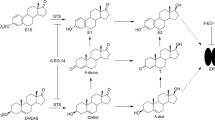
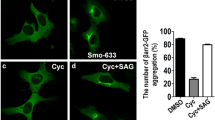
Abstract
Calcitriol, vitamin D3 (VD3), and structurally related VD3 analogues are inhibitors of Hh signaling in multiple contexts and are promising anti-cancer agents in Hh-dependent forms of cancer; however, the cellular mechanisms through which these compounds regulate Hh signal transmission are not clearly defined. Previous studies in this area have implicated both Smoothened, a key mediator of Hh signaling, and the vitamin D receptor (VDR) as potential mediators of Hh inhibition for this class of seco-steroids. We have performed a series of in vitro studies to more fully probe the cellular mechanisms that govern seco-steroid-mediated inhibition of Hh signaling. Our results support a role for both the Hh and VDR pathways in this process, as well as the possibility that other, as yet unidentified proteins, are also central to seco-steroid-mediated inhibition of Hh signaling.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haussler MR, Whitfield GK, Haussler CA, Hsieh J-C, Thompson PD, Selznick SH, Dominguez CE, Jurutka PW (1998) The nuclear vitamin D receptor: biological and molecular regulatory properties revealed. J Bone Min Res 13:325–349
Bijlsma MF, Spek CA, Zivkovic D, van de Water S, Rezaee F, Peppelenbosch MP (2006) Repression of smoothened by patched-dependent (pro-)vitamin D3 secretion. PLoS Biol 4:e232
Uhmann A, Niemann H, Lammering B, Henkel C, Heb I, itzki F, Fritsch A, Prüfer N, Rosenberger A, Dullin C, Schraepler A, Reifenberger J, Schweyer S, Pietsch T, Strutz F, Schultz-Schaeffer W, Hahn H (2011) Antitumoral effects of calcitriol in basal cell carcinomas involve inhibition of hedgehog signaling and induction of vitamin D receptor signaling and differentiation. Mol Cancer Ther 10:2179–2188
Briscoe J, Thérond PP (2013) The mechanisms of hedgehog signaling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:418–431
Amayke D, Jagani Z, Dorsch M (2013) Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Med 19:1410–1422
Tang JY, Xiao TZ, Oda Y, Chang KS, Shpall E, Wu A, So P-L, Hebert J, Bikle D, Epstein EH (2011) Vitamin D3 inhibits hedgehog signaling and proliferation in murine basal cell carcinomas. Cancer Prev Res 4:744–741
Uhmann A, Niemann H, Lammering B, Henkel C, Heb I, Rosenberger A, Dullin C, Schraepler A, Schultz-Schaeffer W, Hahn H, Calcitriol inhibits hedgehog signaling and induces vitamin D receptor signaling and differentiation in the Patched mouse model of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, Sarcoma 2012 (2012) 357040
DeBerardinis AM, Banerjee U, Hadden MK (2013) Identification of vitamin D3-based hedgehog pathway inhibitors that incorporate an aromatic A-ring isostere, ACS Med. Chem Lett 4:590–595
DeBerardinis AM, Madden DJ, Banerjee U, Sail V, Raccuia DS, DeCarlo D, Lemieux SM, Meares A, Hadden MK (2014) Structure-activity relationships for vitamin D-based aromatic A-ring analogues as hedgehog pathway inhibitors. J Med Chem 54:3724–3736
Banerjee U, DeBerardinis AM, Hadden MK (2015) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of hybrid vitamin D3 side chain analogues as hedgehog pathway inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 23:548–555
DeBerardinis AM, Raccuia DS, Maschinot CA, Thompson E, Hadden MK (2015) Vitamin D3 analogues that contain modified A- and seco-B-rings as hedgehog pathway inhibitors. Euro J Med Chem 93:156–171
Yauch RL, Dijkgraaf GJP, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn CP, Holcomb T, Pujara K, Stinson J, Callahan CA, Tang T, Bazan JF, Kan Z, Seshagiri S, Hann CL, Gould SE, Low JA, Rudin CM (2009) F.J. de Savage, smoothened mutation confers resistance to a hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science 326:572–574
