Abstract
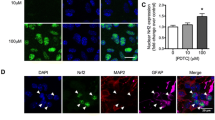
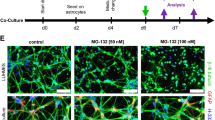
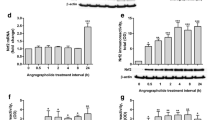
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) is a pleiotropic molecule that can have both protective and detrimental effects in neurodegeneration. Here we have investigated the temporal effects of TNFα on the inducible Nrf2 system in astrocyte-rich cultures by determination of glutathione (GSH) levels, γglutamylcysteine ligase (γGCL) activity, the protein levels of Nrf2, Keap1, the catalytic and modulatory subunit of γGCL (γGCL-C and γGCL-M respectively). Astrocyte-rich cultures were exposed for 24 or 72 h to different concentrations of TNFα. Acute exposure (24 h) of astrocyte-rich cultures to 10 ng/mL of TNFα increased GSH, γGCL activity, the protein levels of γGCL-M, γGCL-C and Nrf2 in parallel with decreased levels of Keap1. Antioxidant responsive element (ARE)-mediated transcription was blocked by inhibitors of ERK1/2, JNK and Akt whereas inactivation of p38 and GSK3β further enhanced transcription. In contrast treatment with TNFα for 72 h decreased components of the Nrf2 system in parallel with an increase of Keap1. Stimulation of the Nrf2 system by tBHQ was intact after 24 h but blocked after 72 h treatment with TNFα. This down-regulation after 72 h correlated with activation of p38 MAPK and GSK3β, since inhibition of these signalling pathways reversed this effect. The upregulation of the Nrf2 system by TNFα (24 h treatment) protected the cells from oxidative stress through elevated γGCL activity whereas the down-regulation (72 h treatment) caused pronounced oxidative toxicity. One of the important implications of the results is that in a situation where Nrf2 is decreased, such as in Alzheimer’s disease, the effect of TNFα is detrimental.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant responsive element
- BSO:
-
Buthionine sulfoxide
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- FBS:
-
Foetal bovine serum
- γGCL:
-
Gamma-glutamylcysteine ligase
- γGCL-C:
-
Gamma-glutamylcysteine ligase catalytic subunit
- γGCL-M:
-
Gamma-glutamylcysteine ligase modulatory subunit
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSK3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular regulated kinase
- FBS:
-
Foetal bovine serum
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccaride
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MCM:
-
Microglia-conditioned medium
- MEK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
- MEM:
-
Modified Eagle’s Medium
- MnSOD:
-
Manganese superoxide dismutase
- NDA:
-
Naphthalene-2,3-dicarboxaldehyde
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- 5-SSA:
-
5-Sulfosalicylic acid
- tBHQ:
-
Tert-butylhydroquinone
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
References
Allaman I, Belanger M, Magistretti PJ (2011) Astrocyte-neuron metabolic relationships: for better and for worse. Trends Neurosci 34:76–87
Bruce-Keller AJ, Geddes JW, Knapp PE, McFall RW, Keller JN, Holtsberg FW, Parthasarathy S, Steiner SM, Mattson MP (1999) Anti-death properties of TNF against metabolic poisoning: mitochondrial stabilization by MnSOD. J Neuroimmunol 93:53–71
Brywe KG, Mallard C, Gustavsson M, Hedtjarn M, Leverin AL, Wang X, Blomgren K, Isgaard J, Hagberg H (2005) IGF-I neuroprotection in the immature brain after hypoxia-ischemia, involvement of Akt and GSK3beta? Eur J Neurosci 21:1489–1502
Chen S, Owens GC, Makarenkova H, Edelman DB (2010) HDAC6 regulates mitochondrial transport in hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10848
Cheng B, Christakos S, Mattson MP (1994) Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis. Neuron 12(1):139–153
Correa F, Ljunggren E, Mallard C, Nilsson M, Weber SG, Sandberg M (2011) The Nrf2-inducible antioxidant defense in astrocytes can be both up- and down-regulated by activated microglia: involvement of p38 MAPK. Glia 59:785–799
Correa F, Mallard C, Nilsson M, Sandberg M (2011) Activated microglia decrease histone acetylation and Nrf2-inducible anti-oxidant defence in astrocytes: restoring effects of inhibitors of HDACs, p38 MAPK and GSK3beta. Neurobiol Dis 44:142–151
Cui J, Shao L, Young LT, Wang JF (2007) Role of Glutathione in neuroprotective effects of mood stabilizing drugs lithium and valproate. Neuroscience 144:1447–1453
