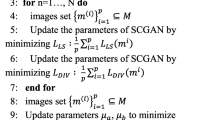Abstract
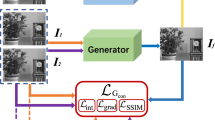
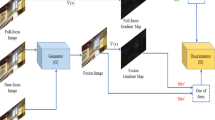
Recently, most existing learning-based fusion methods are not fully end-to-end, which still predict the decision map and recover the fused image by the refined decision map. However, in practice, these methods are hard to predict the decision map precisely. Inaccurate prediction further degrades the performance of fusing, resulting in edge blurring and artefacts. This paper proposes an end-to-end multi-focus image fusion model based on conditional generative adversarial network (MFFGAN). In MFFGAN, we introduce a pioneering use of the conditional generative adversarial network to the field of image fusion. Moreover, we introduce the simple and efficient relativistic discriminator to our network, so the network converges faster. More importantly, MFFGAN is fully trained in this adversarial relationship to produce visually perceptive images that contain rich texture information and avoid the post-processing phase. Considering the detailed information of source images, we introduce the widely used perceptual loss to improve fused image performance. Thanks to the element-wise fusion criterion, our model can conveniently and efficiently fuse multiple images. Additionally, extensive experimental results show that the proposed model achieves excellent performance in subjective and objective evaluations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslantas V, Bendes E (2015) A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences. AEU Int J Electron Commun 69(12):1890–1896
Chen J, Luo S, Xiong M, Peng T, Zhu P, Jiang M, Qin X (2020) Hybridgan: hybrid generative adversarial networks for mr image synthesis. Multimed Tools Appl Applications 79(37), 27615–27631
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conf Compu Vis Pattern Recognit pp 248–255
Du C, Gao S (2017) Image segmentation-based multi-focus image fusion through multi-scale convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 5(99):15750–15761
Everingham M, Eslami S, Gool L, Williams C, Winn J, Zisserman A (2015) The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. Int J Comput Vision 111(1):98–136
Goodfellow I (2016) Nips 2016 tutorial: Generative adversarial networks
Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A (2016) Deep learning. MIT press
Guo X, Nie R, Cao J, Zhou D, Mei L, He K (2019) Fusegan: Learning to fuse multi-focus image via conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans Multimedia 21(8):1982–1996
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) vol 2016-, pp 770–778
Hossny M, Nahavandi S, Creighton D (2008) Comments on’information measure for performance of image fusion’. Electron Lett 44(18):1066–1067
Johnson J, Alahi A, Li FF (2016) Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. arXivorg
Jolicoeur-Martineau A (2018) The relativistic discriminator: a key element missing from standard gan. arXivorg
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:14126980
Lai WS, Huang JB, Ahuja N, Yang MH (2019) Fast and accurate image super-resolution with deep laplacian pyramid networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(11):2599–2613
Ledig C, Theis L, Huszar F, Caballero J, Cunningham A, Acosta A, Aitken A, Tejani A, Totz J, Wang Z, Shi W (2017) Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. arXivorg
Li H, Wu X (2019) Densefuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(5):2614–2623
Li H, Chai Y, Yin H, Liu G (2012) Multifocus image fusion and denoising scheme based on homogeneity similarity. Opt Commun 285(2):91–100
Li Q, Yang X, Wu W, Liu K, Jeon G (2018) Multi-focus image fusion method for vision sensor systems via dictionary learning with guided filter. Sensors 18(7):2143
Li Q, Lu L, Li Z, Wu W, Liu Z, Jeon G, Yang X (2019) Coupled gan with relativistic discriminators for infrared and visible images fusion. IEEE Sens J
Li S, Yang B, Hu J (2011) Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion. Information Fusion 12(2), 74–84
Li S, Kang X, Hu J (2013) Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society 22(7), 2864–75
Liu Y, Liu S, Wang Z (2015) A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Information Fusion 24:147–164
Liu Y, Chen X, Ward RK, Wang ZJ (2016) Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process Lett 23(12):1882–1886
Liu Y, Chen X, Peng H, Wang Z (2017) Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Information Fusion 36:191–207
