Abstract
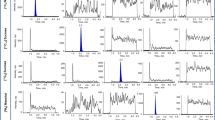
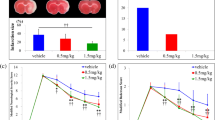
Hepatic encephalopathy that is associated with severe liver failure may compromise the blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity. However, the effects of less severe liver diseases, in the absence of overt encephalopathy, on the BBB are not well understood. The goal of the current study was to investigate the effects of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury on the BBB tight junction permeability to small, hydrophilic molecules using the widely used [14C]sucrose and recently-proposed alternative [13C]sucrose as markers. Rats were subjected to 20 min of hepatic ischemia or sham surgery, followed by 8 h of reperfusion before administration of a single bolus dose of [14C] or [13C]sucrose and collection of serial (0–30 min) blood and plasma and terminal brain samples. The concentrations of [14C] and [13C]sucrose in the samples were determined by measurement of total radioactivity (nonspecific) and LC-MS/MS (specific), respectively. IR injury significantly increased the blood, plasma, and brain concentrations of both [14C] and [13C]sucrose. However, when the brain concentrations were corrected for their respective area under the blood concentration-time curve, only [14C]sucrose showed significantly higher (30%) BBB permeability values in the IR animals. Because [13C]sucrose is a more specific BBB permeability marker, these data indicate that our animal model of hepatic IR injury does not affect the BBB tight junction permeability to small, hydrophilic molecules. Methodological differences among studies of the effects of liver diseases on the BBB permeability may confound the conclusions of such studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behrends M, Hirose R, Park YH, Tan V, Dang K, Xu F, Park SH, Niemann CU (2008) Remote renal injury following partial hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Gastrointest Surg 12:490–495
Behrens M, Huwel S, Galla HJ, Humpf HU (2015) Blood-brain barrier effects of the Fusarium mycotoxins deoxynivalenol, 3 acetyldeoxynivalenol, and moniliformin and their transfer to the brain. PLoS One 10:e0143640
Bernal W, Wendon J (2013) Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med 369:2525–2534
Bickel U, Schumacher OP, Kang YS, Voigt K (1996) Poor permeability of morphine 3-glucuronide and morphine 6-glucuronide through the blood-brain barrier in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:107–113
Bickel U, Grave B, Kang YS, del Rey A, Voigt K (1998) No increase in blood-brain barrier permeability after intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in the rat. J Neuroimmunol 85:131–136
Butterworth RF (2013) The liver-brain axis in liver failure: neuroinflammation and encephalopathy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:522–528
Butterworth RF (2016) The concept of "the inflamed brain" in acute liver failure: mechanisms and new therapeutic opportunities. Metab Brain Dis 31:1283–1287
Cannon RE, Peart JC, Hawkins BT, Campos CR, Miller DS (2012) Targeting blood-brain barrier sphingolipid signaling reduces basal P-glycoprotein activity and improves drug delivery to the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:15930–15935
Cauli O, Lopez-Larrubia P, Rodrigo R, Agusti A, Boix J, Nieto-Charques L, Cerdan S, Felipo V (2011) Brain region-selective mechanisms contribute to the progression of cerebral alterations in acute liver failure in rats. Gastroenterology 140:638–645
Chastre A, Belanger M, Nguyen BN, Butterworth RF (2013) Lipopolysaccharide precipitates hepatic encephalopathy and increases blood-brain barrier permeability in mice with acute liver failure. Liver Int 34:353–361
Chavarria L, Oria M, Romero-Gimenez J, Alonso J, Lope-Piedrafita S, Cordoba J (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging supports the cytotoxic origin of brain edema in a rat model of acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 138:1566–1573