Cullinan SB, Gordan JD, Jin J, Harper JW, Diehl JA (2004) The Keap1-BTB protein is an adaptor that bridges Nrf2 to a Cul3-based E3 ligase: oxidative stress sensing by a Cul3-Keap1 ligase. Mol Cell Biol 24:8477–8486
De Lella Ezcurra AL, Chertoff M, Ferrari C, Graciarena M, Pitossi F (2010) Chronic expression of low levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the substantia nigra elicits progressive neurodegeneration, delayed motor symptoms and microglia/macrophage activation. Neurobiol Dis 37:630–640
Dringen R, Pfeiffer B, Hamprecht B (1999) Synthesis of the antioxidant glutathione in neurons: supply by astrocytes of CysGly as precursor for neuronal glutathione. J Neurosci 19:562–569
Eftekharpour E, Holmgren A, Juurlink BH (2000) Thioredoxin reductase and glutathione synthesis is upregulated by t-butylhydroquinone in cortical astrocytes but not in cortical neurons. Glia 31:241–248
Figiel I (2008) Pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha as a neuroprotective agent in the brain. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 68:526–534
Fiore M, Angelucci F, Alleva E, Branchi I, Probert L, Aloe L (2000) Learning performances, brain NGF distribution and NPY levels in transgenic mice expressing TNF-alpha. Behav Brain Res 112:165–175
Gavillet M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ (2008) Modulation of astrocytic metabolic phenotype by proinflammatory cytokines. Glia 56(9):975–989
Goven D, Boutten A, Lecon-Malas V, Boczkowski J, Bonay M (2009) Prolonged cigarette smoke exposure decreases heme oxygenase-1 and alters Nrf2 and Bach1 expression in human macrophages: roles of the MAP kinases ERK(1/2) and JNK. FEBS Lett 583:3508–3518
Hansson E (1984) Cellular composition of a cerebral hemisphere primary culture. Neurochem Res 9:153–172
Hubbs AF, Benkovic SA, Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP, Battelli L, Schwegler-Berry D, Ma Q (2007) Vacuolar leukoencephalopathy with widespread astrogliosis in mice lacking transcription factor Nrf2. Am J Pathol 170:2068–2076
Innamorato NG, Rojo AI, Garcia-Yague AJ, Yamamoto M, de Ceballos ML, Cuadrado A (2008) The transcription factor Nrf2 is a therapeutic target against brain inflammation. J Immunol 181:680–689
Jain A, Lamark T, Sjottem E, Larsen KB, Awuh JA, Overvatn A, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Johansen T (2010) p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J Biol Chem 285:22576–22591
Jia JP, Meng R, Sun YX, Sun WJ, Ji XM, Jia LF (2005) Cerebrospinal fluid tau, Abeta1-42 and inflammatory cytokines in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Neurosci Lett 383:12–16
Kawai Y, Garduno L, Theodore M, Yang J, Arinze IJ (2011) Acetylation-deacetylation of the transcription factor Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2) regulates its transcriptional activity and nucleocytoplasmic localization. J Biol Chem 286:7629–7640
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S (2007) Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:89–116
Kim HJ, Vaziri ND (2010) Contribution of impaired Nrf2-Keap1 pathway to oxidative stress and inflammation in chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:F662–F671
Kim JE, You DJ, Lee C, Ahn C, Seong JY, Hwang JI (2010) Suppression of NF-kappaB signaling by KEAP1 regulation of IKKbeta activity through autophagic degradation and inhibition of phosphorylation. Cell Signal 22:1645–1654
Kozlova EN, Takenaga K (2005) A procedure for culturing astrocytes from white matter and the application of the siRNA technique for silencing the expression of their specific marker, S100A4. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 15(2):59–65
Lavoie S, Chen Y, Dalton TP, Gysin R, Cuenod M, Steullet P, Do KQ (2009) Curcumin, quercetin, and tBHQ modulate glutathione levels in astrocytes and neurons: importance of the glutamate cysteine ligase modifier subunit. J Neurochem 108:1410–1422
Liu GH, Qu J, Shen X (2008) NF-kappaB/p65 antagonizes Nrf2-ARE pathway by depriving CBP from Nrf2 and facilitating recruitment of HDAC3 to MafK. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:713–727
Lung HL, Leung KN, Stadlin A, Ma CM, Tsang D (2001) Induction of tumor necrosis factor receptor type 2 gene expression by tumor necrosis factor-α in rat primary astrocytes. Life Sci 68:2081–2091
