Abstract
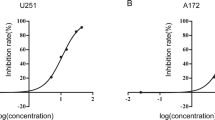
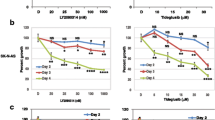
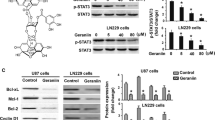
Glioblastoma, the most common type of primary malignant brain tumor, is a devastating disease associated with a median survival of approximately 12 months. Here, we have tested E804, the commercially available indirubin derivatives, against U251 and U87 glioblastoma cells. Treatment with E804 significantly inhibits the growth of human glioblastoma cells lines via induction of differentiation and apoptosis. Differentiation induction is coupled with increased expression of glial fibriliary acidic protein, a marker for mature astrocytes. Apoptosis is associated with activation of Caspase 3 and reduction of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1. Furthermore, we demonstrate that E804 reduces signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) signaling to a remarkable extent, suggesting that inactivation of Stat3, at least in part, mediates the effects of this indirubin derivative. Consistently, reduction of Stat3 activity promotes E804-mediated anti-tumor effects, whereas overexpression of Stat3C mutant recues cell apoptosis induced by E804. Taken together, our results indicate that E804 can effectively suppress tumor cell growth, induce tumor cell differentiation and apoptosis mediated partially by Stat3 signaling pathway, suggesting that E804 could be useful for a potential anti-glioblastoma therapeutic approach.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK, DePinho RA (2001) Malignant glioma: genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev 15:1311–1333. doi:10.1101/gad.891601
Germain D, Frank DA (2007) Targeting the cytoplasmic and nuclear functions of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:5665–5669. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2491
Johnston PA, Grandis JR (2011) STAT3 signaling: anticancer strategies and challenges. Mol Interv 11:18–26. doi:10.1124/mi.11.1.4
Silva CM (2004) Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 23:8017–8023. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208159
Gao SP, Mark KG, Leslie K, Pao W, Motoi N, Gerald WL, Travis WD, Bornmann W, Veach D, Clarkson B, Bromberg JF (2007) Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas. J Clin Invest 117:3846–3856. doi:10.1172/JCI31871
Levy DE, Lee CK (2002) What does Stat3 do? J Clin Invest 109:1143–1148. doi:10.1172/JCI15650
Rahaman SO, Harbor PC, Chernova O, Barnett GH, Vogelbaum MA, Haque SJ (2002) Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene 21:8404–8413. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206047
Zhang Y, Hao H, Zhao S, Liu Q, Yuan Q, Ni S, Wang F, Liu S, Wang L, Hao A (2011) Downregulation of GRIM-19 promotes growth and migration of human glioma cells. Cancer Sci 102:1991–1999. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02059.x
Kim JE, Patel M, Ruzevick J, Jackson CM, Lim M (2014) STAT3 activation in glioblastoma: biochemical and therapeutic implications. Cancers (Basel) 6:376–395. doi:10.3390/cancers6010376
Vogt PK, Hart JR (2011) PI3 K and STAT3: a new alliance. Cancer Discov 1:481–486. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0218
Niu G, Bowman T, Huang M, Shivers S, Reintgen D, Daud A, Chang A, Kraker A, Jove R, Yu H (2002) Roles of activated Src and Stat3 signaling in melanoma tumor cell growth. Oncogene 21:7001–7010. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205859
Brantley EC, Benveniste EN (2008) Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3: a molecular hub for signaling pathways in gliomas. Mol Cancer Res 6:675–684. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2180
Nelson EA, Sharma SV, Settleman J, Frank DA (2011) A chemical biology approach to developing STAT inhibitors: molecular strategies for accelerating clinical translation. Oncotarget 2:518–524
Nam S, Buettner R, Turkson J, Kim D, Cheng JQ, Muehlbeyer S, Hippe F, Vatter S, Merz KH, Eisenbrand G, Jove R (2005) Indirubin derivatives inhibit Stat3 signaling and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5998–6003. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409467102
Xiao Z, Hao Y, Liu B, Qian L (2002) Indirubin and meisoindigo in the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia in China. Leuk Lymphoma 43:1763–1768. doi:10.1080/1042819021000006295
Braig S, Kressirer CA, Liebl J, Bischoff F, Zahler S, Meijer L, Vollmar AM (2013) Indirubin derivative 6BIO suppresses metastasis. Cancer Res 73:6004–6012. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4358
Khanal P, Choi HK, Namgoong GM, Ahn SG, Yoon JH, Sohn H, Choi HS (2011) 5′-Nitro-indirubinoxime inhibits epidermal growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced AP-1 activity and cell transformation through inhibition of phosphorylation of Pin1. Mol Carcinog 50:961–971. doi:10.1002/mc.20761
Choi SJ, Lee JE, Jeong SY, Im I, Lee SD, Lee EJ, Lee SK, Kwon SM, Ahn SG, Yoon JH, Han SY, Kim JI, Kim YC (2010) 5,5′-substituted indirubin-3′-oxime derivatives as potent cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors with anticancer activity. J Med Chem 53:3696–3706. doi:10.1021/jm100080z
See AP, Han JE, Phallen J, Binder Z, Gallia G, Pan F, Jinasena D, Jackson C, Belcaid Z, Jeong SJ, Gottschalk C, Zeng J, Ruzevick J, Nicholas S, Kim Y, Albesiano E, Pardoll DM, Lim M (2012) The role of STAT3 activation in modulating the immune microenvironment of GBM. J Neurooncol 110:359–368. doi:10.1007/s11060-012-0981-6
Konnikova L, Kotecki M, Kruger MM, Cochran BH (2003) Knockdown of STAT3 expression by RNAi induces apoptosis in astrocytoma cells. BMC Cancer 3:23. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-3-23
