Abstract
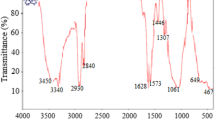
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the biodistribution of polyethylene glycol (PEG) coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles radiolabeled with 68Ga in normal mice after intravenous administration of this probe. Three mice were sacrificed at specific time intervals. The biodistribution data revealed high uptake by liver and spleen (60.62 and 12.65 %ID/g at 120 min post injection for liver and spleen, respectively). The clearance of other organs was fast. These results suggest that 68Ga-PEG-SPIONs has magnificent capabilities for applying in (PET-MRI) as a theranostic agent for detection of liver and spleen malignancies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A, Hajipour MJ, Ghavami M, Azhdarzadeh M (2015) External magnetic fields affect the biological impacts of superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 136:1107–1112
Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian MA, Lahooti A, Abdollahi M, Haeri SA, Amanlou M, Daha FJ, Allen BJ (2013) Estimated background doses of [67Ga]-DTPA-USPIO in normal Balb/c mice as a potential therapeutic agent for liver and spleen cancers. Nucl Med Commun 34:915–925
Najafian N, Shanehsazzadeh S, Hajesmaeelzadeh F, Lahooti A, Gruettner C, Oghabian MA (2015) Effect of functional group and surface charge of PEG and dextran-coated USPIO as a contrast agent in MRI on relaxivity constant. Appl Magn Reson 46:685–692
Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A (2014) Biodistribution of 80 nm iron oxide nanoparticles labeled with 99mTc in Balb/c mice. Nucl Med Biol 41:625
Douziech-Eyrolles L, Marchais H, Hervé K, Munnier E, Soucé M, Linassier C, Dubois P, Chourpa I (2007) Nanovectors for anticancer agents based on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 2:541–550
Koneracka M, Muckova M, Zavisova V, Tomasovicova N, Kopcansky P, Timko M, Jurikova A, Csach K, Kavecansky V, Lancz G (2008) Encapsulation of anticancer drug and magnetic particles in biodegradable polymer nanospheres. J Phys: Condens Matter 20:204151
Nosrati S, Shanehsazzadeh S, Yousefnia H, Gholami A, Grüttner C, Jalilian A, Hosseini R, Lahooti A (2016) Biodistribution evaluation of 166Ho–DTPA–SPION in normal rats. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 307:1559–1566
Mirsadeghi S, Shanehsazzadeh S, Atyabi F, Dinarvand R (2016) Effect of PEGylated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) under magnetic field on amyloid beta fibrillation process. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 59:390–397
Shanehsazzadeh S, Gruettner C, Lahooti A, Mahmoudi M, Allen BJ, Ghavami M, Daha FJ, Oghabian MA (2015) Monoclonal antibody conjugated magnetic nanoparticles could target MUC-1-positive cells in vitro but not in vivo. Contrast Media Mol I 10:225–236
Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian M, Allen B, Amanlou M, Masoudi A, Daha F (2013) Evaluating the effect of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for a long-term magnetic cell labeling. J Med Phys 38:34–40
Yang BY, Moon SH, Seelam SR, Jeon MJ, Lee YS, Lee DS, Chung JK, Kim YI, Jeong JM (2015) Development of a multimodal imaging probe by encapsulating iron oxide nanoparticles with functionalized amphiphiles for lymph node imaging. Nanomedicine-UK 10:1899–1910
Shanehsazzadeh S, Yousefnia H, Jalilian AR, Zolghadri S, Lahooti A (2015) Estimated human absorbed dose for 68Ga-ECC based on mice data: comparison with 67Ga-ECC. Ann Nucl Med 29:475–481
Velikyan I (2014) Prospective of 68Ga-Radiopharmaceutical Development. Theranostics 4:47–80
Madru R, Tran TA, Axelsson J, Ingvar C, Bibic A, Ståhlberg F, Knutsson L, Strand S-E (2014) 68Ga-labeled superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for multi-modality PET/MR/Cherenkov luminescence imaging of sentinel lymph nodes. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 4:60–69
Aghanejad A, Jalilian AR, Ardaneh K, Bolourinovin F, Yousefnia H, Bahrami-Samani A (2015) Preparation and Quality Control of 68Ga-Citrate for PET Applications. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol 3:99–106
Garcia J, Tang T, Louie AY (2015) Nanoparticle-based multimodal PET/MRI probes. Nanomedicine (Lond) 10(8):1343–1359
Jalilian A, Panahifar A, Mahmoudi M, Akhlaghi M, Simchi A (2009) Preparation and biological evaluation of [67Ga]-labeled-superparamagnetic nanoparticles in normal rats. Radiochim Acta 97:51–56
Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian MA, Lahooti A, Allen BJ (2013) Development of ultra small super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles labeled with Gallium 67 as a dual modality probe. J Label Compd Rad 56:S236–S236
Jalilian AR, Shanehsazzadeh S, Akhlaghi M, Garousi J, Rajabifar S, Tavakoli M (2008) Preparation and biodistribution of [67Ga]-DTPA-gonadorelin in normal rats. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:123–129
Council B (1987) Guidelines on the use of living animals in scientific investigations. Biol Counc
Sadeghzadeh M, Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A (2015) Assessment of the effective absorbed dose of 4-benzyl-1-(3-[125I]-iodobenzylsulfonyl) piperidine in humans on the basis of biodistribution data of rats. Nucl Med Commun 36:90–94
Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A, Sadeghi HR, Jalilian AR (2011) Estimation of human effective absorbed dose of 67Ga–cDTPA–gonadorelin based on biodistribution rat data. Nucl Med Commun 32:37–43
Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A, Shirmardi SP, Erfani M (2015) Comparison of estimated human effective dose of 67Ga-and 99mTc-labeled bombesin based on distribution data in mice. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 305:513–520
Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A, Yousefnia H, Geramifar P, Jalilian AR (2015) Comparison of estimated human dose of 68Ga-MAA with 99 mTc-MAA based on rat data. Ann Nucl Med 29:745–753
Yousefnia H, Zolghadri S, Sadeghi HR, Naderi M, Jalilian AR, Shanehsazzadeh S (2016) Preparation and biological assessment of 177Lu-BPAMD as a high potential agent for bone pain palliation therapy: comparison with 177Lu-EDTMP. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 307:1243–1251
Lahooti A, Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian MA, Allen BJ (2013) Assessment of human effective absorbed dose of Tc-99m-USPIO based on biodistribution rat data. Journal of Labelled Compounds & Radiopharmaceuticals. Wiley, Hoboken, pp S258–S258
Kievit FM, Zhang M (2011) Surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Acc Chem Res 44(10):853–862
Varna M, Ratajczak P, Ferreira I, Leboeuf C, Bousquet G, Janin A (2012) In vivo distribution of inorganic nanoparticles in preclinical models. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol 3:269–279
Campbell SB, Patenaude M, Hoare T (2013) Injectable superparamagnets: highly elastic and degradable poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION) composite hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 14:644–653
Prabha S, Zhou WZ, Panyam J, Labhasetwar V (2002) Size-dependency of nanoparticle-mediated gene transfection: studies with fractionated nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 244:105–115
Cormode DP, Skajaa T, Fayad ZA, Mulder WJM (2009) Nanotechnology in medical imaging: probe design and applications. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:992–1000
Wang H, Thorling CA, Liang X, Bridle KR, Grice JE, Zhu Y, Crawford DHG, Xu ZP, Liu X, Roberts MS (2015) Diagnostic imaging and therapeutic application of nanoparticles targeting the liver J Mate Chem B 3:939–958
Dai L, Liu Y, Wang Z, Guo F, Shi D, Zhang B (2014) One-pot facile synthesis of PEGylated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI contrast enhancement. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 41:161–167
Shanehsazzadeh S, Grüttner C, Yousefnia H, Lahooti A, Gholami A, Nosrati S, Zolghadri S, Anijdan SHM, Lotfabadi A, Shiri Varnamkhasti B (2016) Development of 177Lu-DTPA-SPIO conjugates for potential use as a dual contrast SPECT/MRI imaging agent. Radiochim Acta 104(5):337–344
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support of the International Atomic Energy Organization under ‘CRP F22064’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahooti, A., Sarkar, S., Saligheh Rad, H. et al. PEGylated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles labeled with 68Ga as a PET/MRI contrast agent: a biodistribution study. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 311, 769–774 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-5058-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-5058-0