Abstract
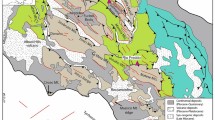
Variation in earth gas level like radon in soil and groundwater is a proven technique for tracing the changes in stresses due to seismotectonic activities. Radon concentrations were measured and investigated in Jooshan hot spring complex, SE of Iran, near Golbaf-Sirch fault sytem from December 2011 until March 2012. Afterward, by considering and studying environmental parameters, the relationship between radon anomalous decline and all earthquakes with ratio D/R that introducing by Dobrovolsky et al. was examined. So before earthquakes, the correlation between this ratio and level of variation in radon concentration in magnitude ranging from 2.6 to 5.4 has been studied and the correlation coefficient of 0.74 was obtained. This research shows a good correlation between groundwater radon variations and such earthquake parameters.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Environmental Protection Agency.
References
Igarashi G, Saeki S, Takahata N, Sumikawa K, Tasaka S, Sasaki Y, Takahashi M, Sano Y (1995) Ground-water radon anomaly before the Kobe earthquake in Japan. Science 269(5220):60–61. doi:10.1126/science.269.5220.60
Ghosh D, Deb A, Sengupta R (2009) Anomalous radon emission as precursor of earthquake. J Appl Geophys 69(2):67–81. doi:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2009.06.001
Seidel JL, Monnin M, Cejudo J, Chalot JF, Segovia N, de la Cruz S, Mena M, Malavassi E, Barquero J, Fernandez E, Avila G, Van der Laat R (1984) Radon emanometry in active volcanoes. Nucl Tracks Radiat Meas 8(1–4):411–414. doi:10.1016/0735-245x(84)90132-7
Musavi Nasab S, Negarestani A, Mohammadi S (2011) Modeling of the radon exhalation from water to air by a hybrid electrical circuit. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288(3):813–818. doi:10.1007/s10967-011-1003-4
Negarestani A, Setayeshi S, Ghannadi-Maragheh M, Akashe B (2003) Estimation of the radon concentration in soil related to the environmental parameters by a modified Adaline neural network. Appl Radiat Isot 58(2):269–273. doi:10.1016/s0969-8043(02)00304-4
Iakovleva VS, Ryzhakova NK (2003) A method for estimating the convective radon transport velocity in soils. Radiat Meas 36(1–6):389–391. doi:10.1016/s1350-4487(03)00157-4
Bujdosó E (1991) Radon in the environment. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 152(2):525–541. doi:10.1007/bf02104705
Cigolini C, Poggi P, Ripepe M, Laiolo M, Ciamberlini C, Delle Donne D, Ulivieri G, Coppola D, Lacanna G, Marchetti E, Piscopo D, Genco R (2009) Radon surveys and real-time monitoring at Stromboli volcano: influence of soil temperature, atmospheric pressure and tidal forces on Rn-222 degassing. J Volcanol Geoth Res 184(3–4):381–388. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2009.04.019
Shahabpour J (2005) Tectonic evolution of the orogenic belt in the region located between Kerman and Neyriz. J Asian Earth Sci 24(4):405–417. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.11.007
Berberian M, Asudeh I, Arshadi S (1977) Surface rupture and mechanism of the Bob-Tangol (southeastern Iran) earthquake of 19. Earth Planet Sci Lett 42(3):456–462. doi:10.1016/0012-821x(79)90055-4
Walker RT, Talebian M, Saiffori S, Sloan RA, Rasheedi A, MacBean N, Ghassemi A (2010) Active faulting, earthquakes, and restraining bend development near Kerman city in southeastern Iran. J Struct Geol 32(8):1046–1060. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2010.06.012
Dobrovolsky IP, Zubkov SI, Miachkin VI (1979) Estimation of the size of earthquake preparation zones. Pure Appl Geophys 117(5):1025–1044. doi:10.1007/bf00876083
Tsunomori F, Kuo T (2010) A mechanism for radon decline prior to the 1978 Izu-Oshima-Kinkai earthquake in Japan. Radiat Meas 45(1):139–142. doi:10.1016/j.radmeas.2009.08.003