Liu Y, Chen X, Wang Z, Wang ZJ, Ward RK, Wang X (2018) Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects. Information Fusion 42:158–173
Liu Z, Blasch E, Xue Z, Zhao J, Laganiere R, Wu W (2011) Objective assessment of multiresolution image fusion algorithms for context enhancement in night vision: a comparative study. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(1):94–109
Maas AL, Hannun AY, Ng AY (2013) Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proc ICML vol 30, p 3
Mirza M, Osindero S (2014) Conditional generative adversarial nets
Nair V, Hinton GE (2010) Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: ICML
Nathan Silberman PK Derek Hoiem, Fergus R (2012) Indoor segmentation and support inference from rgbd images. In: ECCV
Nejati M, Samavi S, Shirani S (2015) Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Information Fusion 25:72–84
Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, Killeen T, Lin Z, Gimelshein N, Antiga L et al (2019) Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. arXiv preprint arXiv:191201703
Qu G, Zhang D, Yan P (2002) Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron Lett 38(7):313–315
Saeedi J, Faez K (2013) A classification and fuzzy-based approach for digital multi-focus image fusion. Pattern Analysis and Applications 16(3), 365–379
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015 - Conference Track Proceedings, International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR
Teichmann MT, Cipolla R (2018) Convolutional crfs for semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:180504777
Vakaimalar E, Mala K et al (2019) Multifocus image fusion scheme based on discrete cosine transform and spatial frequency. Multimed Tools Appl 78(13):17573–17587
Wang Q, Shen Y, Jin J (2008) Performance evaluation of image fusion techniques. Image Fusion: Algorithms and Applications 19:469–492
Wang X, Yu K, Wu S, Gu J, Liu Y, Dong C, Qiao Y, Change Loy C (2018) Esrgan: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In: The European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops
Wen Y, Yang X, Celik T, Sushkova O, Albertini MK (2020) Multifocus image fusion using convolutional neural network. Multimed Tools Appl
Xu H, Fan F, Zhang H, Le Z, Huang J (2020a) A deep model for multi-focus image fusion based on gradients and connected regions. IEEE Access 8:26316–26327
Xu H, Ma J, Le Z, Jiang J, Guo X (2020b) Fusiondn: A unified densely connected network for image fusion. In: AAAI, pp 12484–12491
Xydeas C, Petrovic V (2000) Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron Lett 36(4):308–309
Yan H, Yu X, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Zhao X, Zhang L (2019) Single image depth estimation with normal guided scale invariant deep convolutional fields. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(1):80–92
Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N (2015) Learning to compare image patches via convolutional neural networks. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit vol 07-12-, pp 4353–4361
Zhang Q, Long Guo B (2009) Multifocus image fusion using the nonsubsampled contourlet transform. Signal Process 89(7):1334–1346
Zhang Y, Bai X, Wang T (2017) Boundary finding based multi-focus image fusion through multi-scale morphological focus-measure. Information Fusion 35:81–101
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Sun P, Yan H, Zhao X, Zhang L (2020) Ifcnn: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Information Fusion 54:99–118
Zhao Y, Zheng Z, Wang C, Gu Z, Fu M, Yu Z, Zheng H, Wang N, Zheng B (2020) Fine-grained facial image-to-image translation with an attention based pipeline generative adversarial framework. Multimed Tools Appl pp 1–20
Zhou Z, Li S, Wang B (2014) Multi-scale weighted gradient-based fusion for multi-focus images. Information Fusion 20:60–72
Zhou Z, Wang B, Li S, Dong M (2016) Perceptual fusion of infrared and visible images through a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with gaussian and bilateral filters. Information Fusion 30:15–26
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Sichuan University under grant 2020SCUNG205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Q., Yang, X., Zhang, R. et al. Multi-focus images fusion via residual generative adversarial network. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 12305–12323 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11278-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11278-0