Markus T, Cronberg T, Cilio C, Pronk C, Wieloch T, Ley D (2009) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 is essential for LPS-induced sensitization and tolerance to oxygen–glucose deprivation in murine neonatal organotypic hippocampal slices. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:73–86
McCoy MK, Tansey MG (2008) TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J Neuroinflamm 5:45
Mehindate K, Sahlas DJ, Frankel D, Mawal Y, Liberman A, Corcos J, Dion S, Schipper HM (2001) Proinflammatory cytokines promote glial heme oxygenase-1 expression and mitochondrial iron deposition: implications for multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem 77:1386–1395
Morales A, García-Ruiz C, Mirandai M, Marí M, Colelli A, Ardite E, Fernández-Checa JC (1997) Tumor necrosis factor increases hepatocellular glutathione by transcriptional regulation of the heavy subunit chain of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase. J Biol Chem 272(48):30371–30379
Morgan MJ, Liu ZG (2010) Reactive oxygen species in TNFalpha-induced signaling and cell death. Mol Cells 30:1–12
Naidu S, Vijayan V, Santoso S, Kietzmann T, Immenschuh S (2009) Inhibition and genetic deficiency of p38 MAPK up-regulates heme oxygenase-1 gene expression via Nrf2. J Immunol 182:7048–7057
Niture SK, Jaiswal AK (2011) INrf2 (Keap1) targets Bcl-2 degradation and controls cellular apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 18:439–451
Nodin C, Nilsson M, Blomstrand F (2005) Gap junction blockage limits intercellular spreading of astrocytic apoptosis induced by metabolic depression. J Neurochem 94:1111–1123
Perry SW, Dewhurst S, Bellizzi MJ, Gelbard HA (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in normal and diseased brain: conflicting effects via intraneuronal receptor crosstalk? J Neurovirol 8:611–624
Poizat C, Puri PL, Bai Y, Kedes L (2005) Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of p300 by doxorubicin-activated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in cardiac cells. Mol Cell Biol 25:2673–2687
Popkie AP, Zeidner LC, Albrecht AM, D’Ippolito A, Eckardt S, Newsom DE, Groden J, Doble BW, Aronow B, McLaughlin KJ, White P, Phiel CJ (2010) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3 K) signaling via glycogen synthase kinase-3 (Gsk-3) regulates DNA methylation of imprinted loci. J Biol Chem 285:41337–41347
Ramsey CP, Glass CA, Montgomery MB, Lindl KA, Ritson GP, Chia LA, Hamilton RL, Chu CT, Jordan-Sciutto KL (2007) Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:75–85
Rojo AI, Sagarra MR, Cuadrado A (2008) GSK-3beta down-regulates the transcription factor Nrf2 after oxidant damage: relevance to exposure of neuronal cells to oxidative stress. J Neurochem 105:192–202
Ruedig C, Dringen R (2004) TNFα increases activity of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase in cultured rat astroglial cells. J Neurosci Res 75:536–543
Saha RN, Liu X, Pahan K (2006) Up-regulation of BDNF in astrocytes by TNF-α: a case for the neuroprotective role of cytokine. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1(3):212–222
Salazar M, Rojo AI, Velasco D, de Sagarra RM, Cuadrado A (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibits the xenobiotic and antioxidant cell response by direct phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of the transcription factor Nrf2. J Biol Chem 281:14841–14851
Sawada M, Suzumura A, Marunouchi T (1992) TNF alpha induces IL-6 production by astrocytes but not by microglia. Brain Res 583(1–2):296–299
Shen G, Hebbar V, Nair S, Xu C, Li W, Lin W, Keum YS, Han J, Gallo MA, Kong AN (2004) Regulation of Nrf2 transactivation domain activity. The differential effects of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and synergistic stimulatory effect of Raf and CREB-binding protein. J Biol Chem 279:23052–23060
Shen G, Kong AN (2009) Nrf2 plays an important role in coordinated regulation of Phase II drug metabolism enzymes and Phase III drug transporters. Biopharm Drug Dispos 30:345–355
Shih AY, Johnson DA, Wong G, Kraft AD, Jiang L, Erb H, Johnson JA, Murphy TH (2003) Coordinate regulation of Glutathione biosynthesis and release by Nrf2-expressing glia potently protects neurons from oxidative stress. J Neurosci 23(8):3394–3406
