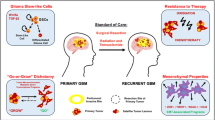
Abstract
Our knowledge of the causes of brain tumors has steadily increased and is leading to a refined understanding of the signaling pathways that may be essential for tumor formation. At the same time, we are gaining insights into the developmental processes that regulate the formation of the diverse range of cell types in the normal brain. Interestingly, many of these pathways seem to overlap and suggest common mechanisms regulating tumor formation and cellular development. This overlap may also inform us about the nature of the cell of origin for different types of brain tumors. By appreciating the inter-relationship between tumor formation and development, we may be able to design new therapeutics targeting tumors for new modes of treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DJ: Stem cells and pattern formation in the nervous system: the possible versus the actual. Neuron 30: 19–35, 2001
Sauvageot CM, Stiles CD: Molecular mechanisms controlling cortical gliogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12: 244–249, 2002
DeAngelis LM: Brain tumors. N Engl J Med 344: 114–123, 2001
Kleihues P, Cavanee W (eds): Tumours of the Nervous System. WHO Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics. IARC Press, Lyon, 2000
Dai C, Holland EC: Astrocyte differentiation states and glioma formation. Cancer J 9: 72–81, 2003
Dahlstrand J, Collins VP, Lendahl U: Expression of the class VI intermediate filament nestin in human central nervous system tumors. Cancer Res 52: 5334–5341, 1992
Kashima T, Vinters HV, Campagnoni AT: Unexpected expression of intermediate filament protein genes in human oligodendroglioma cell lines. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54: 23–31, 1995
Ross SE, Greenberg ME, Stiles CD: Basic helix-loop-helix factors in cortical development. Neuron 39: 13–25, 2003
Nieto M, Schuurmans C, Britz O, Guillemot F: Neural bHLH genes control the neuronal versus glial fate decision in cortical progenitors. Neuron 29: 401–413, 2001
Lyden D, Young AZ, Zagzag D, Yan W, Gerald W, O'Reilly R, Bader BL, Hynes RO, Zhuang Y, Manova K, Benezra R: Id1 and Id3 are required for neurogenesis, angiogenesis and vascularization of tumour xenografts. Nature 401: 670–677, 1999
Kornblum HI, Hussain R, Wiesen J, Miettinen P, Zurcher SD, Chow K, Derynck R, Werb Z: Abnormal astrocyte development and neuronal death in mice lacking the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Neurosci Res 53: 697–717, 1998
Sibilia M, Steinbach JP, Stingl L, Aguzzi A, Wagner EF: A strain-independent postnatal neurodegeneration in mice lacking the EGF receptor. Embo J 17: 719–731, 1998
Burrows RC, Lillien L, Levitt P: Mechanisms of progenitor maturation are conserved in the striatum and cortex. Dev Neurosci 22: 7–15, 2000
Hidalgo A, Kinrade EF, Georgiou M: The Drosophila neuregulin vein maintains glial survival during axon guidance in the CNS. Dev Cell 1: 679–690, 2001
Bergmann A, Tugentman M, Shilo BZ, Steller H: Regulation of cell number by MAPK-dependent control of apoptosis: a mechanism for trophic survival signaling. Dev Cell 2: 159–170, 2002
Bonni A, Sun Y, Nadal-Vicens M, Bhatt A, Frank DA, Rozovsky I, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Greenberg ME: Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science 278: 477–483, 1997
Sun Y, Nadal-Vicens M, Misono S, Lin MZ, Zubiaga A, Hua X, Fan G, Greenberg ME: Neurogenin promotes neurogenesis and inhibits glial differentiation by independent mechanisms. Cell 104: 365–376, 2001
Takizawa T, Nakashima K, Namihira M, Ochiai W, Uemura A, Yanagisawa M, Fujita N, Nakao M, Taga T: DNA methylation is a critical cell-intrinsic determinant of astrocyte differentiation in the fetal brain. Dev Cell 1: 749–758, 2001
