Abstract
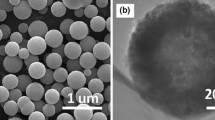
This brief article reports a suitable preparation of TiO2 hollow particles using titanium tetra-isopropoxide (TTIP) as a precursor and highly dispersed calcium carbonate (CaCO3) particle templates prepared from CaCl2 and dimethylcarbonate in the presence of the dispersing agent polyvinylpyrrolidone. The synthesis of TiO2 hollow particles was optimized considering certain experimental conditions: (a) the amount of TTIP, (b) the hydrolysis rate of TTIP in water/ethanol solvent, and (c) the mass of CaCO3 template particulates. The morphology and particle sizes of the resulting hollow particles (CaCO3 templates removed on addition of acid) were assessed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM and SEM-EDX); their crystalline phase (anatase) was determined by X-ray diffraction techniques and the specific surface area by the BET method. A formation mechanism of the TiO2 particles is described in terms of the TiO2 particulates generated under each experimental condition. The photoactivity of the TiO2 hollow particles was subsequently examined through the transformation of a volatile organic pollutant (iso-propanol) in air whose faster rate of photodegradation relative to TiO2 particles (synthesized without CaCO3) correlates with the greater specific surface area of these hollow particles (19.0 vs. 65.1 m2 g−1).
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDonald CJ, Devon MJ (2002) Hollow latex particles: synthesis and applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 99:181–213
Wicks Z, Jones F, Pappas SP (1992) Organic coatings, science and technology, vol 1. Wiley, New York, pp 306–320
Lee C-F, Hsu M-L, Chu C-H, Wu T-Y (2014) Synthesis and characteristics of poly(methyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid)/poly(methacrylic acid-co-N-isopropylacrylamide) thermosensitive semi-hollow latex particles and their application to drug carriers. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 52:3441–3451
Fujiwara M, Shiokawa K, Hayashi K, Morigaki K, Nakahara YJ (2007) Direct encapsulation of BSA and DNA into silica microcapsules (hollow spheres). Mater Res A 81:103–112
Kondo Y, Yoshikawa H, Awaga K, Murayama M, Mori T, Sunada K, Bandow S, Iijima S (2008) preparation, photocatalytic activities, and dye-sensitized solar-cell performance of submicron-scale TO2 hollow spheres. Langmuir 24:547–550
Cho HJ, Jung D (2011) The application of TiO2 hollow spheres on dye-sensitized solar cells. Bull Korean Chem Soc 32:4382
Wang H, Miyauchi M, Ishikawa Y, Pyatenko A, Koshizaki N, Li Y, Li L, Li X, Bando Y, Golberg D (2011) Single-crystalline rutile TiO2 hollow spheres: room-temperature synthesis, tailored visible-light-extinction, and effective scattering layer for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 133:19102–19109
Geng H, Cao X, Zhang Y, Geng K, Qu G, Tang M, Zheng J, Yang Y, Gu H (2015) Hollow nanospheres composed of titanium dioxide nanocrystals modified with carbon and gold for high performance lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 294:465–472
Tsai M-C, Lee J-Y, Chen P-C, Chang Y-W, Chang Y-C, Yang M-H, Chiu H-T, Lin I-N, Lee R-K, Lee C-Y (2014) Effects of size and shell thickness of TiO2 hierarchical hollow spheres on photocatalytic behavior: an experimental and theoretical study. Appl Catal B Environ 147:499–507
Bala H, Yu Y, Zhang Y (2008) Synthesis and photocatalytic oxidation properties of titania hollow spheres. Mater Lett 62:2070–2073
Zurmühl C, Popescu R, Gerthsen D, Feldmann C (2011) Microemulsion-based synthesis of nanoscale TiO2 hollow spheres. Solid State Sci 13:1505–1509
Yu J, Zhang J (2010) A simple template-free approach to TiO2 hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Dalton Trans 39:5860–5867
Zhang Q, Li W, Liu S (2011) Controlled fabrication of nanosized TiO2 hollow sphere particles via acid catalytic hydrolysis/hydrothermal treatment. Powder Technol 212:145–150
Jia C, Cao Y, Yang P (2013) TiO2 hollow spheres: one-pot synthesis and enhanced photocatalysis. Funct Mater Lett 6:1350025
Yang G, Hu P, Cao Y, Yuan F, Xu R (2010) Fabrication of porous TiO2 hollow spheres and their application in gas sensing. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:1437–1441
Zou H, Wu S, Shen J (2008) Polymer/silica nanocomposites: preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem Rev 108:3893–3957
Zimmermann C, Feldmann C, Wanner M, Gerthsen D (2007) Nanoscale gold hollow spheres through an emulsion approach. Small 3:1347–1349
