cultured DH neurons. These data suggest that ATP-induced [Ca2+]i elevation in cultured DH neurons is mediated by P2X receptor. Subsequently, we noticed that, in cultured rat DH neurons, ATP-induced Ca2+ mobilization was inhibited after pretreated with CP55940 with a concentration-dependent manner, which implies that the opening of P2X receptor channels are down-regulated by activation of cannabinoid receptor. The inhibitory effect of CP55940 on ATP-induced Ca2+ response was mimicked by ACEA (CB1R agonist), but was not influenced by AM1241 (CB2R agonist). Moreover, the inhibitory effect of CP55940 on ATP-induced Ca2+ mobilization was blocked by AM251 (CB1 receptor antagonist), but was not influenced by AM630 (CB2 receptor antagonist). In addition, we also observed that forskolin (an activator of adenylate cyclase) and 8-Br-cAMP (a cell-permeable cAMP analog) reversed the inhibitory effect of CP55940, respectively. In a summary, our observations raise a possibility that CB1R rather than CB2R can downregulate the opening of P2X receptor channels in DH neurons. The reduction of cAMP/PKA signaling is a key element in the inhibitory effect of CB1R on P2X-channel-induced Ca2+ mobilization.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Woodhams SG, Sagar DR, Burston JJ, Chapman V (2015) The role of the endocannabinoid system in pain. Handb Exp Pharmacol 227:119–143
Ulugöl A (2014) The endocannabinoid system as a potential therapeutic target for pain modulation. Balkan Med J 31:115–120
Farquhar-Smith WP, Egertová M, Bradbury EJ, McMahon SB, Rice AS, Elphick MR (2000) Cannabinoid CB(1) receptor expression in rat spinal cord. Mol Cell Neurosci 15:510–521
Hegyi Z, Kis G, Holló K, Ledent C, Antal M (2009) Neuronal and glial localization of the cannabinoid-1 receptor in the superficial spinal dorsal horn of the rodent spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci 30: 251–262
Yang F, Xu Q, Shu B, Tiwari V, He SQ, Vera-Portocarrero LP, Dong X, Linderoth B, Raja SN, Wang Y, Guan Y (2016) Activation of cannabinoid CB1 receptor contributes to suppression of spinal nociceptive transmission and inhibition of mechanical hypersensitivity by Aβ-fiber stimulation. Pain 157(11):2582–2593
Bardoni R, Goldstein PA, Lee CJ, Gu JG, MacDermott AB (1997) ATP P2Xreceptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 17:5297–5304
Gu JG, MacDermott AB (1997) Activation of ATP P2X receptors elicits glutamate release from sensory neuron synapses. Nature 389:749–753
Nakatsuka T, Gu JG (2001) ATP P2X receptor-mediated enhancement of glutamate release and evoked EPSCs in dorsal horn neurons of the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 21(17):6522–6531
Collo G, North RA, Kawashima E, Merlo-Pich E, Neidhart S, Surprenant A, Buell G (1996) Cloning of P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J Neurosci 16:2495–2507
Aoyama R, Okada Y, Yokota S, Yasui Y, Fukuda K, Shinozaki Y, Yoshida H, Nakamura M, Chiba K, Yasui Y, Kato F, Toyama Y (2011) Spatiotemporal and anatomical analyses of P2X receptor-mediated neuronal and glial processing of sensory signals in the rat dorsal horn. Pain 152:2085–2097
Jo YH, Schlichter R (1999) Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons. Nat Neurosci 2:241–245
Paukert M, Osteroth R, Geisler HS, Brandle U, Glowatzki E, Ruppersberg JP, Gründer S (2001) Inflammatory mediators potentiate ATP-gated channels through the P2X(3) subunit. J Biol Chem 276(24):21077–21082
Vial C, Tobin AB, Evans RJ (2004) G-protein-coupled receptor regulation of P2X1 receptors does not involve direct channel phosphorylation. Biochem J 382(Pt 1):101–110
Brown DA, Yule DI (2007) Protein kinase C regulation of P2X3 receptors is unlikely to involve direct receptor phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773(2):166–175
Wang C, Gu Y, Li GW, Huang LY (2007) A critical role of the cAMP sensor Epac in switching protein kinase signalling in prostaglandin E2-induced potentiation of P2X3 receptor currents in inflamed rats. J Physiol 584(Pt 1):191–203
Liu XH, Zeng JW, Zhao YD, Chen PH, Xiao Z, Ruan HZ (2008) Rapid inhibition of ATP-induced currents by corticosterone in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pharmacology 82(2):164–170