Kuo T, Fan K, Kuochen H, Han Y, Chu H, Lee Y (2006) Anomalous decrease in groundwater radon before the Taiwan M 6.8 Chengkung earthquake. J Environ Radioact 88(1):101–106. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2006.01.005
Tsvetkova T, Przylibski TA, Nevinsky I, Nevinsky V (2005) Measurement of radon in the East Europe under the ground. Radiat Meas 40(1):98–105. doi:10.1016/j.radmeas.2004.04.013
Hauksson E (1981) Radon content of groundwater as an earthquake precursor: evaluation of worldwide data and physical basis. J Geophys Res 86(B10):9397–9410. doi:10.1029/jb086ib10p09397
Sakoda A, Ishimori Y, Yamaoka K (2011) A comprehensive review of radon emanation measurements for mineral, rock, soil, mill tailing and fly ash. Appl Radiat Isot 69(10):1422–1435. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.06.009
Baciu AC (2005) Radon and thoron progeny concentration variability in relation to meteorological conditions at Bucharest (Romania). J Environ Radioact 83(2):171–189. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2005.02.015
Klusman RW, Webster JD (1981) Meteorological noise in crustal gas emission and relevance to geochemical exploration. J Geochem Explor 15(1–3):63–76. doi:10.1016/0375-6742(81)90056-x
Sundal AV, Valen V, Soldal O, Strand T (2008) The influence of meteorological parameters on soil radon levels in permeable glacial sediments. Sci Total Environ 389(2–3):418–428. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.09.001
Chen KH, Nadeau RM, Rau R-J (2008) Characteristic repeating earthquakes in an arc-continent collision boundary zone: the Chihshang fault of eastern Taiwan. Earth Planet Sci Lett 276(3–4):262–272. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.09.021
Bányai L (1992) The role of the elastic rebound theory in design and evaluation of deformation surveys. Tectonophysics 202(2–4):107–110. doi:10.1016/0040-1951(92)90087-m
Berberian M, Qorashi M (1994) Coseismic fault-related folding during the South Golbaf earthquake of November 20, 1989, in southeast Iran. Geology 22(6):531–534. doi:10.1016/0148-9062(94)90054-x Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 31(6):268
Utkin VI, Yurkov AK (2010) Radon as a tracer of tectonic movements. Russ Geol Geophys 51(2):220–227. doi:10.1016/j.rgg.2009.12.022
Walker R, Jackson J (2002) Offset and evolution of the Gowk fault, SE Iran: a major intra-continental strike-slip system. J Struct Geol 24(11):1677–1698. doi:10.1016/s0191-8141(01)00170-5
Teisseyre R (1985) New earthquake rebound theory. Phys Earth Planet Inter 39(1):1–4. doi:10.1016/0031-9201(85)90110-4
Angelier J (2002) Détermination du tenseur des contraintes par inversion de mécanismes au foyer de séismes sans choix de plans nodaux. CR Geosci 334(1):73–80. doi:10.1016/s1631-0713(02)01712-1
Knappett JA, Haigh SK, Madabhushi SPG (2006) Mechanisms of failure for shallow foundations under earthquake loading. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 26(2–4):91–102. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2004.11.021
Kuo T, Su C, Chang C, Lin C, Cheng W, Liang H, Lewis C, Chiang C (2010) Application of recurrent radon precursors for forecasting large earthquakes (Mw > 6.0) near Antung, Taiwan. Radiat Meas 45(9):1049–1054. doi:10.1016/j.radmeas.2010.08.009
Acknowledgments
The authors are extremely grateful to prof. Jamshid Shahabpour for his kind guidance during the data interpreting. Also special thanks to Dr. Mohammad Mahani, Dr. Mohammad Reza Rezaei and Mohammad Mehdi Hosseini Bioki for editing the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namvaran, M., Negarestani, A. Measuring the radon concentration and investigating the mechanism of decline prior an earthquake (Jooshan, SE of Iran). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298, 1–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2162-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2162-7