Abstract
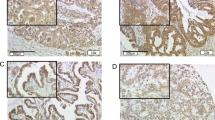
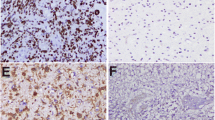
Estrogen receptors alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ) and their co-regulatory proteins are key components of complex signaling networks that specifically regulate the growth and development of various tissues and tumors. Still, their protein expression profiles and possible role in the pathogenesis of astrocytic tumors remain largely unknown. The purpose of the present study is to evaluate the differential protein expression of ΕRα, ERβ, and their co-activators, AIB1, TIF2, and PELP1 in astrocytic tumors of World Health Organization (WHO) grade II–IV, using immunohistochemistry. Potential correlations with clinicopathological parameters and patient prognosis were also explored. ERα protein expression was undetectable while ERβ levels were significantly decreased with progression of tumor grade (P < 0.001). High expression of ERβ was an independent favorable prognostic factor on multivariate analysis (P = 0.003). Expression of AIB1, TIF2, and PELP1 was not correlated with ERβ expression and followed an opposite trend, with increasing levels in high-grade relative to low-grade tumors (P < 0.001). Univariate survival analysis revealed that high AIB1, TIF2, and PELP1 expression was associated with worse prognosis (P = 0.049, P = 0.033, and P = 0.020, respectively). ERβ and ER co-activators AIB1, TIF2, and PELP1 appear to play an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of astrocytic tumors and might have prognostic significance. The mechanisms underlying their involvement in astrocytic tumorigenesis, as well as their utility for prognostic and therapeutic purposes merit further investigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohgaki H (2009) Epidemiology of brain tumors. Methods Mol Biol 472:323–342. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-492-0_14
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (2007) WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507. doi:359/5/492[pii]10.1056/NEJMra0708126
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996. doi:352/10/987[pii]10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, Chin L, DePinho RA, Cavenee WK (2007) Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21(21):2683–2710. doi:21/21/2683[pii]10.1101/gad.1596707
Macarthur BD, Ma’ayan A, Lemischka IR (2009) Systems biology of stem cell fate and cellular reprogramming. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(10):672–681. doi:nrm2766[pii]10.1038/nrm2766
Barone TA, Gorski JW, Greenberg SJ, Plunkett RJ (2009) Estrogen increases survival in an orthotopic model of glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 95(1):37–48. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9904-6
Matthews J, Gustafsson JA (2003) Estrogen signaling: a subtle balance between ER alpha and ER beta. Mol Interv 3(5):281–292. doi:10.1124/mi.3.5.2813/5/281[pii]
Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M, Strom A, Treuter E, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2007) Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev 87(3):905–931. doi:87/3/905[pii]10.1152/physrev.00026.2006
Acconcia F, Kumar R (2006) Signaling regulation of genomic and nongenomic functions of estrogen receptors. Cancer Lett 238(1):1–14. doi:S0304-3835(05)00567-7[pii]10.1016/j.canlet.2005.06.018
Zhao C, Dahlman-Wright K, Gustafsson JA (2008) Estrogen receptor beta: an overview and update. Nucl Recept Signal 6:e003. doi:10.1621/nrs.06003
Leung YK, Mak P, Hassan S, Ho SM (2006) Estrogen receptor (ER)-beta isoforms: a key to understanding ER-beta signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(35):13162–13167. doi:0605676103[pii]10.1073/pnas.0605676103
Pearce ST, Jordan VC (2004) The biological role of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 50(1):3–22. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2003.09.003S1040842803002506[pii]
Bardin A, Boulle N, Lazennec G, Vignon F, Pujol P (2004) Loss of ERbeta expression as a common step in estrogen-dependent tumor progression. Endocr Relat Cancer 11(3):537–551
Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2010) The role of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) in malignant diseases—a new potential target for antiproliferative drugs in prevention and treatment of cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396(1):63–66. doi:S0006-291X(10)00378-5[pii]10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.144