Liu XH, Zeng JW, Zhao YD, Xiao Z, Fang CQ, Ruan HZ (2010) Inhibition of ATP-induced Ca2+ influx by corticosterone in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem Res 35(5):804–810
Han JZ, Lin W, Chen YZ (2005) Inhibition of ATP-induced calcium influx in HT4 cells by glucocorticoids: involvement of protein kinase A. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26(2):199–204
Dalton GD, Bass CE, Van Horn C, Howlett AC (2009) Signal transduction via cannabinoid receptors. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 8:422–431
Jo YH, Stoeckel ME, Freund-Mercier MJ, Schlichter R (1998) Oxytocin modulates glutamatergic synaptic transmission between cultured neonatal spinal cord dorsal horn neurons. J Neurosci 18:2377–2386
Gee KR, Brown KA, Chen WN, Bishop-Stewart J, Gray D, Johnson I (2000) Chemical and physiological characterization of fluo-4 Ca2+-indicator dyes. Cell Calcium 27:97–106
Lai KM, Wong PC (1991) Metabolism of extracellular adenine nucleotides by cultured rat brain astrocytes. J Neurochem 57(5):1510–1515
Prendergast J, Umanah GK, Yoo SW, Lagerlöf O, Motari MG, Cole RN, Huganir RL, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Schnaar RL (2014) Ganglioside regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking. J Neurosci 34(39):13246–13258
Zeng JW, Liu XH, Zhao YD, Xiao Z, He WJ, Hu ZA, Ruan HZ (2009) Role of P2Y1 receptor in neuron-to-glia signaling at dorsal spinal cord. J Neurosci Res 87(12):2667–2676
Solymosi K, Köfalvi A (2017) Cannabis: a treasure trove or pandora’s box? Mini Rev Med Chem 17(13):1223–1291
Tomiyama K, Funada M (2014) Cytotoxicity of synthetic cannabinoids on primary neuronal cells of the forebrain: the involvement ofcannabinoid CB1 receptors and apoptotic cell death. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 274(1):17–23
Grabiec U, Koch M, Kallendrusch S, Kraft R, Hill K, Merkwitz C, Ghadban C, Lutz B, Straiker A, Dehghani F (2012) The endocannabinoid N-arachidonoyldopamine (NADA) exerts neuroprotective effects after excitotoxic neuronal damage via cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB(1)). Neuropharmacology 62(4):1797–1807
Felder CC, Joyce KE, Briley EM, Glass M, Mackie KP, Fahey KJ, Cullinan GJ, Hunden DC, Johnson DW, Chaney MO, Koppel GA, Brownstein M (1998) LY320135, a novel cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, unmasks coupling of the CB1 receptor to stimulation of cAMP accumulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:291–297
Glass M, Felder C (1997) Concurrent stimulation of cannabinoid CB1 and dopamine D2 receptors augments cAMP accumulation in striatal neurons: evidence for a G s linkage to the CB1 receptor. J Neurosci 17:5327–5333
McAllister SD, Glass M (2002) CB(1) and CB(2) receptor-mediated signalling: a focus on endocannabinoids. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 66:161–171
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther 110(3):433–454
Donnelly-Roberts DL, Jarvis MF (2007) Discovery of P2X7 receptor selective antagonists offers new insights into P2X7 receptor function and indicates a role in chronic pain states. Br J Pharmacol 151(5):571–579
Andó RD, Méhész B, Gyires K, Illes P, Sperlágh B (2010) A comparative analysis of the activity of ligands acting at P2X and P2Y receptor subtypes in models of neuropathic, acute and inflammatory pain. Br J Pharmacol 159(5):1106–1117
Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Burnstock G (2001) P2X receptors in peripheral neurons. Prog Neurobiol 65:107–134
Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50:413–492
Zeng JW, Liu XH, Zhang JH, Wu XG, Ruan HZ (2008) P2Y1 receptor-mediated glutamate release from cultured dorsal spinal cord astrocytes. J Neurochem 106(5):2106–2118
Zeng J, Wang G, Liu X, Wang C, Tian H, Liu A, Jin H, Luo X, Chen Y (2014) P2Y13 receptor-mediated rapid increase in intracellular calcium induced by ADP in cultured dorsal spinal cord microglia. Neurochem Res 39(11):2240–2250
Jahr CE, Jessell TM (1983) ATP excites a subpopulation of rat dorsal horn neurones. Nature 304(5928):730–733
Li J, Perl ER (1995) ATP modulation of synaptic transmission in the spinal substantia gelatinosa. J Neurosci 15:3357–3365
Burston JJ, Sagar DR, Shao P, Bai M, King E, Brailsford L, Turner JM, Hathway GJ, Bennett AJ, Walsh DA, Kendall DA, Lichtman A, Chapman V (2013) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors regulate central sensitization and pain responses associated with osteoarthritis of the knee joint. PLoS ONE 8(11):e80440