Ogura T, Shibata H, Sakai K, Sakai H, Abe M (2009) Direct preparation of highly ordered multilayer-type silica nanocapsules using spontaneously formed vesicles as templates. Chem Lett 38:120–121
Langevin D (1988) Microemulsions. Acc Chem Res 21:255–260
Horikoshi S, Akao Y, Ogura T, Sakai H, Abe M, Serpone N (2010) On the stability of surfactant-free water-in-oil emulsions and synthesis of hollow SiO2 nanospheres. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 372:55–60
Zhang D, Zhu J, Zhang N, Liu T, Chen L, Liu X, Ma R, Zhang H, Qiu G (2015) Controllable fabrication and magnetic properties of double-shell cobalt oxides hollow particles. Sci Rep 5:8737. doi:10.1038/srep08737
Li Y, Zhou P, Dai Z, Hu Z, Sun P, Bao J (2006) A facile synthesis of PdCo bimetallic hollow nanospheres and their application to Sonogashira reaction in aqueous media. New J Chem 30:832–837
Zhu Y-Z, Chen H-B, Wang Y-P, Li Z-H, Cao Y-L, Chi Y-B (2006) Mesoscopic photonic crystals made of TiO2 hollow spheres connected by cylindrical tubes. Chem Lett 35:756–757
Chen GC, Kuo CY, Lu SY (2005) A general process for preparation of core–shell particles of complete and smooth shells. J Am Ceram Soc 88:277–283
Kaczmarek H, Kamińska A, Świątek M, Rabek JF (1998) Photo-oxidative degradation of some water-soluble polymers in the presence of accelerating agents. Die Angew Makromol Chem 261(262):109–121
Horikoshi S, Minatodani Y, Sakai H, Abe M, Serpone N (2011) Characteristics of microwaves on second generation nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their effect on photoassisted processes. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 217:191–200
Cui J, Sun D, Zhou W, Liu H, Hu P, Ren N, Qin H, Huang Z, Lin J, Ma H (2011) Electrocatalytic oxidation of nucleobases by TiO2 nanobelts. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:9232–9237
Hall WH (1949) X-ray line broadening in metals. Proc Phys Soc A 62:741–743
Mittemeijer EJ, Welzel U (2008) The “state of the art” of the diffraction analysis of crystallite size and lattice strain. Z Kristallogr 223:552–560
Ungár T (1997) Strain broadening caused by dislocations, JCPDS-International Centre for diffraction data. http://www.icdd.com/resources/axa/vol40/V40_612.pdf. Accessed Nov 2015
Ungár T (2008) Dislocation model of strain anisotropy, JCPDS-International Centre for diffraction data, pp 76–87; ISSN 1097-0002; http://www.icdd.com/resources/axa/vol51/v51_11.pdf. Accessed Nov 2015
Kapoor K, Lahiri D, Rao SVR, Sanyal T, Kashyap BP (2004) X-ray diffraction line profile analysis for defect study in Zr-2 × 5 % Nb material. Bull Mater Sci 27:59–67
Sanz-Hervas A, Villar C, Garrido M, Valtuena JF, Aguilar M, David JPR, Roberts JS, Halliwell MAG, Abril EJ, Lopez M, Izpura I (1999) Asymmetric lattice distortion in pseudomorphic multilayers grown on misoriented substrates, JCPDS-International Centre for diffraction data, pp 120–129
Braslavsky SE, Braun AM, Emeline AV, Litter MI, Palmisano L, Parmon VN, Serpone N (2011) Glossary of terms used in photocatalysis and radiation catalysis. Pure Appl Chem 83:931–1014
Sacco O, Stoller M, Vaiano V, Ciambelli P, Chianese A, Sannino D (2012) Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes under visible light on N-doped photocatalysts. Int J Photoenergy 2012:626759
Tayade RJ, Surolia PK, Kulkarni RG, Jasra RV (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes and organic contaminants in water using nanocrystalline anatase and rutile TiO2. Sci Technol Adv Mater 8:455–462
Rochkind M, Pasternak S, Paz Y (2015) Using dyes for evaluating photocatalytic properties: a critical review. Molecules 20:88–110
In S-I, Vesborg PCK, Abrams BL, Hou Y, Chorkendorff I (2011) J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 222:258–262
Acknowledgments
S.H. is grateful to the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for financial support (JSPS; Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research No. C-25420820) and to Sophia University for a grant from the Sophia University-wide Collaborative Research Fund to S.H. One of us (N.S.) thanks Prof. Albini of the University of Pavia (Italy) for his continued hospitality in his laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horikoshi, S., Oshimo, K., Sumi, T. et al. Synthesis of TiO2 hollow particles with highly dispersed CaCO3 template particulates and their photoactivity toward a VOC pollutant. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 78, 373–381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3939-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3939-2