Chen F, Ohashi N, Li W, Eckman C, Nguyen JH (2009) Disruptions of occludin and claudin-5 in brain endothelial cells in vitro and in brains of mice with acute liver failure. Hepatology 50:1914–1923
Chen F, Radisky ES, Das P, Batra J, Hata T, Hori T, Baine AM, Gardner L, Yue MY, Bu G, Del Zoppo G, Patel TC, Nguyen JH (2013) TIMP-1 attenuates blood-brain barrier permeability in mice with acute liver failure. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:1041–1049
Ferguson RK, Woodbury DM (1969) Penetration of 14C-inulin and 14C-sucrose into brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and skeletal muscle of developing rats. Exp Brain Res 7:181–194
Gjedde A (1981) High- and low-affinity transport of D-glucose from blood to brain. J Neurochem 36:1463–1471
Hawkins BT, Ocheltree SM, Norwood KM, Egleton RD (2007) Decreased blood-brain barrier permeability to fluorescein in streptozotocin-treated rats. Neurosci Lett 411:1–5
Hawkins BT, Sykes DB, Miller DS (2010) Rapid, reversible modulation of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein transport activity by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Neurosci 30:1417–1425
Huai-Yun H, Secrest DT, Mark KS, Carney D, Brandquist C, Elmquist WF, Miller DW (1998) Expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) in brain microvessel endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 243:816–820
Huber JD, Hau VS, Borg L, Campos CR, Egleton RD, Davis TP (2002) Blood-brain barrier tight junctions are altered during a 72-h exposure to lambda-carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H1531–H1537
Jin L, Nation RL, Li J, Nicolazzo JA (2013) Species-dependent blood-brain barrier disruption of lipopolysaccharide: amelioration by colistin in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:4336–4342
Kochi S, Takanaga H, Matsuo H, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Sawada Y (1999) Effect of cyclosporin a or tacrolimus on the function of blood-brain barrier cells. Eur J Pharmacol 372:287–295
Lee HT, Park SW, Kim M, D'Agati VD (2009) Acute kidney injury after hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice. Lab Investig 89:196–208
Lee SY, Kim DH, Sung SA, Kim MG, Cho WY, Kim HK, Jo SK (2011) Sphingosine-1-phosphate reduces hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury through attenuation of endothelial injury in mice. Nephrology (Carlton) 16:163–173
Lo WD, Ennis SR, Goldstein GW, McNeely DL, Betz AL (1987) The effects of galactosamine-induced hepatic failure upon blood-brain barrier permeability. Hepatology 7:452–456
Lochhead JJ, McCaffrey G, Sanchez-Covarrubias L, Finch JD, Demarco KM, Quigley CE, Davis TP, Ronaldson PT (2012) Tempol modulates changes in xenobiotic permeability and occludin oligomeric assemblies at the blood-brain barrier during inflammatory pain. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H582–H593
Loscher W, Potschka H (2005) Blood-brain barrier active efflux transporters: ATP-binding cassette gene family. NeuroRx 2:86–98
McMillin MA, Frampton GA, Seiwell AP, Patel NS, Jacobs AN, DeMorrow S (2015) TGFbeta1 exacerbates blood-brain barrier permeability in a mouse model of hepatic encephalopathy via upregulation of MMP9 and downregulation of claudin-5. Lab Investig 95:903–913
Miah MK, Shaik IH, Bickel U, Mehvar R (2014) Effects of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury on the P-glycoprotein activity at the liver canalicular membrane and blood-brain barrier determined by in vivo administration of rhodamine 123 in rats. Pharm Res 31:861–873
Miah MK, Shaik IH, Bickel U, Mehvar R (2015) Effects of Pringle maneuver and partial hepatectomy on the pharmacokinetics and blood-brain barrier permeability of sodium fluorescein in rats. Brain Res 1618:249–260
Miah MK, Bickel U, Mehvar R (2016) Development and validation of a sensitive UPLC-MS/MS method for the quantitation of [13C]sucrose in rat plasma, blood, and brain: its application to the measurement of blood-brain barrier permeability. J Chromatogr B 1015:105–110
Miah MK, Chowdhury EA, Bickel U, Mehvar R (2017) Evaluation of [14C] and [13C]sucrose as blood-brain barrier permeability markers. J Pharm Sci. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2017.1002.1011