Hitoshi S, Alexson T, Tropepe V, Donoviel D, Elia AJ, Nye JS, Conlon RA, Mak TW, Bernstein A, van der Kooy D: Notch pathway molecules are essential for the maintenance, but not the generation, of mammalian neural stem cells. Genes Dev 16: 846–858, 2002
Gaiano N, Fishell G: The role of notch in promoting glial and neural stem cell fates. Annu Rev Neurosci 25: 471–490, 2002
Ge W, Martinowich K, Wu X, He F, Miyamoto A, Fan G, Weinmaster G, Sun YE: Notch signaling promotes astrogliogenesis via direct CSL-mediated glial gene activation. J Neurosci Res 69: 848–860, 2002
Nakashima K, Takizawa T, Ochiai W, Yanagisawa M, Hisatsune T, Nakafuku M, Miyazono K, Kishimoto T, Kageyama R, Taga T: BMP2-mediated alteration in the developmental pathway of fetal mouse brain cells from neurogenesis to astrocytogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 5868–5873, 2001
Raff MC, Miller RH, Noble M: A glial progenitor cell that develops in vitro into an astrocyte or an oligodendrocyte depending on culture medium. Nature 303: 390–396, 1983
Lu QR, Sun T, Zhu Z, Ma N, Garcia M, Stiles CD, Rowitch DH: Common developmental requirement for Olig function indicates a motor neuron/oligodendrocyte connection. Cell 109: 75–86, 2002
Raff MC, Lillien LE, Richardson WD, Burne JF, Noble MD: Platelet-derived growth factor from astrocytes drives the clock that times oligodendrocyte development in culture. Nature 333: 562–565, 1988
Calver AR, Hall AC, Yu WP, Walsh FS, Heath JK, Betsholtz C, Richardson WD: Oligodendrocyte population dynamics and the role of PDGF in vivo. Neuron 20: 869–882, 1998
Fruttiger M, Karlsson L, Hall AC, Abramsson A, Calver AR, Bostrom H, Willetts K, Bertold CH, Heath JK, Betsholtz C, Richardson WD: Defective oligodendrocyte development and severe hypomyelination in PDGF-A knockout mice. Development 126: 457–467, 1999
Park HC, Appel B: Delta-Notch signaling regulates oligodendrocyte specification. Development 130: 3747–3755, 2003
Wang S, Sdrulla AD, diSibio G, Bush G, Nofziger D, Hicks C, Weinmaster G, Barres BA: Notch receptor activation inhibits oligodendrocyte differentiation. Neuron 21: 63–75, 1998
Givogri MI, Costa RM, Schonmann V, Silva AJ, Campagnoni AT, Bongarzone ER: Central nervous system myelination in mice with deficient expression of Notch 1 receptor. J Neurosci Res 67: 309–320, 2002
Hu QD, Ang BT, Karsak M, Hu WP, Cui XY, Duka T, Takeda Y, Chia W, Sankar N, Ng YK, Ling EA, Maciag T, Small D, Trifonova R, Kopan R, Okano H, Nakafuku M, Chiba S, Hirai H, Aster JC, Schachner M, Pallen CJ, Watanabe K, Xiao ZC: F3/contactin acts as a functional ligand for Notch during oligodendrocyte maturation. Cell 115: 163–175, 2003
Zhou Q, Choi G, Anderson DJ: The bHLH transcription factor Olig2 promotes oligodendrocyte differentiation in collaboration with Nkx2.2. Neuron 31: 791–807, 2001
Alberta JA, Park SK, Mora J, Yuk D, Pawlitzky I, Iannarelli P, Vartanian T, Stiles CD, Rowitch DH: Sonic hedgehog is required during an early phase of oligodendrocyte development in mammalian brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 18: 434–441, 2001
Zhou Q, Anderson DJ: The bHLH transcription factors OLIG2 and OLIG1 couple neuronal and glial subtype specification. Cell 109: 61–73, 2002
Kondo T, Raff M: The Id4 HLH protein and the timing of oligodendrocyte differentiation. Embo J 19: 1998–2007, 2000
Wang S, Sdrulla A, Johnson JE, Yokota Y, Barres BA: A role for the helix-loop-helix protein Id2 in the control of oligodendrocyte development. Neuron 29: 603–614, 2001
Seri B, Garcia-Verdugo JM, McEwen BS, Alvarez-Buylla A: Astrocytes give rise to new neurons in the adult mammalian hippocampus. J Neurosci 21: 7153–7160, 2001