Sharpe HJ, Pau G, Dijkgraaf GJ, Basset-Seguin N, Modrusan Z, Januario T, Tsui V, Durham AB, Dlugosz AA, Haverty PM, Bourgon R, Tang JY, Sarin KY, Dirix L, Fisher DC, Rudin CM, Sofen H, Midgen MR, Yauch RL (2015) F.J. de Savage, genomic analysis of smoothened inhibitor resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 27:327–341
Atwood SX, Sarin KY, Whitson RJ, Li JR, Kim G, Rezaee M, Ally MS, Kim J, Yao C, Chang ALS, Oro AE, Tang JY (2015) Smoothened variants explain the majority of drug resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 27:342–353
Du P, Kibbe WA (2008) S.M. Lin, lumi: a pipeline for processing Ilumina microarray. Bioinformatics 24:1547–1548
Lin SM, Du P, Kibbe WA (2008) Model-based variance-stabilizing transformation for Illumina microarray data. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e11
Du P, Kibbe WA, Lin SM (2008) nuID: a universal naming schema of oligonucleotides for Illumina, affymetrix, and other microarrays. Biol Dir 2:16
Lauth M, Bergström Å, Toftgård R (2007) Phorbol esters inhibit the hedgehog signaling pathway downstream of suppressor of fused, but upstream of Gli. Oncogene 26:5163–5168
Szeto FJ, Sun J, Kong J, Duan Y, Liao A, Madara JL, Li YC (2007) Involvement of the vitamin D receptor in the regulation of NG-κB activity in fibroblasts. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 103:563–566
Mi H, Poudel S, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT, Thomas PD (2016) PANTHER version 10: expanded protein families and functions, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D336-D342
Mi H, Muruganujam A, Casagrande JT, Thomes PD (2013) Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system. Nat Protoc 8:1551–1566
Javelaud D, Alexavi VI, Dennler S, Mohammad KS, Guise TA, Mauviel A (2011) TGF-β/SMAD/GLI2 signaling axis in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Res 71:5606–5610
Akhurst RJ, Hata A (2015) TGF-β/Smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front Physiol 6:e82
Hu L, Lin X, Lu H, Chen B, Bai Y (2015) An overview of hedgehog signaling in fibrosis. Mol Pharmacol 87:174–182
Clark RA, McCoy GA, Folkvord JM, McPherson JM, TGF-beta 1 stimulates cultured human fibroblasts to proliferate and produce tissue-like fibroplasia: a fibronectin matrix-dependent event. 170 (1997) 69–80
Xiao L, Du Y, Shen Y, He Y, Zhao H, Li Z (2012) TGF-beta 1 induced fibroblast proliferation is mediated by the FGF-2/ERK pathway. Front Biosci 17:2667–2674
Nakano N, Itoh S, Watanabe Y, Maeyama K, Itoh F, Kato M (2010) Requirement of TCF7L2 for TGF-beta-dependent transcriptional activation of the TMEPAI gene. J Biol Chem 285:38023–38033
Akhurst RJ, Hata A (2010) Targeting the TGF-β signaling pathway in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:790–811
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge support of this work by the American Cancer Society (RSG-13-131-01), the National Science Foundation (1515808), and the University of Connecticut Research Foundation. The Ptch−/− and Sufu−/− MEFs were a kind gift from Matthew Scott (Stanford University). The VDR−/− MEFs were a kind gift from Jun Sun (University of Illinois College of Medicine). Smo−/− MEFs were a kind gift from Philip Beachy (Stanford University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in regard to the information presented in this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, E.N., Sail, V., Raccuia, D.S. et al. Probing seco-steroid inhibition of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 450, 75–85 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3374-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3374-0