Abstract
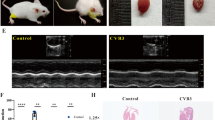
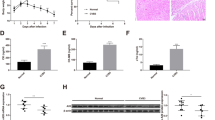
Viral myocarditis is a common cardiovascular disease, which seriously endangers the health of people and even leads to sudden unexpected death. MicroRNAs play very important roles in various physical and pathological processes including cardiogenesis and heart diseases. In recent years, miR-20b has been implicated in various diseases such as breast cancer, gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, cardiovascular diseases. However, the function of miR-20b in the pathological progress of viral myocarditis has not been reported. In this study, we found that miR-20b was up-regulated in mouse heart tissues post Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) infection. Bioinformatics analysis identified ZFP-148, a transcription factor that plays essential roles in the regulation of virus replication, is one of the predicted targets of miR-20b. MiR-20b expression was found to be up-regulated and ZFP-148 protein level was markedly repressed during viral myocarditis. Further studies demonstrated that miR-20b directly binds to the 3′-UTR of ZFP-148 and suppresses its translation. Moreover, aberrant expression of miR-20b promoted the expression of anti-apoptosis proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, suggesting that altered gene expression might promote cardiomyocytes survival in viral myocarditis. Our findings indicated that miR-20b might be a potential therapeutic target for CVB3-induced viral myocarditis and a useful marker for the diagnosis of viral myocarditis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 November 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04598-8
References
K hl U, Rohde M, Lassner D, Gross UM, Escher F, Schultheiss HP (2012) miRNA as activity markers in Parvo B19 associated heart disease. Herz 37:637–643
Kuhl U(2005) Viral persistence in the myocardium is associated with progressive cardiac dysfunction. Circulation, 112:1965–1970.
Gaaloul I, Riabi S, Harrath R, Evans M, Salem NH, Mlayeh S, Huber S, Aouni M (2012) Sudden unexpected death related to enterovirus myocarditis: histopathology, immunohistochemistry and molecular pathology diagnosis at post-mortem. BMC Infect Dis 12:212
K hl U, Schultheiss H (2010) Myocarditis in children. Heart Fail Clin 6:483–496
Wang L, Dong C, Chen DE, Song Z (2014) Visceral pathology of acute systemic injury in newborn mice on the onset of Coxsackie virus infection. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:890–904
Di Filippo S (2016) Improving outcomes of acute myocarditis in children. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 14:117–125
Kearney MT, Cotton JM, Richardson PJ, Shah AM (2001) Viral myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy: mechanisms, manifestations, and management. Postgrad Med J 77:4–10
Weithauser A, Bobbert P, Antoniak S, B hm A, Rauch BH, Klingel K, Savvatis K, Kroemer HK, Tschope C, Stroux A, Zeichhardt H, Poller W, Mackman N, Schultheiss H, Rauch U (2013) Protease-activated receptor-2 regulates the innate immune response to viral infection in a Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol 62:1737–1745
He F, Yao H, Wang J, Xiao Z, Xin L, Liu Z, Ma X, Sun J, Jin Q, Liu Z (2015) Coxsackievirus B3 engineered to contain MicroRNA targets for muscle-specific microRNAs displays attenuated cardiotropic virulence in mice. J Virol 89:908–916
Wu J, Shen L, Chen J, Xu H, Mao L (2015) The role of microRNAs in enteroviral infections. Braz J Infect Dis 19:510–516
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs Cell 116:281–297
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Nelson P, Kiriakidou M, Sharma A, Maniataki E, Mourelatos Z (2003) The microRNA world: small is mighty. Trends Biochem Sci 28:534–540
Ambros V (2003) MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113:673–676
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2003) Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113:25–36