Shih AY, Li P, Murphy TH (2005) A small-molecule-inducible Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response provides effective prophylaxis against cerebral ischemia in vivo. J Neurosci 25:10321–10335
Singh I, Pahan K, Khan M, Singh AK (1998) Cytokine-mediated induction of ceramide production is redox-sensitive. Implications to proinflammatory cytokine-mediated apoptosis in demyelinating diseases. J Biol Chem 273(32):20354–20362
Song IS, Tatebe S, Dai W, Kuo MT (2005) Delayed mechanism for induction of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit mRNA stability by oxidative stress involving p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Biol Chem 280:28230–28240
Sun X, Erb H, Murphy TH (2005) Coordinate regulation of glutathione metabolism in astrocytes by Nrf2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326:371–377
Tanaka N, Ikeda Y, Ohta Y, Deguchi K, Tian F, Shang J, Matsuura T, Abe K (2011) Expression of Keap1-Nrf2 system and antioxidative proteins in mouse brain after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Brain Res 1370:246–253
Tarkowski E, Liljeroth AM, Minthon L, Tarkowski A, Wallin A, Blennow K (2003) Cerebral pattern of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in dementias. Brain Res Bull 61:255–260
Vargas MR, Johnson DA, Sirkis DW, Messing A, Johnson JA (2008) Nrf2 activation in astrocytes protects against neurodegeneration in mouse models of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 28:13574–13581
Wang X, Svedin P, Nie C, Lapatto R, Zhu C, Gustavsson M, Sandberg M, Karlsson JO, Romero R, Hagberg H, Mallard C (2007) N-acetylcysteine reduces lipopolysaccharide-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Ann Neurol 61:263–271
Xu C, Yuan X, Pan Z, Shen G, Kim JH, Yu S, Khor TO, Li W, Ma J, Kong AN (2006) Mechanism of action of isothiocyanates: the induction of ARE-regulated genes is associated with activation of ERK and JNK and the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Mol Cancer Ther 5:1918–1926
Yang H, Magilnick N, Ou X, Lu SC (2005) Tumour necrosis factor alpha induces co-ordinated activation of rat GSH synthetic enzymes via nuclear factor kappaB and activator protein-1. Biochem J 391:399–408
Yin W, Signore AP, Iwai M, Cao G, Gao Y, Johnnides MJ, Hickey RW, Chen J (2007) Preconditioning suppresses inflammation in neonatal hypoxic ischemia via Akt activation. Stroke 38:1017–1024
Yoon K, Jung EJ, Lee SY (2008) TRAF6-mediated regulation of the PI3 kinase (PI3 K)-Akt-GSK3beta cascade is required for TNF-induced cell survival. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 371:118–121
Yu M, Li H, Liu Q, Liu F, Tang L, Li C, Yuan Y, Zhan Y, Xu W, Li W, Chen H, Ge C, Wang J, Yang X (2011) Nuclear factor p65 interacts with Keap1 to repress the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Cell Signal 23:883–892
Yu R, Chen C, Mo YY, Hebbar V, Owuor ED, Tan TH, Kong AN (2000) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways induces antioxidant response element-mediated gene expression via a Nrf2-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 275:39907–39913
Zhao Z, Chen Y, Wang J, Sternberg P, Freeman ML, Grossniklaus HE, Cai J (2011) Age-related retinopathy in NRF2-deficient mice. PLoS ONE 6:e19456
Acknowledgments
The expert technical assistance of Barbro Jilderos, Anne-Marie Alborn and Birgit Linder is gratefully acknowledged. The work was supported by the Swedish Research Council/Medicine, Parkinson-fonden and Åhlén-stiftelsen. MS is supported by the National Institutes of Health (GM 44842). CM is supported by Neurobid (241778).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
LDH levels of astroglial-enriched cultures subjected to different treatments for 24 h (A, B, C and D) or 72 h (E and F) before the exposure to H2O2 250 μM. As seen in the figure, neither treatment for 24 or 72 induced any significant cell loss. (n = 6–8) (TIFF 68 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correa, F., Mallard, C., Nilsson, M. et al. Dual TNFα-Induced Effects on NRF2 Mediated Antioxidant Defence in Astrocyte-Rich Cultures: Role of Protein Kinase Activation. Neurochem Res 37, 2842–2855 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0878-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0878-y