Molofsky AV, Pardal R, Iwashita T, Park IK, Clarke MF, Morrison SJ: Bmi-1 dependence distinguishes neural stem cell self-renewal from progenitor proliferation. Nature 425: 962–967, 2003
Groszer M, Erickson R, Scripture-Adams DD, Lesche R, Trumpp A, Zack JA, Kornblum HI, Liu X, Wu H: Negative regulation of neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation by the Pten tumor suppressor gene in vivo. Science 294: 2186–2189, 2001
Doetsch F, Petreanu L, Caille I, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A: EGF converts transit-amplifying neurogenic precursors in the adult brain into multipotent stem cells. Neuron 36: 1021–1034, 2002
Laywell ED, Rakic P, Kukekov VG, Holland EC, Steindler DA: Identification of a multipotent astrocytic stem cell in the immature and adult mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 13883–13888, 2000
Noctor SC, Flint AC, Weissman TA, Dammerman RS, Kriegstein AR: Neurons derived from radial glial cells establish radial units in neocortex. Nature 409: 714–720, 2001
Millen KJ, Millonig JH, Wingate RJ, Alder J, Hatten ME: Neurogenetics of the cerebellar system. J Child Neurol 14: 574–581; discussion 581–582, 1999
Dahmane N, Ruiz-i-Altaba A: Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development 126: 3089–3100, 1999
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP: Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic Hedgehog. Neuron 22: 103–114, 1999
Knoepfler PS, Cheng PF, Eisenman RN: N-myc is essential during neurogenesis for the rapid expansion of progenitor cell populations and the inhibition of neuronal differentiation. Genes Dev 16: 2699–2712, 2002
Galderisi U, Jori FP, Giordano A: Cell cycle regulation and neural differentiation. Oncogene 22: 5208–5219, 2003
Zezula J, Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Ezhevsky SA, Osterhout DJ, Levine JM, Dowdy SF, Chao MV, Koff A: p21cip1 is required for the differentiation of oligodendrocytes independently of cell cycle withdrawal. EMBO Rep 2: 27–34, 2001
Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Tikoo R, Kiyokawa H, Friedrich V, Jr., Chao MV, Koff A: Oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation is perturbed in the absence of the cyclindependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip 1. Genes Dev 11: 2335–2346, 1997
Miyazawa K, Himi T, Garcia V, Yamagishi H, Sato S, Ishizaki Y: A role for p27/Kip 1 in the control of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation. J Neurosci 20: 5756–5763, 2000
Doetsch F, Verdugo JM, Caille I, Alvarez-Buylla A, Chao MV, Casaccia-Bonnefil P: Lack of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 results in selective increase of transit-amplifying cells for adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci 22: 2255–2264, 2002
Xiao A, Wu H, Pandolfi PP, Louis DN, Van Dyke T: Astrocyte inactivation of the pRb pathway predisposes mice to malignant astrocytoma development that is accelerated by PTEN mutation. Cancer Cell 1: 157–168, 2002
Holland EC, Hively WP, DePinho RA, Varmus HE: A constitutively active epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with disruption of G1 cell-cycle arrest pathways to induce glioma-like lesions in mice. Genes Dev 12: 3675–3685, 1998
Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ, Tang Y, DeFrances J, Stover E, Weissleder R, Rowitch DH, Louis DN, DePinho RA: Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell 1: 269–277, 2002
Galderisi U, Melone MA, Jori FP, Piegari E, Di Bernardo G, Cipollaro M, Cascino A, Peluso G, Claudio PP, Giordano A: pRb2/p130 gene overexpression induces astrocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Neurosci 17: 415–425, 2001