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Yi R, Poy MN, Stoffel M, Fuchs E (2008) A skin microRNA promotes differentiation by repressing ‘stemness’. Nature 452:225–229
Tong L, Lin L, Wu S, Guo Z, Wang T, Qin Y, Wang R, Zhong X, Wu X, Wang Y, Luan T, Wang Q, Li Y, Chen X, Zhang F, Zhao W, Zhong Z (2013) MiR-10a* up-regulates Coxsackievirus B3 biosynthesis by targeting the 3D-coding sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 41:3760–3771
Wang L, Qin Y, Tong L, Wu S, Wang Q, Jiao Q, Guo Z, Lin L, Wang R, Zhao W, Zhong Z (2012) MiR-342-5p suppresses Coxsackievirus B3 biosynthesis by targeting the 2 C-coding region. Antivir Res 93:270–279
Tanzer A, Stadler PF (2004) Molecular evolution of a microRNA cluster. J Mol Biol 339:327–335
Chen J, Huang ZP, Seok HY, Ding J, Kataoka M, Zhang Z, Hu X, Wang G, Lin Z, Wang S, Pu WT, Liao R, Wang DZ (2013) mir-17-92 cluster is required for and sufficient to induce cardiomyocyte proliferation in postnatal and adult hearts. Circ Res 112:1557–1566
Zhou M, Cai J, Tang Y, Zhao Q (2013) MiR-17-92 cluster is a novel regulatory gene of cardiac ischemic/reperfusion injury. Med Hypotheses 81:108–110
Chiang DY, Kongchan N, Beavers DL, Alsina KM, Voigt N, Neilson JR, Jakob H, Martin JF, Dobrev D, Wehrens XH, Li N (2014) Loss of microRNA-106b-25 cluster promotes atrial fibrillation by enhancing ryanodine receptor type-2 expression and calcium release. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 7:1214–1222
Li SH, Guo J, Wu J, Sun Z, Han M, Shan SW, Deng Z, Yang BB, Weisel RD, Li RK (2013) miR-17 targets tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 and 2 to modulate cardiac matrix remodeling. FASEB J 27:4254–4265
Marques FZ, Vizi D, Khammy O, Mariani JA, and Kaye DM.(2016) The transcardiac gradient of cardio-microRNAs in the failing heart. Eur J Heart Fail 18:1000–1008
Sayin VI, Nilton A, Ibrahim MX, gren P, Larsson E, Petit MM, Hult n LM, St hlman M, Johansson BR, Bergo MO, Lindahl P (2013) Zfp148 deficiency causes lung maturation defects and lethality in newborn mice that are rescued by deletion of p53 or antioxidant treatment. PLoS ONE 8:e55720
Bai L, Merchant JL (2000) Transcription factor ZBP-89 cooperates with histone acetyltransferase p300 during butyrate activation of p21 waf1 transcription in human cells. J Biol Chem 275:30725–30733
Bai L, Merchant JL (2001) ZBP-89 promotes growth arrest through stabilization of p53. Mol Cell Biol 21:4670–4683
Law GL, Itoh H, Law DJ, Mize GJ, Merchant JL, Morris DR (1998) Transcription factor ZBP-89 regulates the activity of the ornithine decarboxylase promoter. J Biol Chem 273:19955–19964
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pang L, Koren G, Wang Z, Nattel S (2003) Tissue-specific expression of two human Ca(v)1.2 isoforms under the control of distinct 5′ flanking regulatory elements. FEBS Lett 546:349–354
Luo X, Xiao J, Lin H, Li B, Lu Y, Yang B, Wang Z (2007) Transcriptional activation by stimulating protein 1 and post-transcriptional repression by muscle-specific microRNAs of IKs-encoding genes and potential implications in regional heterogeneity of their expressions. J Cell Physiol 212:877
Caplen NJ, Parrish S, Imani F, Fire A, Morgan RA (2001) Specific inhibition of gene expression by small double-stranded RNAs in invertebrate and vertebrate systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9742–9747
Ye X, Liu Z, Hemida MG, Yang D (2011) Targeted delivery of mutant tolerant anti-Coxsackievirus artificial microRNAs using folate conjugated bacteriophage Phi29 pRNA. PLoS ONE 6:e21215
Si X, Gao G, Wong J, Wang Y, Zhang J, Luo H (2008) Ubiquitination is required for effective replication of Coxsackievirus B3. PLoS ONE 3:e2585
Omura S, Kawai E, Sato F, Martinez NE, Chaitanya GV, Rollyson PA, Cvek U, Trutschl M, Alexander JS, Tsunoda I (2014) Bioinformatics multivariate analysis determined a set of phase-specific biomarker candidates in a novel mouse model for viral myocarditis. Circulation: Cardiovasc Genet 7:444–454
Xu H, Ding Y, Shen Y, Xue A, Xu H, Luo C, Li B, Liu Y, Zhao Z (2012) MicroRNA- 1 represses Cx43 expression in viral myocarditis. Mol Cell Biochem 362:141–148