Ohno K, Pettigrew KD, Rapoport SI (1978) Lower limits of cerebrovascular permeability to nonelectrolytes in the conscious rat. Am J Phys 235:H299–H307
Oppenheim HA, Lucero J, Guyot AC, Herbert LM, McDonald JD, Mabondzo A, Lund AK (2013) Exposure to vehicle emissions results in altered blood brain barrier permeability and expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tight junction proteins in mice. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:62
Paulson JR, Roder KE, McAfee G, Allen DD, Van der Schyf CJ, Abbruscato TJ (2006) Tobacco smoke chemicals attenuate brain-to-blood potassium transport mediated by the Na,K,2Cl-cotransporter during hypoxia-reoxygenation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:248–254
Preston E, Haas N (1986) Defining the lower limits of blood-brain barrier permeability: factors affecting the magnitude and interpretation of permeability-area products. J Neurosci Res 16:709–719
Preston E, Webster J (2002) Differential passage of [14C]sucrose and [3H]inulin across rat blood-brain barrier after cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 103:237–242
Preston E, Haas N, Allen M (1984) Reduced permeation of 14C-sucrose, 3H-mannitol and 3H-inulin across blood-brain barrier in nephrectomized rats. Brain Res Bull 12:133–136
Ronaldson PT, Demarco KM, Sanchez-Covarrubias L, Solinsky CM, Davis TP (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta signaling alters substrate permeability and tight junction protein expression at the blood-brain barrier during inflammatory pain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:1084–1098
Smith QR, Ziylan YZ, Robinson PJ, Rapoport SI (1988) Kinetics and distribution volumes for tracers of different sizes in the brain plasma space. Brain Res 462:1–9
Stolp HB, Dziegielewska KM, Ek CJ, Potter AM, Saunders NR (2005) Long-term changes in blood-brain barrier permeability and white matter following prolonged systemic inflammation in early development in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 22:2805–2816
Todd MM, Weeks JB, Warner DS (1992) Cerebral blood flow, blood volume, and brain tissue hematocrit during isovolemic hemodilution with hetastarch in rats. Am J Phys 263:H75–H82
Winkler AW, Parra J (1937) The measurement of glomerular filtration. Creatinine, sucrose and urea clearances in subjects without renal disease. J Clin Invest 16:859–867
Yin D, Wang X, Konda BM, Ong JM, Hu J, Sacapano MR, Ko MK, Espinoza AJ, Irvin DK, Shu Y, Black KL (2008) Increase in brain tumor permeability in glioma-bearing rats with nitric oxide donors. Clin Cancer Res 14:4002–4009
Ziylan YZ, Robinson PJ, Rapoport SI (1983) Differential blood-brain barrier permeabilities to [14C]sucrose and [3H]inulin after osmotic opening in the rat. Exp Neurol 79:845–857
Ziylan YZ, Robinson PJ, Rapoport SI (1984) Blood-brain barrier permeability to sucrose and dextran after osmotic opening. Am J Phys 247:R634–R638
Ziylan YZ, LeFauconnier JM, Bernard G, Bourre JM (1988) Effect of dexamethasone on transport of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and sucrose across the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem 51:1338–1342
Acknowledgements
The Authors would like to thank Dr. Raktima Bhattacharya from Texas Tech University School of Pharmacy for assistance with the radiolabeled studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MKM, UB, and RM designed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. MKM performed the experiments.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Grant support
Financial support for this study was provided by the Center for Blood–Brain Barrier Research at Texas Tech School of Pharmacy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miah, M.K., Bickel, U. & Mehvar, R. Effects of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury on the blood-brain barrier permeability to [14C] and [13C]sucrose. Metab Brain Dis 32, 1903–1912 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0069-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0069-2