Abstract
Background
Cancer cell survival depends on the cross-regulation between apoptosis and autophagy which share common signaling pathways including PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Bcl-2. The aim of this study was to elucidate the modulation patterns between apoptosis and autophagy following dual inhibition by Akt inhibitor erufosine and Bcl-2 inhibitor ABT-737 in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) cell lines, PC-3 (Bax+) and DU-145 (Bax−).
Methods and Results
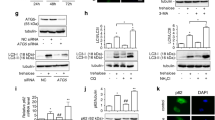
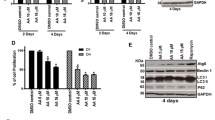
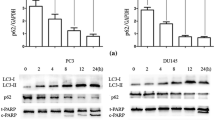
Cell cycle progression, apoptotic and autophagic signaling were examined by flow cytometry, multi-caspase assay, Hoechst staining, acridine orange staining of acidic vesicular organelles (AVOs), qRT-PCR and Western Blot. Dual inhibition increased G2/M arrest in PC-3 and DU-145, but not in the healthy prostate epithelium cells, PNT-1A. Only in PC-3, dual inhibition induced synergistic apoptotic and additive autophagic effects. In DU-145 and PNT-1A cells, ABT-737 did not display any remarkable effect on multicaspase activity and erufosine and ABT-737, neither alone nor in combination induced AVOs. By dual inhibition, AKT, BCL-2 and NF-κB gene expressions were downregulated in PC-3, both ATG-5 and BECLIN-1 gene expressions were upregulated in DU-145 but Beclin-1 protein expression was substantially reduced in both CRPC cells. Dual inhibition-induced synergistic multicaspase activation in PC-3 degrades and disrupts autophagic activity of Beclin-1, enhancing caspase-dependent apoptosis. However, in DU-145, following dual inhibition, rate of multicaspase induction and apoptosis are lower but autophagy is completely abolished despite markedly increased BECLIN-1 gene expression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, antineoplastic drug combinations may display cell-type specific modulation of apoptotic and autophagic signaling and lack of protective autophagy may not necessarily indicate increased chemotherapeutic sensitivity in heterogenous tumor subpopulations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora K, Barbieri CE (2018) Molecular subtypes of prostate cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 20:58
Wolf P (2017) BH3 mimetics for the treatment of prostate cancer. Front Pharmacol 8:557
Huang Y, Jiang X, Liang X, Jiang G (2018) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of castration resistant prostate cancer. Oncol Lett 15:6063–6076
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G (2007) Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:741
Kaleağasıoğlu F, Ali DM, Berger MR (2020) Multiple facets of autophagy and the emerging role of alkylphosphocholines as autophagy modulators. Front Pharmacol 11:547
Kang R, Zeh H, Lotze M, Tang D (2011) The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 18:571–580
Han Z, Liang J, Li Y, He J (2019) Drugs and clinical approaches targeting the antiapoptotic protein: a review. BioMed Res Int 2019:1–6
Talaiezadeh A, Galehdari H, Khodadadi A (2015) Time depended Bcl-2 inhibition might be useful for a targeted drug therapy. Cancer Cell Int 15:105
Huang S, Sinicrope F (2010) Celecoxib-induced apoptosis is enhanced by ABT-737 and by inhibition of autophagy in human colorectal cancer cells. Autophagy 6:256–269
Butler DE, Marlein C, Walker HF, Frame FM, Mann VM, Simms MS et al (2017) Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activates autophagy and compensatory Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signalling in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 8:56698
Ansari SS, Sharma AK, Soni H, Ali DM, Tews B, König R et al (2018) Induction of ER and mitochondrial stress by the alkylphosphocholine erufosine in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis 9:296
Han C, Xing G, Zhang M, Zhong M, Han Z, He C et al (2018) Wogonoside inhibits cell growth and induces mitochondrial-mediated autophagy-related apoptosis in human colon cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 15:4463–4470
Avsar Abdik E, Kaleagasioglu F, Abdik H, Sahin F, Berger MR (2019) ABT-737 and erufosine combination against castration-resistant prostate cancer: a promising but cell-type specific response associated with the modulation of anti-apoptotic signaling. Anticancer Drugs 30:383–393