Zhang Q, Xiao Z, He F, Zou J, Wu S, Liu Z (2013) MicroRNAs regulate the pathogenesis of CVB3-induced viral myocarditis. Intervirology 56:104–113
Zhou W, Shi G, Zhang Q, Wu Q, Li B, Zhang Z (2014) MicroRNA-20b promotes cell growth of breast cancer cells partly via targeting phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN). Cell Biosci 4:62
Cascio S, D’Andrea A, Ferla R, Surmacz E, Gulotta E, Amodeo V, Bazan V, Gebbia N, and Russo A.(2010) miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1α and STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 224:242–249
Hemida MG, Ye X, Zhang HM, Hanson PJ, Liu Z, McManus BM, Yang D (2013) MicroRNA-203 enhances Coxsackievirus B3 replication through targeting zinc finger protein-148. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:277–291
Law DJ, Labut EM, Merchant JL (2006) Intestinal overexpression of ZNF148 suppresses ApcMin/+ neoplasia. Mamm Genome 17:999–1004
To AKY, Chen GG, Chan UPF, Ye C, Yun JP, Ho RLK, Tessier A, Merchant JL, and Lai PBS. ZBP-89 enhances Bak expression and causes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Cell Res 1813: 222–230, 2011.
Sera T (2005) Inhibition of virus DNA replication by artificial zinc finger proteins. J Virol 79:2614–2619
Zimmerman KA, Fischer KP, Joyce MA, Tyrrell DLJ (2008) Zinc finger proteins designed to specifically target duck hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA inhibit viral transcription in tissue culture. J Virol 82:8013–8021
Li Y, Bourlet T, Andreoletti L, Mosnier JF, Peng T, Yang Y, Archard LC, Pozzetto B, Zhang H (2000) Enteroviral capsid protein VP1 is present in myocardial tissues from some patients with myocarditis or dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 101:231–234
Zhang H, Li Y, McClean DR, Richardson PJ, Latif N, Dunn MJ, Archard LC, Florio R, Sheppard M, Morrison K (2004) Detection of enterovirus capsid protein VP1 in myocardium from cases of myocarditis or dilated cardiomyopathy by immunohistochemistry: further evidence of enterovirus persistence in myocytes. Med Microbiol Immunol 193:109–114
Kang MH, Reynolds CP (2009) Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:1126–1132
Fang J, Song XW, Tian J, Chen HY, Li DF, Wang JF, Ren AJ, Yuan WJ, Lin L (2012) Overexpression of microRNA-378 attenuates ischemia-induced apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 expression in cardiac myocytes. Apoptosis 17:410–423
Acknowledgements
We express gratitude for the excellent technical assistance and laboratory equipments provided by Soochow University. Meanwhile, we are grateful for the support of the Institute of cardiovascular diseases at Fudan University. This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81302617 and 571848), and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author Contributions
X.H.F., L.J.Y., and Z.S.H. conception and design of research; X.H.F., G.X.T., L.J.Y., X.X.H., D.Y.J., and Z.S.H. performed experiments; X.H.F., G.X.T., X.X.H., D.Y.J., and Z.S.H. analyzed data; X.H.F., G.X.T., L.J.Y., D.Y.J., and Z.S.H. interpreted results of experiments; X.H.F. prepared figures; X.H.F. and G.X.T. drafted manuscript; X.H.F., G.X.T., L.J.Y., X.X.H., D.Y.J., and Z.S.H. edited and revised manuscript; X.H.F., G.X.T., L.J.Y., X.X.H., D.Y.J., and Z.S.H. approved final version of manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Additional information
Hong-Fei Xu, Xiang-Ting Gao and Jun-Yi Lin have contribute equally to this work and they share first authorship.
Hong-Fei Xu, Yu-Jie Ding, and Shao-Hua Zhu have contribute equally to this work and they share corresponding authorship.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, HF., Gao, XT., Lin, JY. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: MicroRNA-20b suppresses the expression of ZFP-148 in viral myocarditis. Mol Cell Biochem 429, 199–210 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2947-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2947-7