Abstract
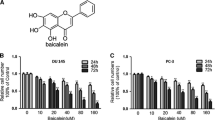
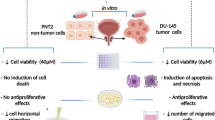
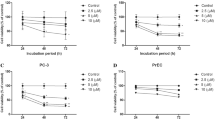
Acacetin (5,7-dihydroxy-4′-methoxyflavone), a flavonoid compound, has anti-peroxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. The effect of acacetin on antimetastasis in human prostate cancer DU-145 cells was investigated. First, the result demonstrated acacetin could exhibit an inhibitory effect on the abilities of the adhesion, invasion, and migration by cell–matrix adhesion assay, wound-healing assay, and Boyden chamber assay. Data also showed acacetin could inhibit the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) involved in the downregulation of the expressions of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PA) at both the protein and mRNA levels. Next, acacetin significantly decreased the nuclear levels of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), c-Fos, and c-Jun. Also, the treatment with acacetin to DU145 cells also leads to a dose-dependent inhibition on the binding ability of NF-κB and activator protein-1 (AP-1). Furthermore, the treatment of inhibitors specific for p38 MAPK (SB203580) to DU145 cells could cause reduced expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9, and u-PA. These results showed acacetin could inhibit the invasion and migration abilities of DU145 cells by reducing MMP-2, MMP-9, and u-PA expressions through suppressing p38 MAPK signaling pathway and inhibiting NF-κB- or AP-1-binding activity. These findings proved acacetin might be offered further application as an antimetastatic agent.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- u-PA:
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- JNK/SAPK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase
- p38 MAPK:
-
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- AP-1:
-
Activator protein-1
- IκB:
-
Inhibitor of NF-κB
References
Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA (2000) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 50:7–33
Yim D, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Lee S, Chi H, Agarwal R (2005) A novel anticancer agent, decursin, induces G1 arrest and apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 65:1035–1044
Sandberg L, Papareddy P, Silver J, Bergh A, Mei YF (2009) Replication-competent Ad11p vector (RCAd11p) efficiently transduces and replicates in hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer cells. Hum Gene Ther 20:361–373
Kraft C, Jenett-Siems K, Siems K, Jakupovic J, Mavi S, Bienzle U, Eich E (2003) In vitro antiplasmodial evaluation of medicinal plants from Zimbabwe. Phytother Res 17:123–128
Pan MH, Lai CS, Wang YJ, Ho CT (2006) Acacetin suppressed LPS-induced up-expression of iNOS and COX-2 in murine macrophages and TPA-induced tumor promotion in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1293–1303
Yin Y, Gong FY, Wu XX, Sun Y, Li YH, Chen T, Xu Q (2008) Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effect of flavones isolated from Artemisia vestita. J Ethnopharmacol 120:1–6
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Lin CC (2004) Acacetin inhibits the proliferation of HepG2 by blocking cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 67:823–829
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Liu CF, Lin CC (2004) Acacetin-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Cancer Lett 212:53–60
Pan MH, Lai CS, Hsu PC, Wang YJ (2005) Acacetin induces apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma cells accompanied by activation of caspase cascades and production of reactive oxygen species. J Agric Food Chem 53:620–630
Shim HY, Park JH, Paik HD, Nah SY, Kim DS, Han YS (2007) Acacetin-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells involves caspase cascade, mitochondria- mediated death signaling and SAPK/JNK1/2-c-Jun activation. Mol Cells 24:95–104
Singh RP, Agrawal P, Yim D, Agarwal C, Agarwal R (2005) Acacetin inhibits cell growth and cell cycle progression, and induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells: structure-activity relationship with linarin and linarin acetate. Carcinogenesis 26:845–854
Weiss L (1990) Metastatic inefficiency. Adv Cancer Res 54:159–211
Huang SC, Ho CT, Lin-Shiau SY, Lin JK (2005) Carnosol inhibits the invasion of B16/F10 mouse melanoma cells by suppressing metalloproteinase-9 through down-regulating nuclear factor-kappa B and c-Jun. Biochem Pharmacol 69:221–232
Bernhard EJ, Gruber SB, Muschel RJ (1994) Direct evidence linking expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (92-kDa gelatinase/collagenase) to the metastatic phenotype in transformed rat embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4293–4297
Duffy MJ, Duggan C (2004) The urokinase plasminogen activator system: a rich source of tumour markers for the individualized management of patients with cancer. Clin Biochem 37:541–548