Litvinov IV, Antony L, Dalrymple SL, Becker R, Cheng L, Isaacs JT (2006) PC3, but not DU145, human prostate cancer cells retain the coregulators required for tumor suppressor ability of androgen receptor. Prostate 66:1329–1338
Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang J et al (2020) Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:1–35
Liu AY (2000) Differential expression of cell surface molecules in prostate cancer cells. Can Res 60:3429–3434
Su C-Y, Huang G-C, Chang Y-C, Chen Y-J, Fang H-W (2021) Analyzing the expression of biomarkers in prostate cancer cell lines. In vivo 35:1545–1548
Dubrovska A, Kim S, Salamone RJ, Walker JR, Maira S-M, García-Echeverría C et al (2009) The role of PTEN/Akt/PI3K signaling in the maintenance and viability of prostate cancer stem-like cell populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:268–273
Hwang E, Hwang S-H, Kim J, Park JH, Oh S, Kim YA et al (2018) ABT-737 ameliorates docetaxel resistance in triple negative breast cancer cell line. Ann Surg Treatment Res 95:240–248
Opydo-Chanek M, Rak A, Cierniak A, Mazur L (2017) Combination of ABT-737 and resveratrol enhances DNA damage and apoptosis in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia MOLT-4 cells. Toxicol Vitro 42:38–46
Shen HP, Wu WJ, Ko JL, Wu TF, Yang SF, Wu CH et al (2019) Effects of ABT-737 combined with irradiation treatment on uterine cervical cancer cells. Oncol Lett 18:4328–4336
Ansari SS, Akgün N, Berger MR (2017) Erufosine increases RhoB expression in oral squamous carcinoma cells independent of its tumor suppressive mode of action-a short report. Cell Oncol 40:89–96
Ansari SS, Sharma AK, Zepp M, Ivanova E, Bergmann F, König R et al (2018) Upregulation of cell cycle genes in head and neck cancer patients may be antagonized by erufosine’s down regulation of cell cycle processes in OSCC cells. Oncotarget 9:5797
Pervaiz A, Akhtar MS, Mahmood S, Sajjad O, Khaliq S, Berger MR (2018) Molecular basis of cell cycle arrest induced by erufosine in metastatic breast cancer cells. AACR Cancer Res 78(13):4307
Broecker-Preuss M, Becher-Boveleth N, Müller S, Mann K (2016) The BH3 mimetic drug ABT-737 induces apoptosis and acts synergistically with chemotherapeutic drugs in thyroid carcinoma cells. Cancer Cell Int 16:1–12
Zhang F, Yu X, Liu X, Zhou T, Nie T, Cheng M et al (2017) ABT-737 potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Oncol Rep 38:2301–2308
Kim L-H, Shin J-A, Jang B, Yang I-H, Won D-H, Jeong JH et al (2017) Sorafenib potentiates ABT-737-induced apoptosis in human oral cancer cells. Arch Oral Biol 73:1–6
Hsin I-L, Chou Y-H, Hung W-L, Ko J-L, Wang P-H (2020) The application of arsenic trioxide in ameliorating ABT-737 target therapy on uterine cervical cancer cells through unique pathways in cell death. Cancers 12:108
Ou Y-C, Li J-R, Wang J-D, Chen W-Y, Kuan Y-H, Yang C-P et al (2018) Aspirin restores ABT-737-mediated apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 502:187–193
Hao J, Mao X, Ding D, Du G, Liu Z (2012) The effect of cell killing by ABT-737 synergized with docetaxel in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Chin J Surg 50:161–165
Parrondo R, de las Pozas A, Reiner T, Perez-Stable G (2013) ABT-737, a small molecule Bcl-2/Bcl-xL antagonist, increases antimitotic-mediated apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. PeerJ 1:144
Tamaki H, Harashima N, Hiraki M, Arichi N, Nishimura N, Shiina H et al (2014) Bcl-2 family inhibition sensitizes human prostate cancer cells to docetaxel and promotes unexpected apoptosis under caspase-9 inhibition. Oncotarget 5:11399
Saleem A, Dvorzhinski D, Santanam U, Mathew R, Bray K, Stein M et al (2012) Effect of dual inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer. Prostate 72:1374–1381
Pandit B, Gartel AL (2010) New potential anti-cancer agents synergize with bortezomib and ABT-737 against prostate cancer. Prostate 70:825–833
Kaleağasıoğlu F, Zaharieva MM, Konstantinov SM, Berger MR (2019) Alkylphospholipids are signal transduction modulators with potential for anticancer therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents) 19:66–91
Fiegl M, Lindner LH, Juergens M, Eibl H, Hiddemann W, Braess J (2008) Erufosine, a novel alkylphosphocholine, in acute myeloid leukemia: single activity and combination with other antileukemic drugs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62:321–329