Mazumder S, Plesca D, Almasan A (2008) Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol 414:13–21
Lin GS, Yang LJ, Wang XF, Chen YP, Tang WL, Chen L, Lin ZX (2014) STAT3 Tyr705 phosphorylation affects clinical outcome in patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial glioblastoma. Med Oncol 31:924. doi:10.1007/s12032-014-0924-5
Liang Q, Ma C, Zhao Y, Gao G, Ma J (2013) Inhibition of STAT3 reduces astrocytoma cell invasion and constitutive activation of STAT3 predicts poor prognosis in human astrocytoma. Plos One 8:e84723. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084723
Ashizawa T, Akiyama Y, Miyata H, Iizuka A, Komiyama M, Kume A, Omiya M, Sugino T, Asai A, Hayashi N, Mitsuya K, Nakasu Y, Yamaguchi K (2014) Effect of the STAT3 inhibitor STX-0119 on the proliferation of a temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cell line. Int J Oncol 45:411–418. doi:10.3892/ijo.2014.2439
Ball S, Li C, Li PK, Lin J (2011) The small molecule, LLL12, inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and induces apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells. Plos One 6:e18820. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018820
Iwamaru A, Szymanski S, Iwado E, Aoki H, Yokoyama T, Fokt I, Hess K, Conrad C, Madden T, Sawaya R, Kondo S, Priebe W, Kondo Y (2007) A novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 26:2435–2444. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210031
Gu J, Li G, Sun T, Su Y, Zhang X, Shen J, Tian Z, Zhang J (2008) Blockage of the STAT3 signaling pathway with a decoy oligonucleotide suppresses growth of human malignant glioma cells. J Neurooncol 89:9–17. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9590-9
Liwak U, Jordan LE, Von-Holt SD, Singh P, Hanson JE, Lorimer IA, Roncaroli F, Holcik M (2013) Loss of PDCD4 contributes to enhanced chemoresistance in Glioblastoma multiforme through de-repression of Bcl-xL translation. Oncotarget 4:1365–1372
Rieger L, Weller M, Bornemann A, Schabet M, Dichgans J, Meyermann R (1998) BCL-2 family protein expression in human malignant glioma: a clinical-pathological correlative study. J Neurol Sci 155:68–75
Day BW, Stringer BW, Spanevello MD, Charmsaz S, Jamieson PR, Ensbey KS, Carter JC, Cox JM, Ellis VJ, Brown CL, Walker DG, Inglis PL, Allan S, Reynolds BA, Lickliter JD, Boyd AW (2011) ELK4 neutralization sensitizes glioblastoma to apoptosis through downregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1. Neuro Oncol 13:1202–1212. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nor119
Turkson J, Bowman T, Garcia R, Caldenhoven E, De Groot RP, Jove R (1998) Stat3 activation by Src induces specific gene regulation and is required for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol 18:2545–2552
Wu J, Feng X, Zhang B, Li J, Xu X, Liu J, Wang X, Wang J, Tong X (2014) Blocking the bFGF/STAT3 interaction through specific signaling pathways induces apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol 120:33–41. doi:10.1007/s11060-014-1529-8
Weissenberger J, Priester M, Bernreuther C, Rakel S, Glatzel M, Seifert V, Kogel D (2010) Dietary curcumin attenuates glioma growth in a syngeneic mouse model by inhibition of the JAK1,2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res 16:5781–5795. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0446
Shin EK, Kim JK (2012) Indirubin derivative E804 inhibits angiogenesis. BMC Cancer 12:164. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-164
Nam S, Scuto A, Yang F, Chen W, Park S, Yoo HS, Konig H, Bhatia R, Cheng X, Merz KH, Eisenbrand G, Jove R (2012) Indirubin derivatives induce apoptosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells involving inhibition of Stat5 signaling. Mol Oncol 6:276–283. doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2012.02.002
Weinstein DE, Shelanski ML, Liem RK (1991) Suppression by antisense mRNA demonstrates a requirement for the glial fibrillary acidic protein in the formation of stable astrocytic processes in response to neurons. J Cell Biol 112:1205–1213
Chen WJ, Liem RK (1994) Reexpression of glial fibrillary acidic protein rescues the ability of astrocytoma cells to form processes in response to neurons. J Cell Biol 127:813–823
Restrepo A, Smith CA, Agnihotri S, Shekarforoush M, Kongkham PN, Seol HJ, Northcott P, Rutka JT (2011) Epigenetic regulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein by DNA methylation in human malignant gliomas. Neuro Oncol 13:42–50. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noq145
Takanaga H, Yoshitake T, Yatabe E, Hara S, Kunimoto M (2004) Beta-naphthoflavone disturbs astrocytic differentiation of C6 glioma cells by inhibiting autocrine interleukin-6. J Neurochem 90:750–757. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02681.x
Heshmati N, Cheng X, Eisenbrand G, Fricker G (2013) Enhancement of oral bioavailability of E804 by self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) in rats. J Pharm Sci 102:3792–3799. doi:10.1002/jps.23696
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81402059); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation(No. 2012M521351); Shandong Natural Science Foundation (No.ZR2012HQ010); Shandong Postdoctoral Science Foundation(No. 201203049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Yanmin Zhang and Zhaoxiao Du these authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Du, Z., Zhuang, Z. et al. E804 induces growth arrest, differentiation and apoptosis of glioblastoma cells by blocking Stat3 signaling. J Neurooncol 125, 265–275 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1917-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1917-8