Batistatou A, Stefanou D, Goussia A, Arkoumani E, Papavassiliou AG, Agnantis NJ (2004) Estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) is expressed in brain astrocytic tumors and declines with dedifferentiation of the neoplasm. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130(7):405–410. doi:10.1007/s00432-004-0548-9
Batistatou A, Kyzas PA, Goussia A, Arkoumani E, Voulgaris S, Polyzoidis K, Agnantis NJ, Stefanou D (2006) Estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) protein expression correlates with BAG-1 and prognosis in brain glial tumours. J Neurooncol 77(1):17–23. doi:10.1007/s11060-005-9005-0
Carroll RS, Zhang J, Dashner K, Sar M, Black PM (1995) Steroid hormone receptors in astrocytic neoplasms. Neurosurgery 37(3):496–503 discussion 503-494
Assimakopoulou M, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Maraziotis T, Varakis J (1998) Does sex steroid receptor status have any prognostic or predictive significance in brain astrocytic tumors? Clin Neuropathol 17(1):27–34
Hall JM, McDonnell DP (2005) Coregulators in nuclear estrogen receptor action: from concept to therapeutic targeting. Mol Interv 5(6):343–357. doi:5/6/343[pii]
Lonard DM, O’Malley BW (2005) Expanding functional diversity of the coactivators. Trends Biochem Sci 30(3):126–132. doi:S0968-0004(05)00019-8[pii]10.1016/j.tibs.2005.01.001
O’Malley BW (2006) Molecular biology. Little molecules with big goals. Science 313(5794):1749–1750. doi:313/5794/1749[pii]10.1126/science.1132509
York B, O’Malley BW (2010) Steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) family: masters of systems biology. J Biol Chem 285(50):38743–38750. doi:R110.193367[pii]10.1074/jbc.R110.193367
Anzick SL, Kononen J, Walker RL, Azorsa DO, Tanner MM, Guan XY, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP, Trent JM, Meltzer PS (1997) AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277(5328):965–968
Voegel JJ, Heine MJ, Zechel C, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H (1996) TIF2, a 160 kDa transcriptional mediator for the ligand-dependent activation function AF-2 of nuclear receptors. EMBO J 15(14):3667–3675
Yan J, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ (2006) SRC-3/AIB1: transcriptional coactivator in oncogenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27(4):387–394. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00315.x
Xu J, Wu RC, O’Malley BW (2009) Normal and cancer-related functions of the p160 steroid receptor co-activator (SRC) family. Nat Rev Cancer 9(9):615–630. doi:nrc2695[pii]10.1038/nrc2695
Vadlamudi RK, Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Kim Y, Shin J, Sahin A, Kumar R (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of PELP1, a novel human coregulator of estrogen receptor alpha. J Biol Chem 276(41):38272–38279. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103783200M103783200[pii]
Rajhans R, Vadlamudi RK (2006) Comprehensive analysis of recent biochemical and biologic findings regarding a newly discovered protein-PELP1/MNAR. Clin Exp Metastasis 23(1):1–7. doi:10.1007/s10585-006-9019-9
Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (2007) Functional and biological properties of the nuclear receptor coregulator PELP1/MNAR. Nucl Recept Signal 5:e004. doi:10.1621/nrs.05004
Wong CW, McNally C, Nickbarg E, Komm BS, Cheskis BJ (2002) Estrogen receptor-interacting protein that modulates its nongenomic activity-crosstalk with Src/Erk phosphorylation cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(23):14783–14788. doi:10.1073/pnas.192569699192569699[pii]
Rajhans R, Nair S, Holden AH, Kumar R, Tekmal RR, Vadlamudi RK (2007) Oncogenic potential of the nuclear receptor coregulator proline-, glutamic acid-, leucine-rich protein 1/modulator of the nongenomic actions of the estrogen receptor. Cancer Res 67(11):5505–5512. doi:67/11/5505[pii]10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3647
Nair S, Vadlamudi RK (2007) Emerging significance of ER-coregulator PELP1/MNAR in cancer. Histol Histopathol 22(1):91–96
Grivas PD, Tzelepi V, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Kefalopoulou Z, Papavassiliou AG, Kalofonos H (2009) Expression of ERalpha, ERbeta and co-regulator PELP1/MNAR in colorectal cancer: prognostic significance and clinicopathologic correlations. Cell Oncol 31(3):235–247. doi:UU3813761N27Q164[pii]10.3233/CLO-2009-0467
Grivas PD, Tzelepi V, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Kefalopoulou Z, Papavassiliou AG, Kalofonos H (2009) Estrogen receptor alpha/beta, AIB1, and TIF2 in colorectal carcinogenesis: do coregulators have prognostic significance? Int J Colorectal Dis 24(6):613–622. doi:10.1007/s00384-009-0647-9