Martelli A, Papa V, Tazzari P, Ricci F, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F et al (2010) Erucylphosphohomocholine, the first intravenously applicable alkylphosphocholine, is cytotoxic to acute myelogenous leukemia cells through JNK-and PP2A-dependent mechanisms. Leukemia 24:687–698
Königs SK, Pallasch CP, Lindner LH, Schwamb J, Schulz A, Brinker R et al (2010) Erufosine, a novel alkylphosphocholine, induces apoptosis in CLL through a caspase-dependent pathway. Leuk Res 34:1064–1069
Zaharieva M, Konstantinov S, Pilicheva B, Karaivanova M, Berger M (2007) Erufosine: a membrane targeting antineoplastic agent with signal transduction modulating effects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1095:182–192
Yosifov DY, Todorov PT, Zaharieva MM, Georgiev KD, Pilicheva BA, Konstantinov SM et al (2011) Erucylphospho-N, N, N-trimethylpropylammonium (erufosine) is a potential antimyeloma drug devoid of myelotoxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:13–25
Yosifov DY, Kaloyanov KA, Guenova ML, Prisadashka K, Balabanova MB, Berger MR et al (2014) Alkylphosphocholines and curcumin induce programmed cell death in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell lines. Leuk Res 38:49–56
Henke G, Meier V, Lindner LH, Eibl H, Bamberg M, Belka C et al (2012) Effects of ionizing radiation in combination with Erufosine on T98G glioblastoma xenograft tumours: a study in NMRI nu/nu mice. Radiat Oncol 7:172
Veenman L, Alten J, Linnemannstöns K, Shandalov Y, Zeno S, Lakomek M et al (2010) Potential involvement of F 0 F 1-ATP (synth) ase and reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induction by the antineoplastic agent erucylphosphohomocholine in glioblastoma cell lines. Apoptosis 15:753–768
Kapoor V, Zaharieva MM, Das SN, Berger MR (2012) Erufosine simultaneously induces apoptosis and autophagy by modulating the Akt–mTOR signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 319:39–48
Ali DM, Ansari SS, Zepp M, Knapp-Mohammady M, Berger MR (2019) Optineurin downregulation induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, chaperone-mediated autophagy, and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Discov 5:1–15
Rudner J, Ruiner C-E, Handrick R, Eibl H-J, Belka C, Jendrossek V (2010) The Akt-inhibitor Erufosine induces apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells and increases the short term effects of ionizing radiation. Radiat Oncol 5:108
Kaleağasıoğlu F, Berger MR (2014) Differential effects of erufosine on proliferation, wound healing and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 31:1407–1416
Lonergan PE, Tindall DJ (2011) Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression. J Carcinog 10:20
Smith R, Liu M, Liby T, Bayani N, Bucher E, Chiotti K et al (2020) Enzalutamide response in a panel of prostate cancer cell lines reveals a role for glucocorticoid receptor in enzalutamide resistant disease. Sci Rep 10:1–13
Pedro JMB-S, Wei Y, Sica V, Maiuri MC, Zou Z, Kroemer G et al (2015) BAX and BAK1 are dispensable for ABT-737-induced dissociation of the BCL2-BECN1 complex and autophagy. Autophagy 11:452–459
Tong Y, You L, Qian W (2012) Perifosine induces protective autophagy and upregulation of ATG5 in human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:542–550
Li M, Gao P, Zhang J (2016) Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis: potential and emerging therapeutic targets for cardiac diseases. Int J Mol Sci 17:332
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank A. Burçin Asutay for technical assistance during flow cytometry analysis.
Funding
This study was funded by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK), Project No: 315S039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EAA: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing—original draft. FK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing, Project administration. HA: Investigation, Formal analysis. DT: Investigation. FS: Funding acquisition, Resources. Martin R. Berger: Resources, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not require ethical statement.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avsar Abdik, E., Abdik, H., Turan, D. et al. Dual Akt and Bcl-2 inhibition induces cell-type specific modulation of apoptotic and autophagic signaling in castration resistant prostate cancer cell lines. Mol Biol Rep 48, 7755–7765 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06786-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06786-z