Itoh Y, Nagase H (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer. Essays Biochem 38:21–36
Chan-Hui PY, Weaver R (1998) Human mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase mediates the stress-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. Biochem J 336:599–609
Trusolino L, Comoglio PM (2002) Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: cell signalling for invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2:289–300
Chen PN, Hsieh YS, Chiou HL, Chu SC (2005) Silibinin inhibits cell invasion through inactivation of both PI3K-Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact 156:141–150
Kwon GT, Cho HJ, Chung WY, Park KK, Moon A, Park JH (2008) Isoliquiritigenin inhibits migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells: possible mediation by decreased JNK/AP-1 signaling. J Nutr Biochem (in press)
Lee SJ, Park SS, Lee US, Kim WJ, Moon SK (2008) Signaling pathway for TNF-alpha -induced MMP-9 expression: mediation through p38 MAP kinase, and inhibition by anti-cancer molecule magnolol in human urinary bladder cancer 5637 cells. Int Immunopharmacol 8:1821–1826
Nagase H, Woessner JF Jr (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem 274:21491–21494
Sliva D (2004) Signaling pathways responsible for cancer cell invasion as targets for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4:327–336
Westermarck J, Kahari VM (1999) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. FASEB J 13:781–792
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P, Aggarwal BB (2008) Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett 269:199–225
Jiang J, Grieb B, Thyagarajan A, Sliva D (2008) Ganoderic acids suppress growth and invasive behavior of breast cancer cells by modulating AP-1 and NF-kappaB signaling. Int J Mol Med 21:577–584
Lee SO, Jeong YJ, Im HG, Kim CH, Chang YC, Lee IS (2007) Silibinin suppresses PMA-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking the AP-1 activation via MAPK signaling pathways in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:165–171
Hoppe-Seyler F, Butz K, Rittmuller C, von Knebel Doeberitz M (1991) A rapid microscale procedure for the simultaneous preparation of cytoplasmic RNA, nuclear DNA binding proteins and enzymatically active luciferase extracts. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5080
Rao JS (2003) Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer 3:489–501
Turner NA, Aley PK, Hall KT, Warburton P, Galloway S, Midgley L, O’regan DJ, Wood IC, Ball SG, Porter KE (2007) Simvastatin inhibits TNFalpha-induced invasion of human cardiac myofibroblasts via both MMP-9-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Mol Cell Cardio 43:168–176
Aquilina JW, Lipsky JJ, Bostwick DG (1999) Androgen deprivation as a strategy for prostate cancer chemoprevention. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:689–696
Kim D, Kim S, Koh H, Yoon SO, Chung AS, Cho KS, Chung J (2001) Akt/PKB promotes cancer cell invasion via increased motility and metalloproteinase production. FASEB J 15:1953–1962
Kleiner DE, Stetler-Stevenson WG (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases and metastasis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 43:S42–S51
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Aznavoorian S, Liotta LA (1993) Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol 9:541–573
Gum R, Lengyel E, Juarez J, Chen JH, Sato H, Seiki M, Boyd D (1996) Stimulation of 92-kDa gelatinase B promoter activity by ras is mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1-independent and requires multiple transcription factor binding sites including closely spaced PEA3/ets and AP-1 sequences. J Biol Chem 271:10672–10680
Hung SH, Shen KH, Wu CH, Liu CL, Shih YW (2009) α-Mangostin suppresses PC-3 human prostate carcinoma cell metastasis by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 and urokinase-plasminogen activator expression through the JNK signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem 57:1291–1298
Rothhammer T, Hahne JC, Florin A, Poser I, Soncin F, Wernert N, Bosserhoff AK (2004) The Ets-1 transcription factor is involved in the development and invasion of malignant melanoma. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:118–128
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the grant from the Subsidized Project of the Chung Hwa University, Tainan, Taiwan (97-HT-08008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, KH., Hung, SH., Yin, LT. et al. Acacetin, a flavonoid, inhibits the invasion and migration of human prostate cancer DU145 cells via inactivation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 333, 279–291 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0229-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0229-8