Tzelepi V, Grivas P, Kefalopoulou Z, Kalofonos H, Varakis JN, Melachrinou M, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G (2009) Estrogen signaling in colorectal carcinoma microenvironment: expression of ERbeta1, AIB-1, and TIF-2 is upregulated in cancer-associated myofibroblasts and correlates with disease progression. Virchows Arch 454(4):389–399. doi:10.1007/s00428-009-0740-z
Tzelepi V, Grivas P, Kefalopoulou Z, Kalofonos H, Varakis JN, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G (2009) Expression of estrogen receptor co-regulators NCoR and PELP1 in epithelial cells and myofibroblasts of colorectal carcinomas: cytoplasmic translocation of NCoR in epithelial cells correlates with better [corrected] prognosis. Virchows Arch 454(1):41–53. doi:10.1007/s00428-008-0708-4
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2005) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2(8):416–422
Zhao C, Lam EW, Sunters A, Enmark E, De Bella MT, Coombes RC, Gustafsson JA, Dahlman-Wright K (2003) Expression of estrogen receptor beta isoforms in normal breast epithelial cells and breast cancer: regulation by methylation. Oncogene 22(48):7600–7606. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.12071001207100[pii]
Stettner M, Kaulfuss S, Burfeind P, Schweyer S, Strauss A, Ringert RH, Thelen P (2007) The relevance of estrogen receptor-beta expression to the antiproliferative effects observed with histone deacetylase inhibitors and phytoestrogens in prostate cancer treatment. Mol Cancer Ther 6(10):2626–2633. doi:1535-7163.MCT-07-0197[pii]10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0197
Torres-Arzayus MI, Font de Mora J, Yuan J, Vazquez F, Bronson R, Rue M, Sellers WR, Brown M (2004) High tumor incidence and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in transgenic mice define AIB1 as an oncogene. Cancer Cell 6(3):263–274. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.027S1535610804002193[pii]10.1128/MCB.00654-06
Gregory CW, He B, Johnson RT, Ford OH, Mohler JL, French FS, Wilson EM (2001) A mechanism for androgen receptor-mediated prostate cancer recurrence after androgen deprivation therapy. Cancer Res 61(11):4315–4319
Kershah SM, Desouki MM, Koterba KL, Rowan BG (2004) Expression of estrogen receptor coregulators in normal and malignant human endometrium. Gynecol Oncol 92(1):304–313. doi:S009082580300711X[pii]
Kurebayashi J, Otsuki T, Kunisue H, Tanaka K, Yamamoto S, Sonoo H (2000) Expression levels of estrogen receptor-alpha, estrogen receptor-beta, coactivators, and corepressors in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6(2):512–518
Carroll RS, Brown M, Zhang J, DiRenzo J, Font De Mora J, Black PM (2000) Expression of a subset of steroid receptor cofactors is associated with progesterone receptor expression in meningiomas. Clin Cancer Res 6(9):3570–3575
Louie MC, Zou JX, Rabinovich A, Chen HW (2004) ACTR/AIB1 functions as an E2F1 coactivator to promote breast cancer cell proliferation and antiestrogen resistance. Mol Cell Biol 24(12):5157–5171. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.12.5157-5171.200424/12/5157[pii]
Louie MC, Revenko AS, Zou JX, Yao J, Chen HW (2006) Direct control of cell cycle gene expression by proto-oncogene product ACTR, and its autoregulation underlies its transforming activity. Mol Cell Biol 26(10):3810–3823. doi:26/10/3810[pii]10.1128/MCB.26.10.3810-3823.2006
Bouras T, Southey MC, Venter DJ (2001) Overexpression of the steroid receptor coactivator AIB1 in breast cancer correlates with the absence of estrogen and progesterone receptors and positivity for p53 and HER2/neu. Cancer Res 61(3):903–907
He LR, Zhao HY, Li BK, Zhang LJ, Liu MZ, Kung HF, Guan XY, Bian XW, Zeng YX, Xie D (2010) Overexpression of AIB1 negatively affects survival of surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol 21(8):1675–1681. doi:mdp592[pii]10.1093/annonc/mdp592
Manavathi B, Nair SS, Wang RA, Kumar R, Vadlamudi RK (2005) Proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein-1 is essential in growth factor regulation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 activation. Cancer Res 65(13):5571–5577. doi:65/13/5571[pii]10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4664
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kefalopoulou, Z., Tzelepi, V., Zolota, V. et al. Prognostic value of novel biomarkers in astrocytic brain tumors: nuclear receptor co-regulators AIB1, TIF2, and PELP1 are associated with high tumor grade and worse patient prognosis. J Neurooncol 106, 23–31 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0637-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0637-y