Romero-Sandoval A, Nutile-McMenemy N, DeLeo JA (2008) Spinal microglial and perivascular cell cannabinoid receptor type 2 activation reduces behavioralhypersensitivity without tolerance after peripheral nerve injury. Anesthesiology 108(4):722–734
Krishtal O, Lozovaya N, Fedorenko A, Savelyev I, Chizhmakov I (2006) The agonists for nociceptors are ubiquitous, but the modulators are specific: P2X receptors in the sensory neurons are modulated by cannabinoids. Pflugers Arch 453:353–360
Sagar DR, Kelly S, Millns PJ, O’Shaughnessey CT, Kendall DA, Chapman V (2005) Inhibitory effects of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists on responses of DRG neurons and dorsal horn neurons in neuropathic rats. Eur J Neurosci 22(2):371–379
Xiong W, Wu X, Li F, Cheng K, Rice KC, Lovinger DM, Zhang L (2012) A common molecular basis for exogenous and endogenous cannabinoid potentiation of glycinereceptors. J Neurosci 32(15):5200–5208
Liu C, Walker JM (2006) Effects of a cannabinoid agonist on spinal nociceptive neurons in a rodent model of neuropathic pain. J Neurophysiol 96(6):2984–2994
Chen XP, Yang W, Fan Y, Luo JS, Hong K, Wang Z, Yan JF, Chen X, Lu JX, Benovic JL, Zhou NM (2010) Structural determinants in the second intracellular loop of the human cannabinoid CB1 receptor mediate selective coupling to G(s) and G(i). Br J Pharmacol 161:1817–1834
Sántha P, Jenes A, Somogyi C, Nagy I (2010) The endogenous cannabinoid anandamide inhibits transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 receptor-mediated currents in rat cultured primary sensory neurons. Acta Physiol Hung 97:149–158
Shen JJ, Liu CJ, Li A, Hu XW, Lu YL, Chen L, Zhou Y, Liu LJ (2007) Cannabinoids inhibit ATP-activated currents in rat trigeminal ganglionic neurons. Sheng Li Xue Bao 59(6):745–752
Brown David A., David I (2010) Yule protein kinase A regulation of P2X4 receptors: requirement for a specific motif in the C-terminus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803(2):275–287
Chow YW, Wang HL (1998) Functional modulation of P2X2 receptors by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Neurochem 70(6):2606–2612
Serpa A, Correia S, Ribeiro JA, Sebastião AM, Cascalheira JF (2015) The combined inhibitory effect of the adenosine A1 and cannabinoid CB1 receptors on cAMP accumulation in the hippocampus is additive and independent of A1 receptor desensitization. Biomed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2015/872684
Veeraraghavan P, Nistri A (2015) Modulatory effects by CB1 receptors on rat spinal locomotor networks after sustained application of agonists or antagonists. Neuroscience 303:16–33
Roscioni SS, Kistemaker LE, Menzen MH, Elzinga CR, Gosens R, Halayko AJ, Meurs H, Schmidt M (2009) PKA and Epac cooperate to augment bradykinin-induced interleukin-8 release from human airway smooth muscle cells. Respir Res 10:88
Oliveira-Fusaro MC, Zanoni CI, Dos Santos GG, Manzo LP, Araldi D, Bonet IJ, Tambeli CH, Dias EV, Parada CA (2017) Antihyperalgesic effect of CB1 receptor activation involves the modulation of P2X3 receptor in the primary afferent neuron. Eur J Pharmacol 798:113–121
Walter L, Dinh T, Stella N (2004) ATP induces a rapid and pronounced increase in 2-arachidonoylglycerol production by astrocytes, a response limited by monoacylglycerol lipase. J Neurosci 24(37):8068–8074
Witting A, Walter L, Wacker J, Möller T, Stella N (2004) P2X7 receptors control 2-arachidonoylglycerol production by microglial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(9):3214–3219
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31360253). We are very grateful to the other staff of Department of Physiology. We also thank Guo Luo (Central Laboratory, Zunyi Medical College) for his technique assistance in laser scanning confocal microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Lei, X., Chen, M. et al. CB1 Receptors Mediated Inhibition of ATP-Induced [Ca2+]i Increase in Cultured Rat Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons. Neurochem Res 43, 267–275 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2414-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2414-6