Abstract
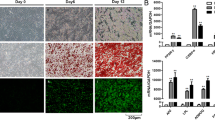
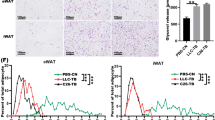
A key feature of cancer cachexia is the loss of adipose tissue, mainly due to increased lipolysis and an impairment of adipogenesis. Recent findings have shown that cancer exosomes promoted lipolysis in adipose tissue. However, effects of cancer exosomes on adipogenesis were not reported. In this study, we found that lung cancer exosomes could be internalized by human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAD-MSCs) and significantly inhibited hAD-MSC adipogenesis as demonstrated by Oil Red O staining and decreased expression of adipogenic-specific genes. Specifically, TGFβ signaling pathway was demonstrated to be involved in the inhibitive effects of lung cancer exosomes on hAD-MSC adipogenesis. Additionally, TGFβ was detected in A549 exosomes. Herein, this study reports that the effect of lung cancer cell exosomes on hAD-MSC adipogenic differentiation was mediated by TGFβ signaling pathway and suggests the involvement of cancer exosomes in weight loss of cancer cachexia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fearon KC, Glass DJ, Guttridge DC (2012) Cancer cachexia: mediators, signaling, and metabolic pathways. Cell Metab 16(2):153–166. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.06.011S1550-4131(12)00248-3
Bing C, Russell S, Becket E, Pope M, Tisdale MJ, Trayhurn P, Jenkins JR (2006) Adipose atrophy in cancer cachexia: morphologic and molecular analysis of adipose tissue in tumour-bearing mice. Br J Cancer 95(8):1028–1037. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603360
Bing C, Brown M, King P, Collins P, Tisdale MJ, Williams G (2000) Increased gene expression of brown fat uncoupling protein (UCP)1 and skeletal muscle UCP2 and UCP3 in MAC16-induced cancer cachexia. Cancer Res 60(9):2405–2410
Agustsson T, Ryden M, Hoffstedt J, van Harmelen V, Dicker A, Laurencikiene J, Isaksson B, Permert J, Arner P (2007) Mechanism of increased lipolysis in cancer cachexia. Cancer Res 67(11):5531–5537. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4585
Yang Z, Bian C, Zhou H, Huang S, Wang S, Liao L, Zhao RC (2011) MicroRNA hsa-miR-138 inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells through adenovirus EID-1. Stem Cells Dev 20(2):259–267. doi:10.1089/scd.2010.0072
Morley JE, Thomas DR, Wilson MM (2006) Cachexia: pathophysiology and clinical relevance. Am J Clin Nutr 83(4):735–743
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9(6):654–659. doi:10.1038/ncb1596
Grange C, Tapparo M, Collino F, Vitillo L, Damasco C, Deregibus MC, Tetta C, Bussolati B, Camussi G (2011) Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 71(15):5346–5356. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-02410008-5472.CAN-11-0241
Chen WX, Cai YQ, Lv MM, Chen L, Zhong SL, Ma TF, Zhao JH, Tang JH (2014) Exosomes from docetaxel-resistant breast cancer cells alter chemosensitivity by delivering microRNAs. Tumour Biol 35(10):9649–9659. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2242-0
Iero M, Valenti R, Huber V, Filipazzi P, Parmiani G, Fais S, Rivoltini L (2008) Tumour-released exosomes and their implications in cancer immunity. Cell Death Differ 15(1):80–88. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402237
Keller S, Ridinger J, Rupp AK, Janssen JW, Altevogt P (2011) Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J Transl Med 9:86. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-9-861479-5876-9-86
Bretz NP, Ridinger J, Rupp AK, Rimbach K, Keller S, Rupp C, Marme F, Umansky L, Umansky V, Eigenbrod T, Sammar M, Altevogt P (2013) Body fluid exosomes promote secretion of inflammatory cytokines in monocytic cells via Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 288(51):36691–36702. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.512806
Sagar G, Sah RP, Javeed N, Dutta SK, Smyrk TC, Lau JS, Giorgadze N, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL, Chari ST, Mukhopadhyay D (2016) Pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer exosome-induced lipolysis in adipose tissue. Gut 65(7):1165–1174. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308350
Cao Y, Sun Z, Liao L, Meng Y, Han Q, Zhao RC (2005) Human adipose tissue-derived stem cells differentiate into endothelial cells in vitro and improve postnatal neovascularization in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332(2):370–379. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.04.135
Ohshima K, Inoue K, Fujiwara A, Hatakeyama K, Kanto K, Watanabe Y, Muramatsu K, Fukuda Y, Ogura S, Yamaguchi K, Mochizuki T (2010) Let-7 microRNA family is selectively secreted into the extracellular environment via exosomes in a metastatic gastric cancer cell line. PLoS ONE 5(10):e13247. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013247
Hood JL, Pan H, Lanza GM, Wickline SA (2009) Paracrine induction of endothelium by tumor exosomes. Lab Invest 89(11):1317–1328. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2009.94
Chae GN, Kwak SJ (2003) NF-kappaB is involved in the TNF-alpha induced inhibition of the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by reducing PPARgamma expression. Exp Mol Med 35(5):431–437. doi:10.1038/emm.2003.56
Huang Z, Li S, Fan W, Ma Q (2017) Transforming growth factor beta1 promotes invasion of human JEG-3 trophoblast cells via TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16826
Kim A, Nam YJ, Shin YK, Lee MS, Sohn DS, Lee CS (2017) Rotundarpene inhibits TNF-alpha-induced activation of the Akt, mTOR, and NF-kappaB pathways, and the JNK and p38 associated with production of reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell Biochem. doi:10.1007/s11010-017-3041-x
Zhang JL, Zhuo XJ, Lin J, Luo LC, Ying WY, Xie X, Zhang HW, Yang JX, Li D, Gao Smith F, Jin SW (2017) Maresin1 stimulates alveolar fluid clearance through the alveolar epithelial sodium channel Na, K-ATPase via the ALX/PI3 K/Nedd4-2 pathway. Lab Invest. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2016.150
Liu CY, Yu T, Huang Y, Cui L, Hong W (2017) ETS dependent transcriptional upregulation of the transcriptional co-activator TAZ promotes cell migration and metastasis in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M117.783787
Webber J, Steadman R, Mason MD, Tabi Z, Clayton A (2010) Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Cancer Res 70(23):9621–9630. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1722
Peinado H, Aleckovic M, Lavotshkin S, Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G, Hergueta-Redondo M, Williams C, Garcia-Santos G, Ghajar C, Nitadori-Hoshino A, Hoffman C, Badal K, Garcia BA, Callahan MK, Yuan J, Martins VR, Skog J, Kaplan RN, Brady MS, Wolchok JD, Chapman PB, Kang Y, Bromberg J, Lyden D (2012) Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat Med 18(6):883–891. doi:10.1038/nm.2753
Chowdhury R, Webber JP, Gurney M, Mason MD, Tabi Z, Clayton A (2015) Cancer exosomes trigger mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into pro-angiogenic and pro-invasive myofibroblasts. Oncotarget 6(2):715–731
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370879), PUMC Youth Fund and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3332013141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Shihua Wang and Xiaoxia Li authors have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Li, X., Xu, M. et al. Reduced adipogenesis after lung tumor exosomes priming in human mesenchymal stem cells via TGFβ signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 435, 59–66 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3056-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3056-3