Shapiro JR: Genetics of brain neoplasms. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 1: 217–224, 2001
Kitange GJ, Templeton KL, Jenkins RB: Recent advances in the molecular genetics of primary gliomas. Curr Opin Oncol 15: 197–203, 2003
Lokker NA, Sullivan CM, Hollenbach SJ, Israel MA, Giese NA: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) autocrine signaling regulates survival and mitogenic pathways in glioblastoma cells: evidence that the novel PDGF-C and PDGF-D ligands may play a role in the development of brain tumors. Cancer Res 62: 3729–3735, 2002
Raffel C, Jenkins RB, Frederick L, Hebrink D, Alderete B, Fults DW, James CD: Sporadic medulloblastomas contain PTCH mutations. Cancer Res 57: 842–845, 1997
Hemmati HD, Nakano I, Lazareff JA, Masterman-Smith M, Geschwind DH, Bronner-Fraser M, Kornblum HI: Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA: 15178–15183, 2003
Ding H, Guha A: Mouse astrocytoma models: embryonic stem cell mediated transgenesis. J Neurooncol 53: 289–296, 2001
Weiss WA, Burns MJ, Hackett C, Aldape K, Hill JR, Kuriyama H, Kuriyama N, Milshteyn N, Roberts T, Wendland MF, DePinho R, Israel MA: Genetic determinants of malignancy in a mouse model for oligodendroglioma. Cancer Res 63: 1589–1595, 2003
Ding H, Shannon P, Lau N, Wu X, Roncari L, Baldwin RL, Takebayashi H, Nagy A, Gutmann DH, Guha A: Oligodendrogliomas result from the expression of an activated mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in a RAS transgenic mouse astrocytoma model. Cancer Res 63: 1106–1113, 2003
Dai C, Celestino JC, Okada Y, Louis DN, Fuller GN, Holland EC: PDGF autocrine stimulation dedifferentiates cultured astrocytes and induces Oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytomas from neural progenitors and astrocytes in vivo. Genes Dev 15: 1913–1925, 2001
Holland EC, Celestino J, Dai C, Schaefer L, Sawaya RE, Fuller GN: Combined activation of Ras and Akt in neural progenitors induces glioblastoma formation in mice. Nat Genet 25: 55–57, 2000
Ding H, Roncari L, Shannon P, Wu X, Lau N, Karaskova J, Gutmann DH, Squire JA, Nagy A, Guha A: Astrocytespecific expression of activated p21-ras results in malignant astrocytoma formation in a transgenic mouse model of human gliomas. Cancer Res 61: 3826–3836, 2001
Weissenberger J, Steinbach JP, Malin G, Spada S, Rulicke T, Aguzzi A: Development and malignant progression of astrocytomas in GFAP-v-src transgenic mice. Oncogene 14: 2005–2013, 1997
Uhrbom L, Dai C, Celestino JC, Rosenblum MK, Fuller GN, Holland EC: Ink4a-Arf loss cooperates with KRas activation in astrocytes and neural progenitors to generate glioblastomas of various morphologies depending on activated Akt. Cancer Res 62: 5551–5558, 2002
Goodrich LV, Milenkovic L, Higgins KM, Scott MP: Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science 277: 1109–1113, 1997
Weiner HL, Bakst R, Hurlbert MS, Ruggiero J, Ahn E, Lee WS, Stephen D, Zagzag D, Joyner AL, Turnbull DH: Induction of medulloblastomas in mice by sonic hedgehog, independent of Glic1. Cancer Res 62: 6385–6389, 2002
Rao G, Pedone CA, Coffin CM, Holland EC, Fults DW: c-Myc enhances sonic hedgehog-induced medulloblastoma formation from nestin-expressing neural progenitors in mice. Neoplasia 5: 198–204, 2003
Marino S, Vooijs M, van Der Gulden H, Jonkers J, Berns A: Induction of medulloblastomas in p53-null mutant mice by somatic inactivation of Rb in the external granular layer cells of the cerebellum. Genes Dev 14: 994–1004, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shih, A.H., Holland, E.C. Developmental neurobiology and the origin of brain tumors. J Neurooncol 70, 125–135 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-2746-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-2746-3